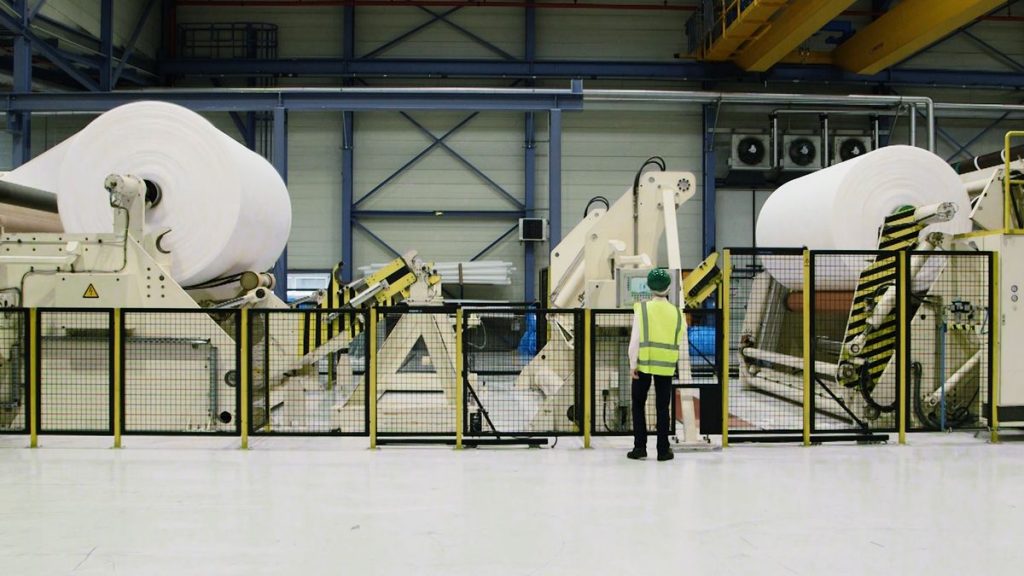
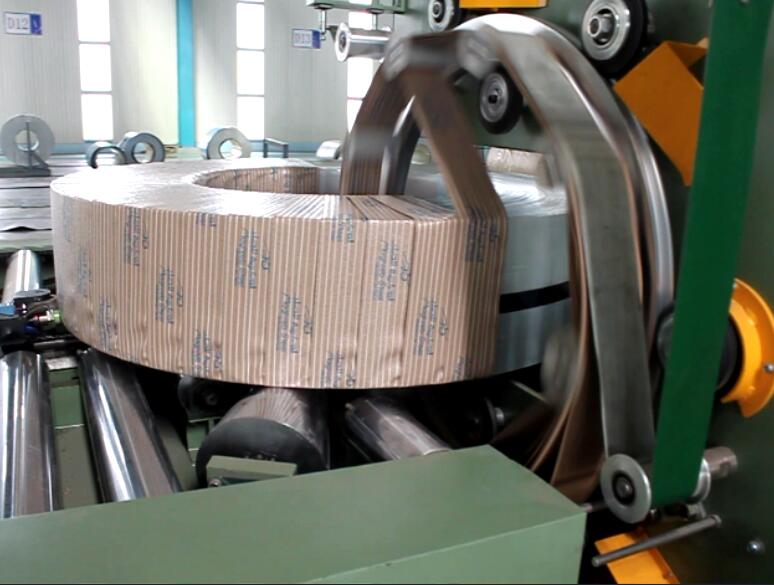
