Optimizing Copper Cathode Handling: The Role of Automated Strapping Systems
Automated strapping systems play a critical role in the downstream logistics of copper electrowinning and refining operations. Specifically engineered copper cathode plate strapping machines are essential for ensuring the secure unitization and safe handling of these valuable, high-purity metal products, directly impacting supply chain integrity and operational efficiency.
The Challenge: Securing High-Value Cathode Stacks
Handling stacks of copper cathodes, often weighing several metric tons, presents unique logistical and quality control challenges. Maintaining bundle integrity throughout intra-plant movement, warehousing, and final shipment is paramount. Any shifting or instability can lead to:
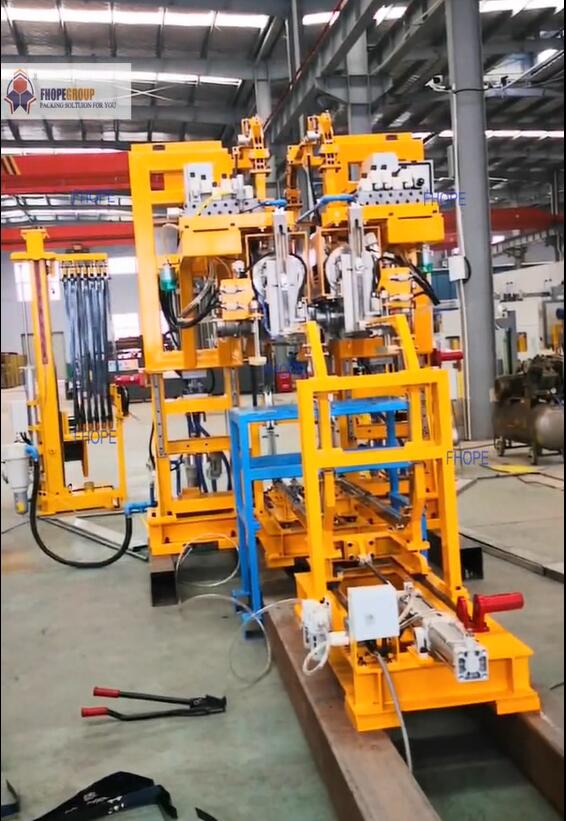

- Surface Damage: Scratches or gouges can compromise the cathode's purity specifications and diminish its market value.
- Handling Safety Risks: Unstable loads pose significant risks to personnel and equipment during lifting and transport.
- Logistical Inefficiencies: Damaged or poorly secured bundles can cause delays and complications in loading and unloading processes.
Traditional manual strapping methods, while sometimes employed, often struggle to provide the consistent tension, throughput speed, and operator safety demanded in modern, high-volume copper production facilities. Research published in materials handling journals consistently highlights the gains in consistency and safety achieved through automation in heavy industries.
Advanced Strapping Technology for Copper Cathodes
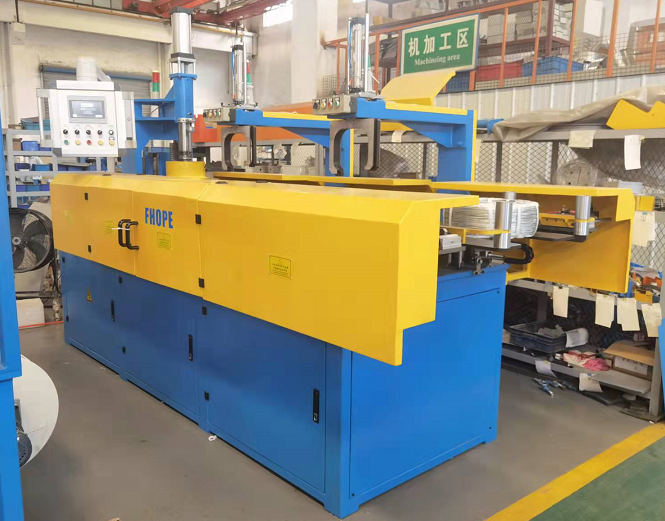
Modern copper cathode strapping machines integrate sophisticated mechanical and control systems to automate the strapping cycle. Key technological features often include:
- Automated Bundle Indexing: Precisely positions the cathode stack for optimal strap placement.
- High-Strength Strap Feeding: Reliably dispenses robust strapping material, typically high-tensile Polyester (PET) or steel strapping, chosen based on load requirements and environmental factors. PET is often favored for its resistance to elongation under load and lack of corrosion, aligning with findings in packaging science studies on load stability.
- Precision Tensioning Systems: Apply consistent, predetermined tension to each strap. This is crucial, as incorrect tension can either fail to secure the load or, conversely, damage the cathode edges. Systems often employ electronically controlled feedback loops, ensuring tension uniformity that surpasses manual capabilities, a principle detailed in various packaging engineering patents (e.g., those related to friction-weld tension control).
