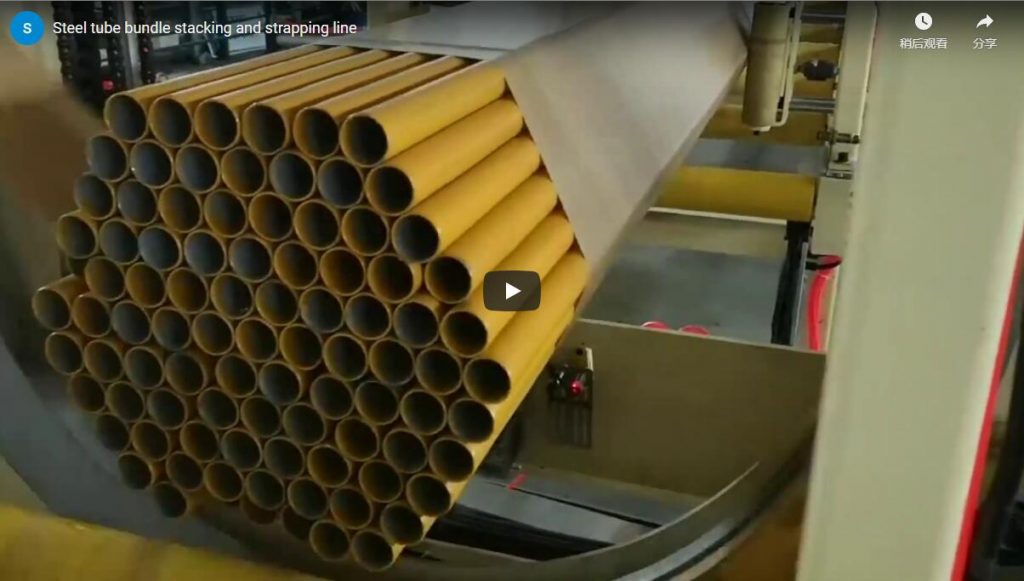
Enhancing Operational Efficiency with Automated Steel Tube Bundling and Strapping Systems
The handling and packaging of steel tubes present significant logistical and operational challenges in industries ranging from construction and automotive manufacturing to energy infrastructure and heavy equipment production. Manual or semi-automated processes often struggle to keep pace with production demands, leading to bottlenecks, increased labor costs, potential safety hazards, and inconsistent package quality. Implementing fully automatic solutions for bundling and strapping steel tubes has become an essential strategy for manufacturers seeking to optimize throughput, ensure product integrity, and enhance workplace safety.
The Imperative for Automation in Tube Handling
Modern manufacturing environments demand high efficiency and reliability. Steel tubes, due to their weight, length, and varying dimensions, pose unique handling difficulties. Traditional methods often involve significant manual labor, increasing the risk of ergonomic injuries and product damage. Automation addresses these critical points:
- Increased Throughput: Automated systems operate continuously with minimal downtime, significantly outpacing manual methods and aligning packaging speed with production output. Cycle times can often be reduced by over 50% compared to manual operations, according to industry benchmarks.
- Improved Consistency and Quality: Automated systems ensure uniform bundle shapes (often hexagonal for stability, a configuration explored in various handling patents like US Patent 5,417,327 A concerning bundle formation) and apply strapping with consistent tension, crucial for secure transport and storage. This minimizes damage caused by loose or improperly formed bundles.
- Enhanced Worker Safety: Automating the heavy lifting, positioning, and strapping tasks dramatically reduces the risk of musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) and other injuries associated with manual handling, aligning with OSHA guidelines and promoting a safer work environment. Studies in Ergonomics in Design frequently highlight the reduction in injury rates post-automation in material handling scenarios.
- Reduced Labor Dependency: In tight labor markets, automation mitigates reliance on manual labor for repetitive and physically demanding tasks, allowing personnel to be reassigned to higher-value activities.
Core Technologies and System Capabilities
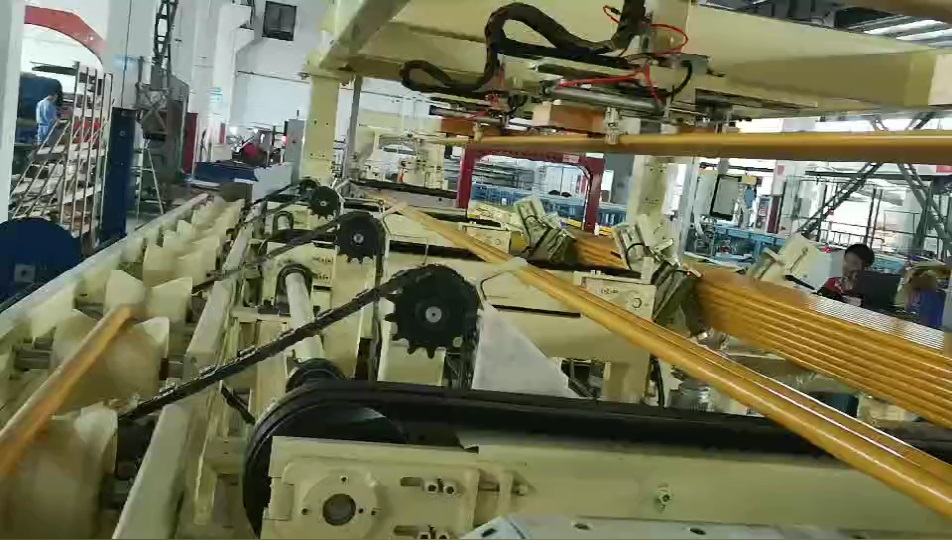
Advanced automatic steel tube bundling and strapping lines integrate several key technologies:
- Material Infeed and Conveying: Robust conveyor systems transport tubes from upstream processes (e.g., cutting, finishing) to the bundling station. Sensors detect tube presence and dimensions.