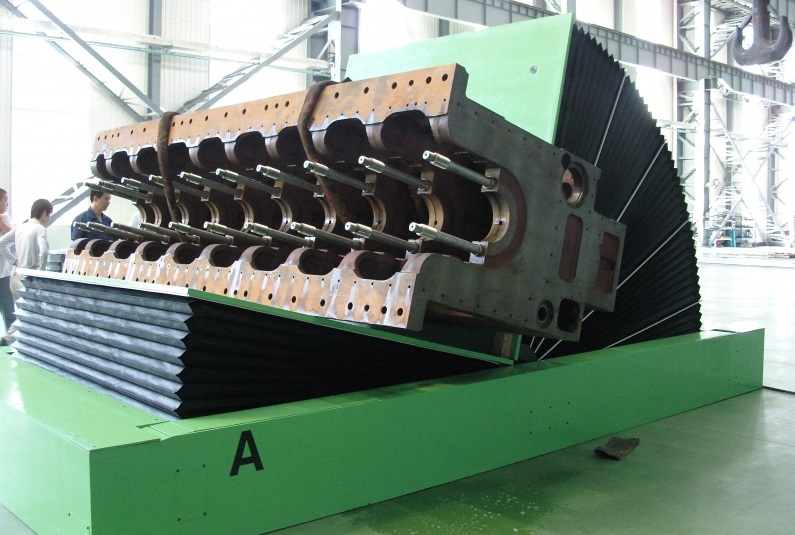
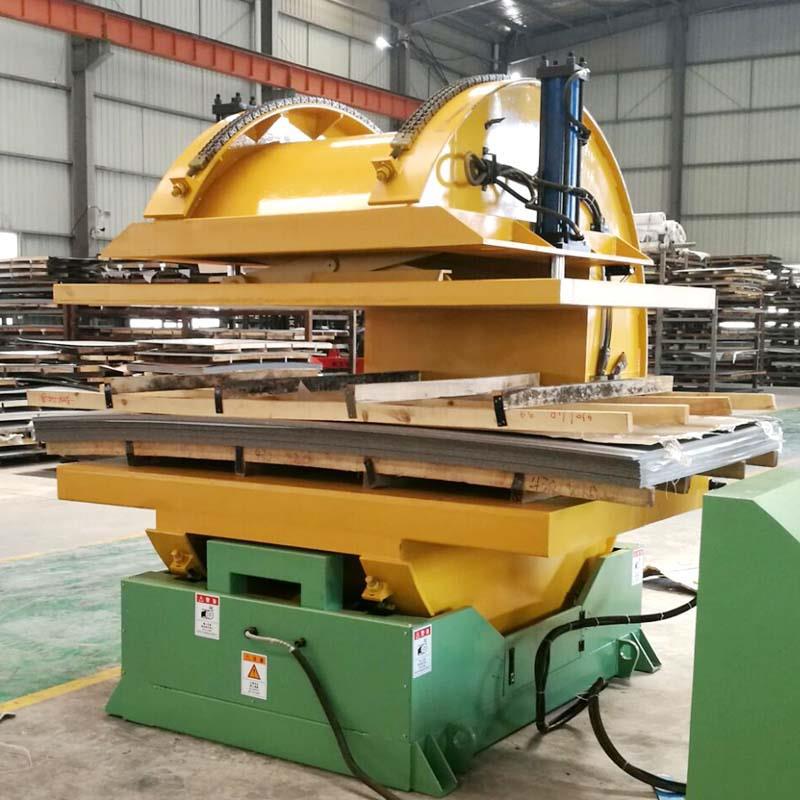
