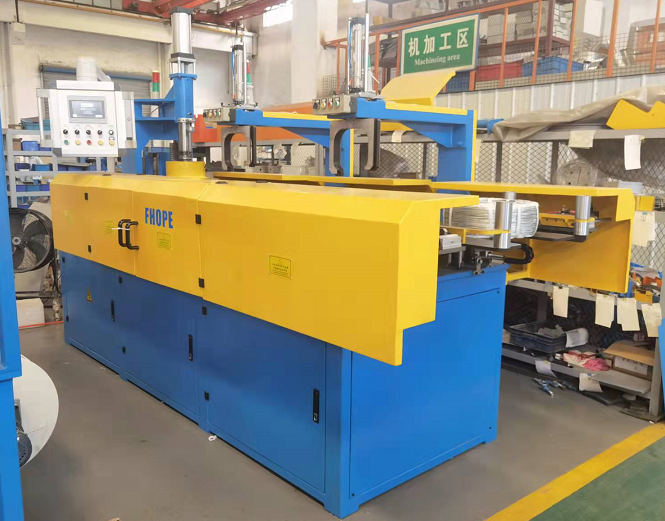
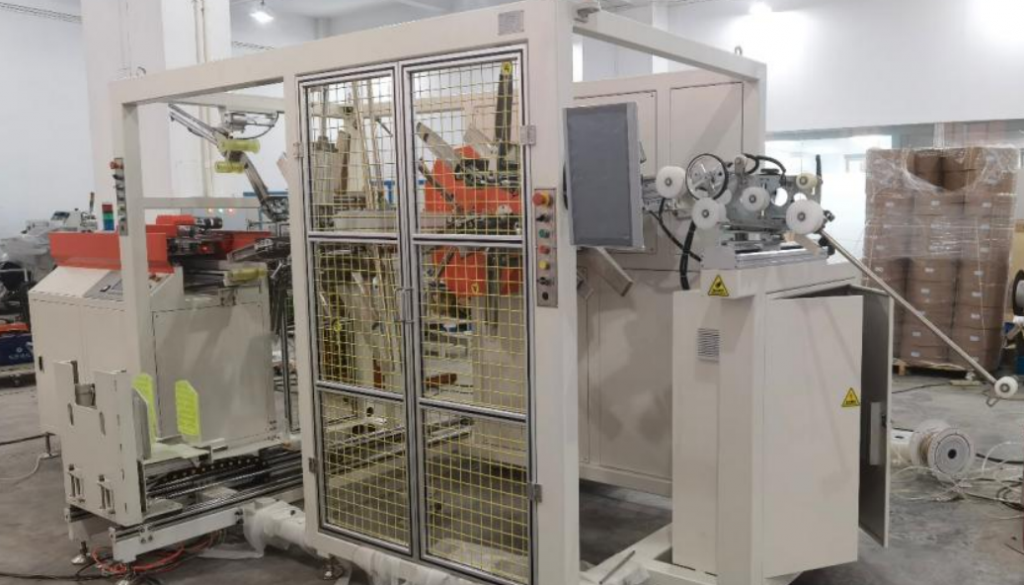
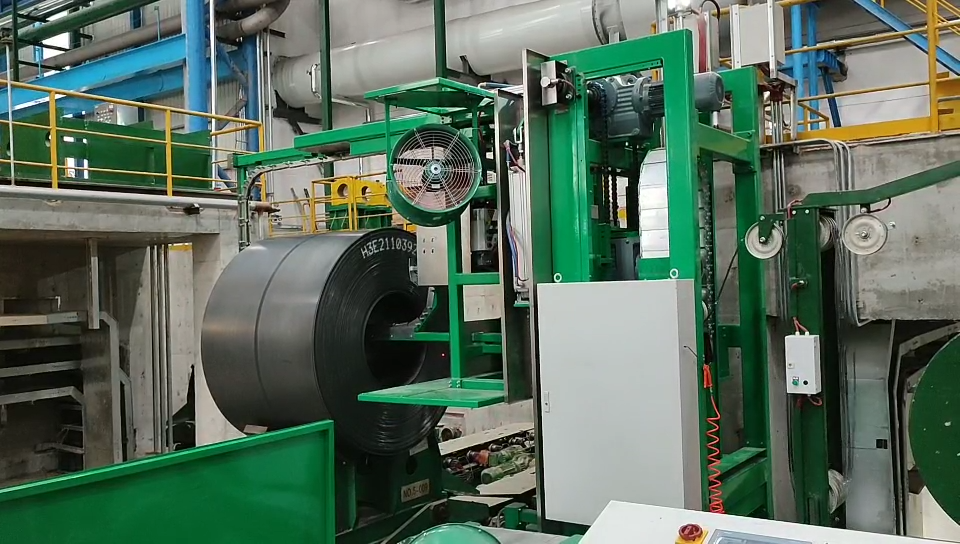
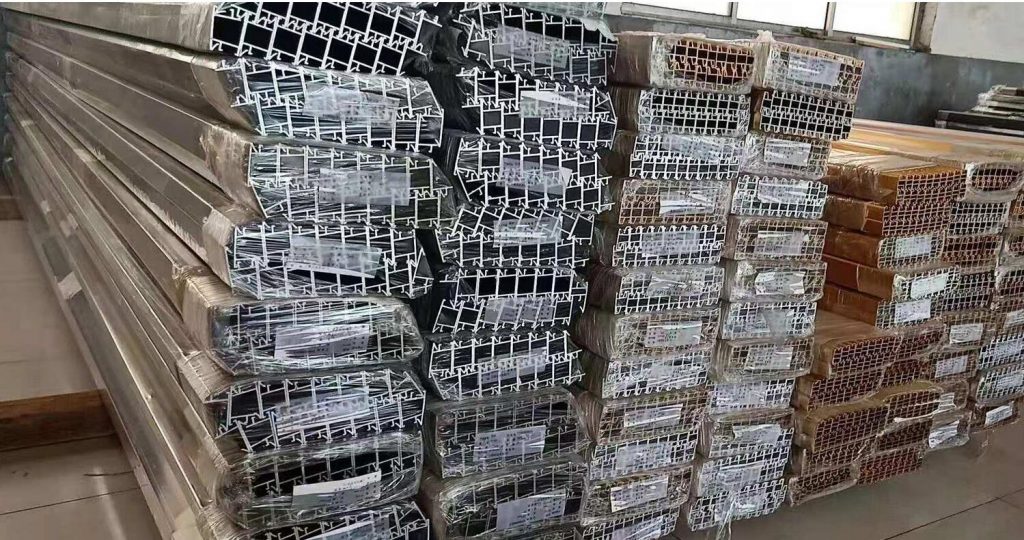
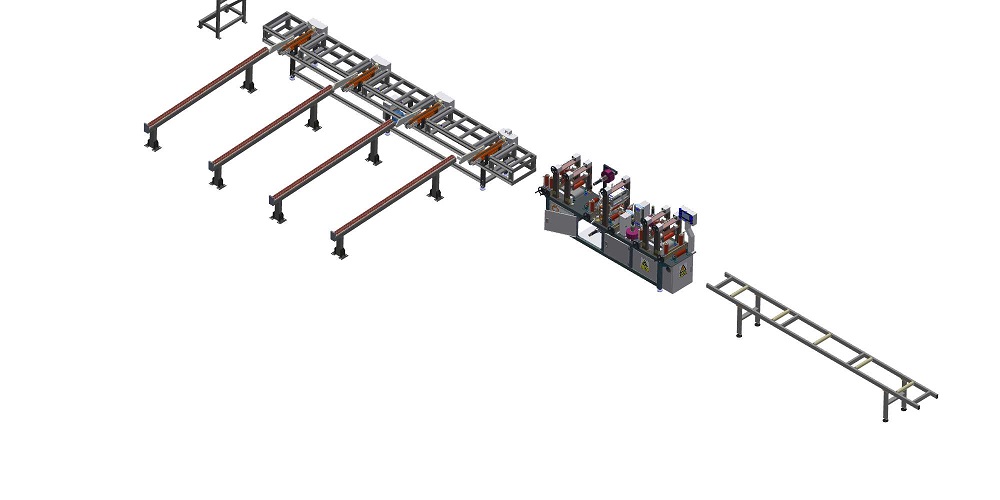
Optimizing Production Flow: The Role of Automatic Stacking Machines for Board and Profile Handling
In today's demanding manufacturing and logistics environments, efficiency, safety, and precision are paramount. Manual handling of large or numerous boards and profiles – whether wood, plastic, metal, or composite – presents significant challenges, including labor costs, risk of worker injury, potential product damage, and inconsistencies in stacking that affect downstream processes and storage. The implementation of an Automatic Stacking Machine for Board and Profile represents a strategic investment in overcoming these hurdles, aligning with modern automation trends highlighted in industry publications like Packaging World.
These sophisticated systems are engineered to seamlessly integrate into production lines, providing reliable, high-speed stacking solutions. Drawing inspiration from advancements documented in material handling research and automation patents, these machines utilize a combination of robust conveyance, precision mechanics, and intelligent control systems.
Core Technology and Operational Principles
An automatic stacking machine is fundamentally designed for the autonomous handling and organized stacking of elongated or flat materials. Key technological components often include:
- Infeed Conveyor System: Transports boards or profiles from upstream processes (e.g., extrusion, cutting, machining) to the stacking area. Variable speed control ensures synchronization with production line throughput.