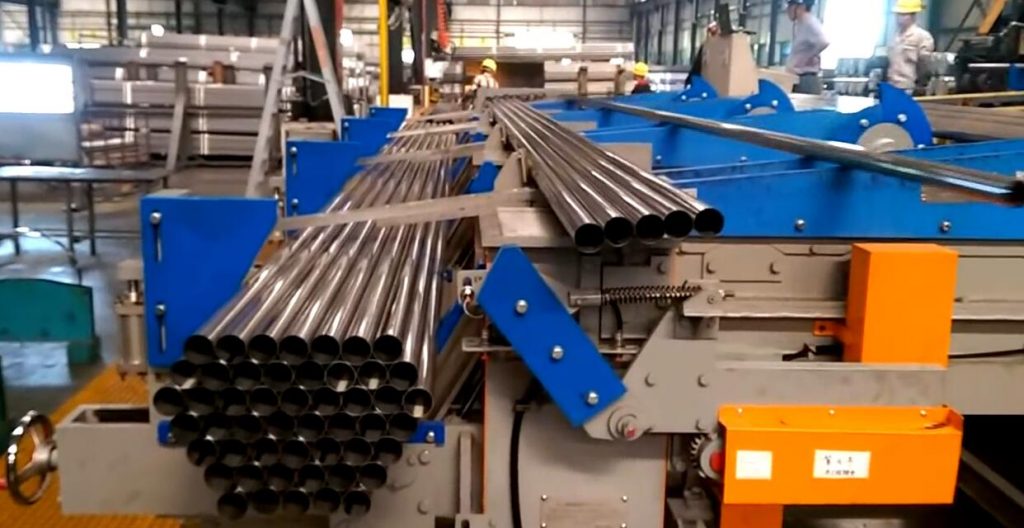
- Bundle Formation Unit: This critical component collects tubes and arranges them into a predefined shape and count. Mechanisms may include chain conveyors, aligning arms, or specialized cradles. Advanced systems can automatically adjust for different tube diameters and desired bundle sizes, often controlled via PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) and HMI (Human-Machine Interface).
- Strapping Heads: State-of-the-art strapping heads automatically feed, tension, seal (often via heat or friction weld for PET straps, or crimping for steel straps), and cut the strapping material (typically PET polyester or steel). Multiple heads can operate simultaneously for faster cycle times on long bundles. Research published in journals like Packaging Technology and Science often details advancements in strap joint efficiency and tension control mechanisms.
- Control System Integration: Sophisticated PLC systems manage the entire sequence, synchronizing conveyors, bundle formers, and strapping heads. These systems can often integrate with plant-level Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) or Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems for data logging, production tracking, and remote diagnostics.
Key Technical Parameters:
- Tube Diameter Range: Systems are configurable, typically handling diameters from 10mm up to 300mm or more.
- Tube Length Range: Accommodates lengths commonly from 3 meters up to 12 meters or longer, depending on system design.
- Bundle Weight Capacity: Designed to handle bundle weights ranging from a few hundred kilograms up to several tons (e.g., 500 kg to 5000 kg).
- Strapping Material: Compatible with PET strap (e.g., 16mm, 19mm, 25mm, 32mm widths) or steel strap.
- Cycle Time: Varies based on bundle size and number of straps, but optimized systems aim for maximum throughput aligned with production needs.
Customization and Safety Assurance
Recognizing that no two production environments are identical, these comprehensive steel tube bundling and strapping lines offer significant customization:
- Layout Flexibility: Modular designs allow configurations tailored to specific plant layouts and workflow requirements.
- Profile Handling: Adaptable for round, square, rectangular, or other profile tubes.
- Integration Options: Designed for seamless integration with upstream cutting/forming lines and downstream storage/shipping systems.
Safety remains paramount. These automated systems incorporate robust safety features:
- Physical Guarding: Protective fencing and barriers restrict access to moving parts.
- Light Curtains & Sensors: Detect operator presence in hazardous zones, triggering immediate system halts.
- Emergency Stops: Strategically placed E-stops allow for rapid shutdown.
- Compliance: Designed and built in accordance with relevant safety standards (e.g., CE marking in Europe, OSHA requirements in the US).
Conclusion: A Strategic Investment
Automatic steel tube bundling and strapping solutions represent a strategic investment for manufacturers handling significant volumes of tubular products. By leveraging automation, companies can achieve substantial improvements in operational efficiency, product protection, workplace safety, and overall competitiveness. As documented in industry publications like Industrial Distribution and Modern Materials Handling, the trend towards automation in packaging and material handling continues to accelerate, driven by clear ROI benefits and the need for resilient, high-performance supply chains. These systems provide a reliable, efficient, and customizable solution essential for modern steel tube processing and distribution.