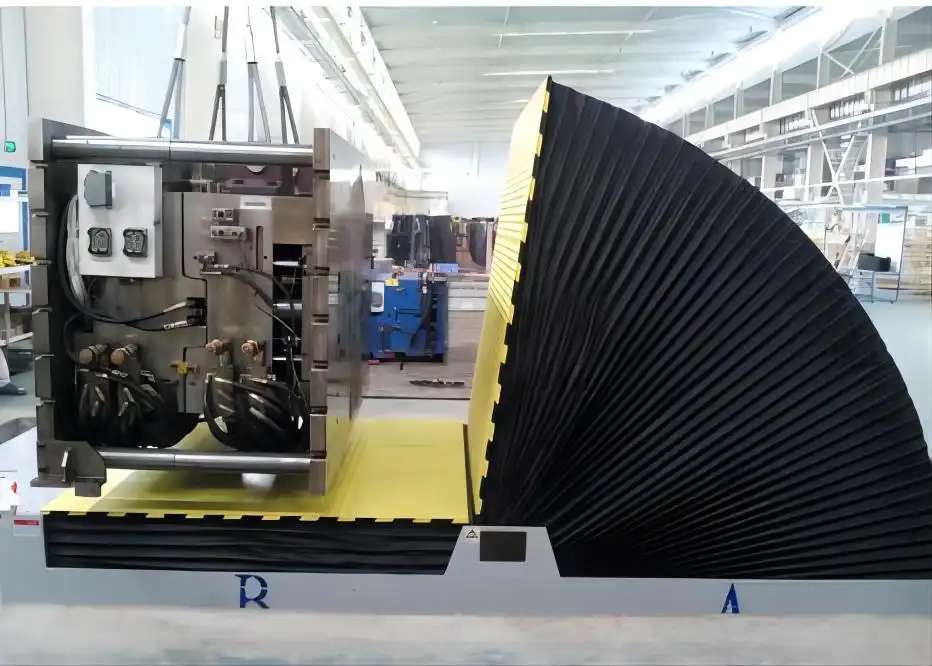
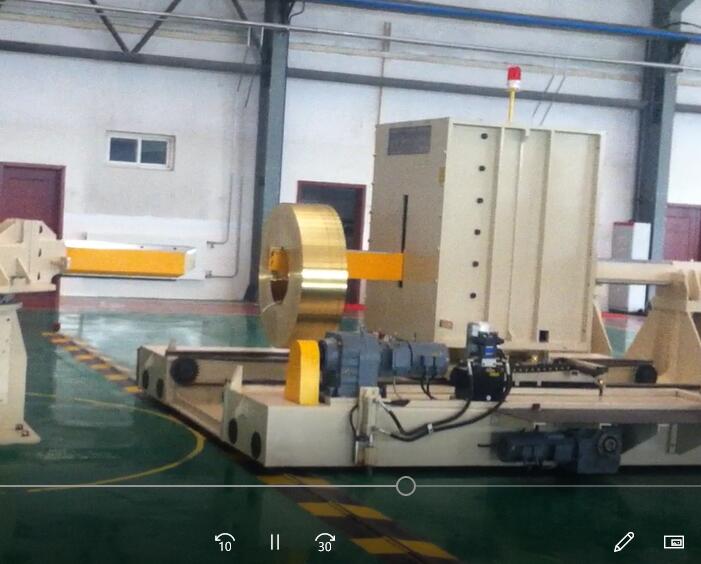
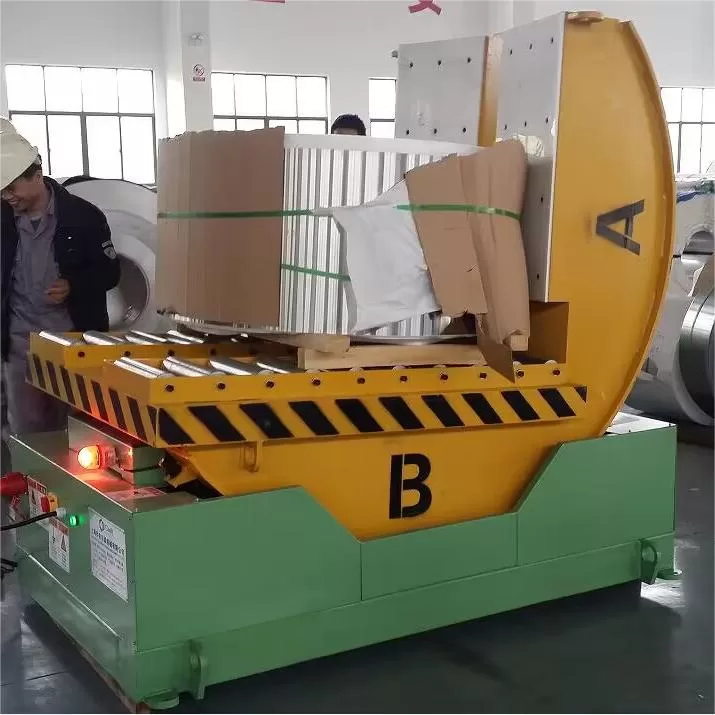