- Stacking Mechanism: This is the heart of the machine. Designs vary based on material and application, potentially incorporating:
- Robotic Arms: Offering high flexibility for complex patterns and gentle handling, often guided by vision systems (as seen in advanced logistics automation research).
- Overhead Gantries with Grippers: Utilizing vacuum suction cups or mechanical clamps tailored to the material's surface and weight. Patent literature often details innovations in gripper design for secure yet non-damaging handling.
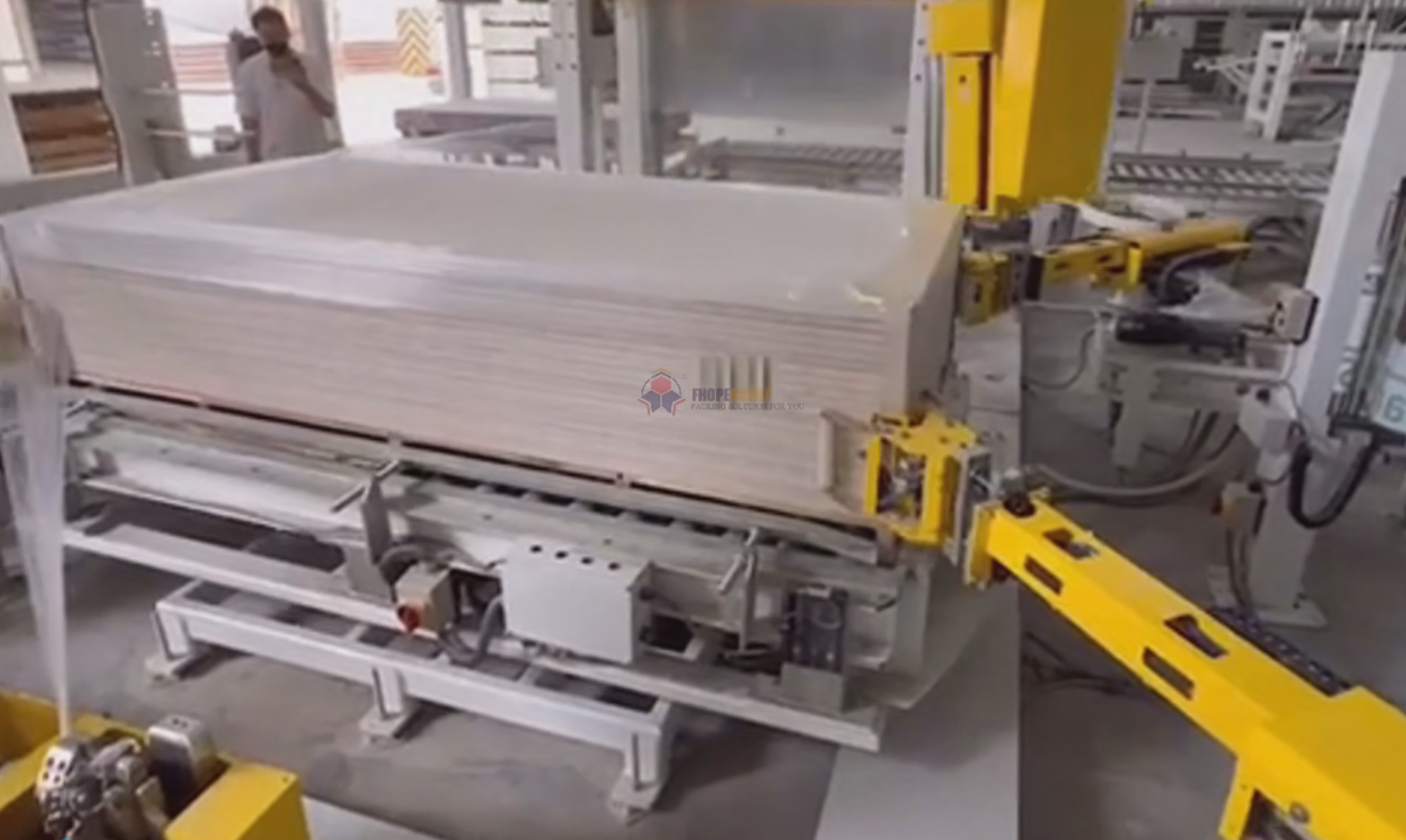

automatic board packing line - Lift-and-Place Systems: Simpler mechanisms for straightforward stacking requirements.
- Control System: Typically PLC-based (Programmable Logic Controller) with a Human-Machine Interface (HMI). This allows operators to:
- Define stacking patterns (e.g., layer configurations, nesting).
- Set stack height or piece count per stack.
- Adjust parameters for different product dimensions.
- Integrate with Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) for production tracking and scheduling.
- Sensors and Actuators: A network of photoelectric sensors, proximity switches, and encoders ensures accurate positioning, alignment, and safe operation, minimizing collision risks and ensuring stack integrity. Research papers often emphasize the role of sensor fusion for enhanced reliability in dynamic industrial environments.