- Secure Sealing Mechanisms:
- PET Strapping: Typically utilizes friction-weld sealing, creating a strong, reliable joint without metal seals, reducing consumable costs and potential indentation points.
- Steel Strapping: Employs notch or seal-less joints, or traditional metal seals, depending on the application's specific strength requirements.
- Automated Strap Cutting: Cleanly severs the strap after sealing.
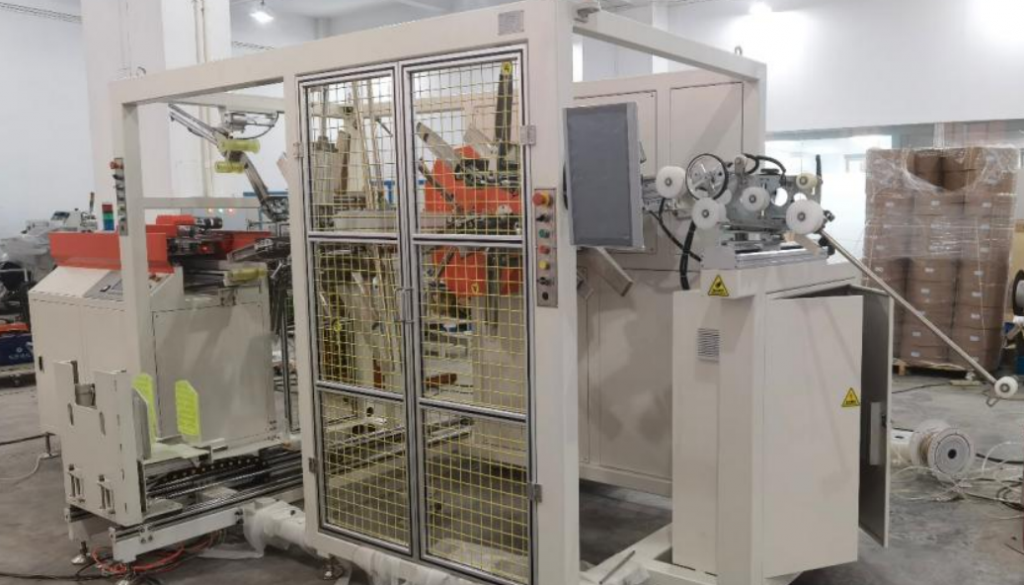
Integration into Plant Automation
Reflecting trends reported in publications like The Fabricator on smart manufacturing, these strapping machines are designed for seamless integration into larger automated systems.
- Conveyor Integration: Connect directly with incoming and outgoing conveyor lines for continuous material flow.
- PLC Control: Interface with plant-level Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) for coordinated operation, status monitoring, and fault diagnostics.
- Data Acquisition: Can log operational data (cycle times, strap count, tension applied) for process optimization and quality assurance traceability.
Key Performance Parameters
While specifications vary, typical performance characteristics influencing selection include:
- Throughput Rate: Measured in bundles strapped per hour, critical for matching production output.
- Cycle Time: The total time required to apply and secure all straps on a single bundle.
- Bundle Capacity: Accommodates specific ranges of cathode stack dimensions (Length x Width x Height) and maximum weight (e.g., up to 5 metric tons).
- Strapping Material: Compatibility with specified PET or steel strap types and dimensions.
- Tension Range: Adjustable tension settings (e.g., 1000 N to 7000 N) to suit varying load requirements.
Operational Benefits and ROI
Investing in automated copper cathode strapping translates to tangible benefits aligned with lean manufacturing principles often discussed in industry publications:
- Enhanced Load Security: Consistent strapping minimizes transit damage and ensures product integrity upon arrival.
- Increased Throughput: Significantly faster cycle times compared to manual methods boost overall plant efficiency.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Automation minimizes the need for manual strapping personnel.
- Improved Workplace Safety: Reduces manual handling of heavy loads and the repetitive motions associated with manual strapping tools, mitigating ergonomic risks.
- Operational Consistency: Eliminates variability inherent in manual processes, ensuring every bundle meets strapping specifications.
Maintenance and Reliability Considerations
Designed for the rigors of metallurgical plant environments, these machines feature robust construction. Reliability is paramount in continuous operations. Preventative maintenance programs, as advocated in industrial maintenance best practice guides, focusing on wear parts (feed wheels, cutters, tensioning components) and system calibration, are essential for maximizing uptime and ensuring long-term performance.
In conclusion, the automated copper cathode plate strapping machine represents a critical investment for copper producers aiming to optimize material handling, protect product value, enhance safety, and maintain competitiveness in the global market. Its role extends beyond simple packaging to become an integral part of efficient and reliable plant operations.