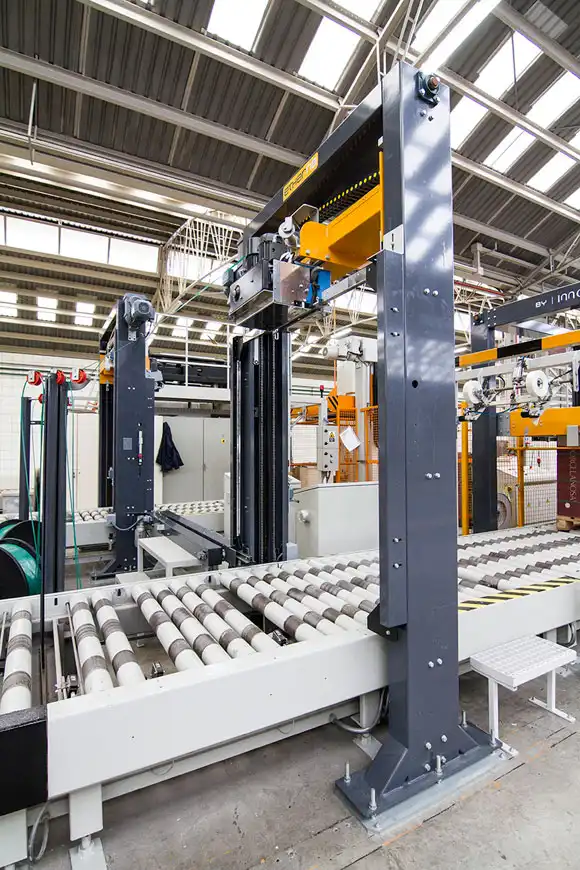
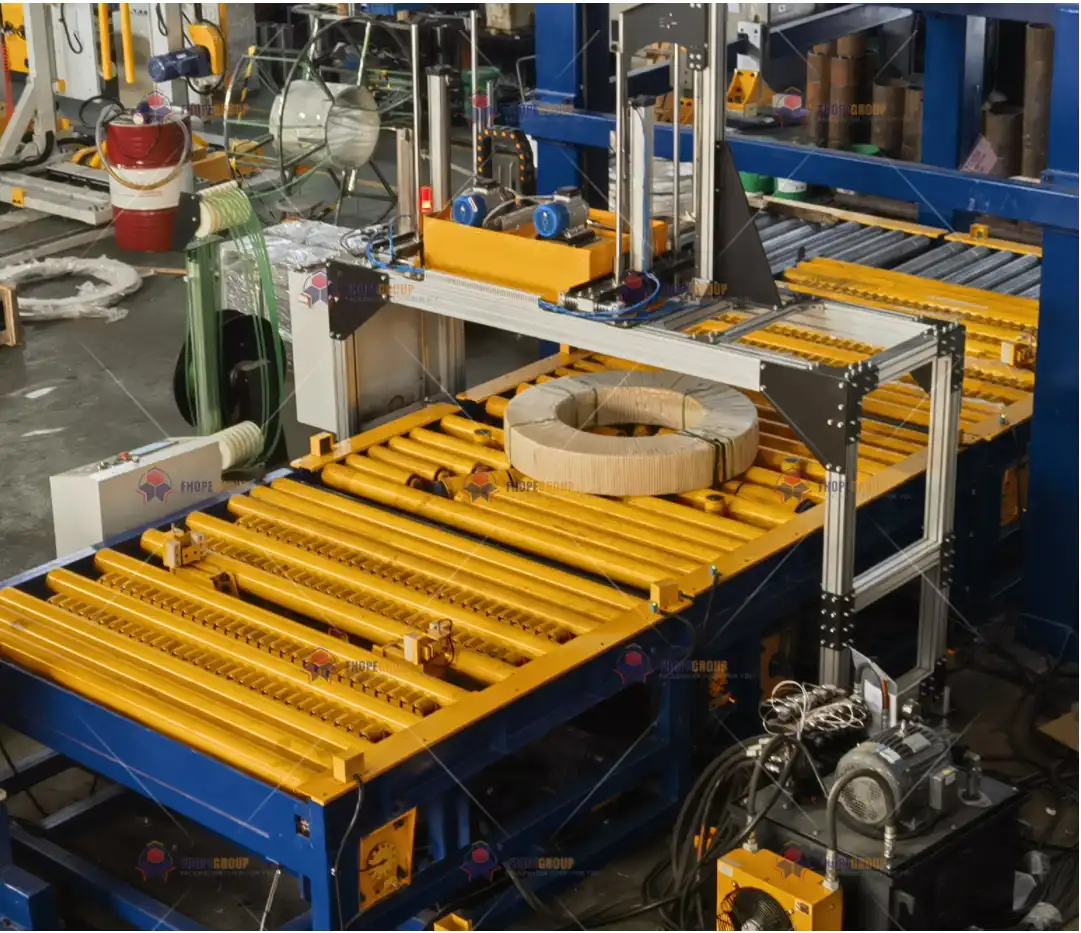