- Outfeed System: Facilitates the removal of completed stacks, often integrating with pallet dispensers, strapping machines, or AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) for fully automated end-of-line solutions.
Representative Technical Specifications
While specific configurations vary widely based on application needs, typical parameters for such systems might include:
- System Type: Automated Stacking System for Boards and Profiles
- Material Compatibility: Wood (Panels, Lumber), Metal (Extrusions, Sheets), Plastics (Profiles, Boards), Composites
- Operational Speed: Variable, potentially reaching cycles capable of handling up to 60-100+ pieces per minute depending on size and weight.
- Maximum Product Dimensions: Customizable, e.g., Length up to 6000mm (or more); Width up to 2400mm; Thickness up to 150mm.
- Stack Height Capacity: Adjustable, commonly up to 2000mm or as required.
- Control Architecture: PLC Control (e.g., Siemens, Allen-Bradley) with Touchscreen HMI.
- Connectivity: Options for Ethernet/IP, Profinet, Modbus TCP/IP for line integration.
- Power Requirements: Typically 380V/415V, 50/60Hz, 3-Phase.
- Safety Compliance: Designed to meet relevant safety standards (e.g., ISO, CE, OSHA) including emergency stops, light curtains, and safety guarding.
- Pneumatic System: Required air pressure and consumption vary based on gripper type and actuation.
Disclaimer: The parameters listed above are illustrative. Exact specifications are tailored to the individual project requirements. Please contact us for a detailed consultation.
Key Benefits Driving Adoption
The implementation of automatic stacking machines delivers tangible benefits across various industries:
- Increased Throughput & Efficiency: Continuous, automated operation significantly outpaces manual stacking, reducing bottlenecks and increasing overall line productivity.
- Enhanced Worker Safety: Eliminates strenuous manual lifting and repetitive motions, drastically reducing the risk of musculoskeletal injuries, aligning with industry best practices for ergonomics.
- Improved Product Quality: Gentle and precise handling minimizes scratches, dents, and breakage often associated with manual stacking, reducing material waste.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Frees up personnel from manual stacking tasks, allowing them to be redeployed to more value-added activities. Addresses challenges related to labor shortages and rising wages.
- Consistent Stack Formation: Ensures uniform, stable stacks crucial for optimized storage, transport, and subsequent processing steps.
- Operational Flexibility: Programmable controls allow quick changeovers between different product sizes and stacking patterns with minimal downtime.
- Data Integration: Modern systems can provide valuable operational data, supporting smart factory initiatives and process optimization efforts.
Industry-Specific Applications
Automatic stacking technology is proving indispensable in several key sectors:
- Furniture Manufacturing: Essential for handling large volumes of wood or composite panels (MDF, particleboard, plywood) emerging from cutting, edge banding, or CNC machining centers. Ensures organized stacks ready for assembly or finishing, supporting lean manufacturing principles.
- Building Materials & Construction: Efficiently stacks lumber, metal profiles (studs, channels), plastic extrusions (pipes, siding), and insulation boards. Facilitates better inventory management in production facilities and distribution centers, ensuring materials are ready for shipment or prefabricated assembly.
- Packaging and Distribution: Crucial for handling flat sheets of corrugated cardboard, plastic sheets for thermoforming, or finished packaged goods needing palletization. Integration with end-of-line packaging equipment (wrappers, strappers) creates fully automated workflows, as frequently highlighted in packaging logistics reports.
- Metal Fabrication: Stacks metal sheets post-cutting or punching, and handles long metal profiles and extrusions common in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications.
- Plastics Processing: Manages the output from extrusion lines producing profiles, pipes, or sheets, ensuring orderly handling for cooling, cutting, and storage.
Integration and Future Trends
The true power of automatic stacking machines is often realized through their integration into broader automated systems. Compatibility with upstream equipment (saws, extruders, presses) and downstream processes (palletizing, wrapping, AGV transport) is critical. Future trends, often discussed in technical papers and industry forums, point towards:
- Greater use of AI and Machine Vision: For enhanced pattern recognition, quality inspection during stacking, and adaptive path planning.
- Improved Energy Efficiency: Utilizing energy-recovery systems and optimized motor controls.
- Cobots (Collaborative Robots): For applications requiring human-robot collaboration in the stacking process.
- Enhanced Data Analytics: Providing deeper insights into machine performance, predictive maintenance needs, and overall line efficiency.
Explore further automation solutions for your production line:
Investing in an automatic stacking machine for board and profile handling is a strategic move towards modernizing operations, enhancing safety, and boosting productivity. By leveraging advanced automation technology, manufacturers and distributors can achieve greater efficiency and maintain a competitive edge in their respective markets. Contact our specialists to discuss how a tailored stacking solution can optimize your specific application.