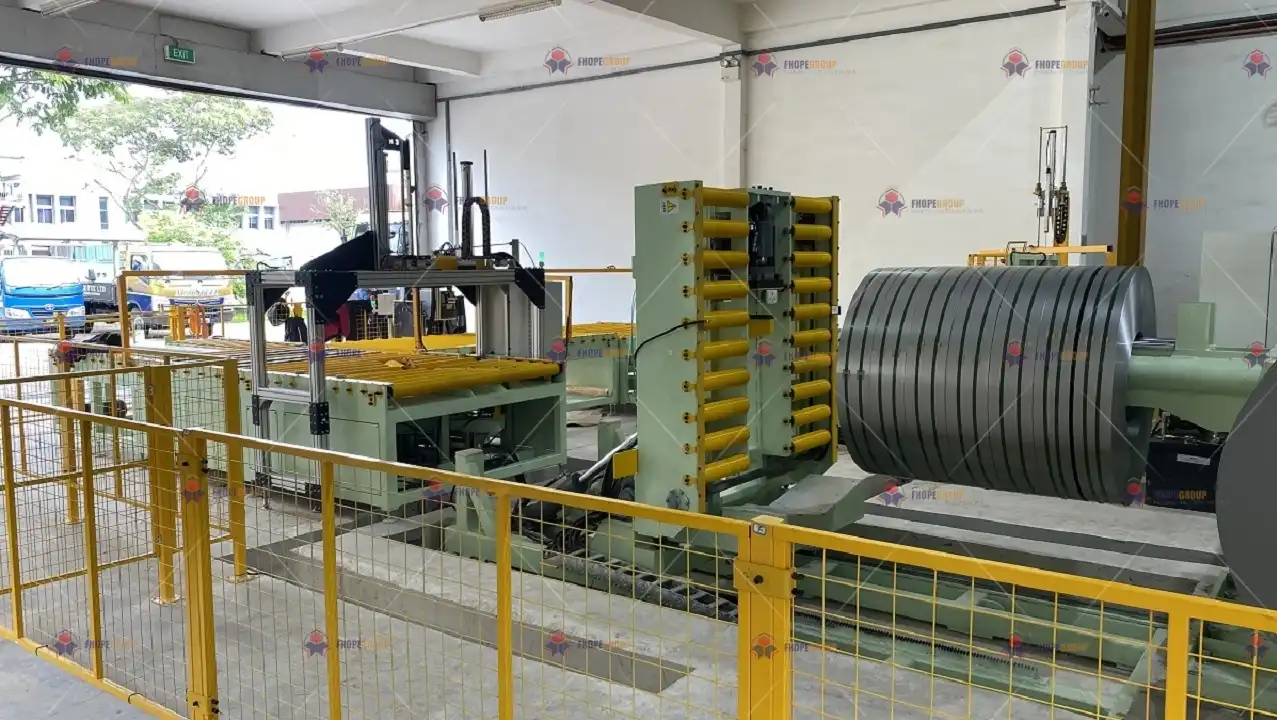
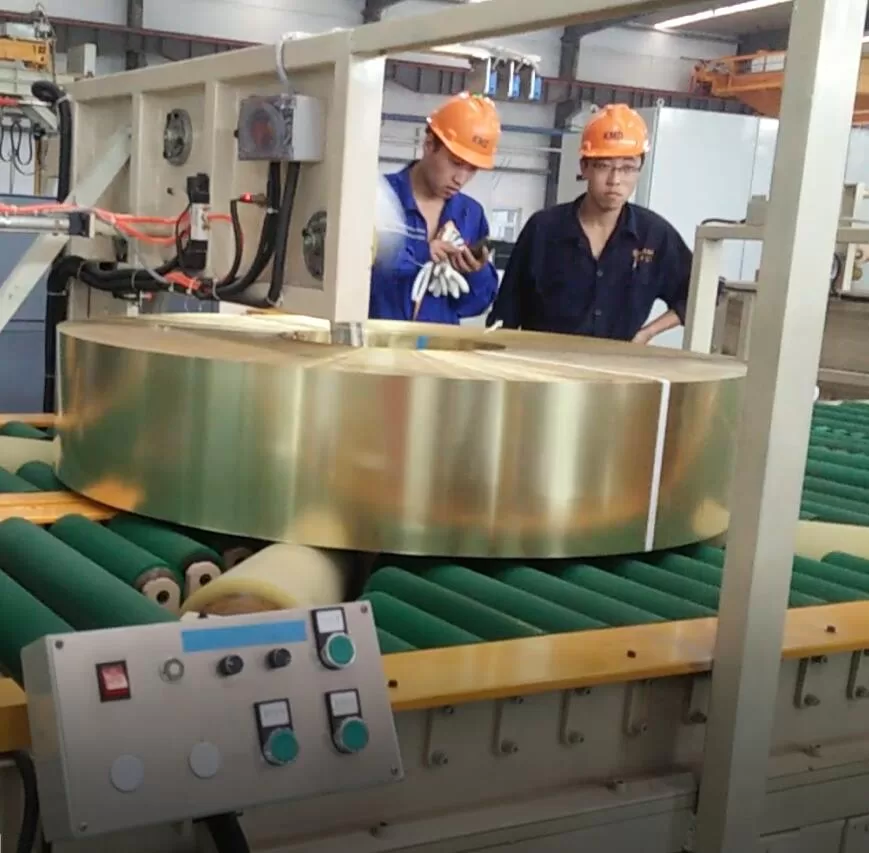
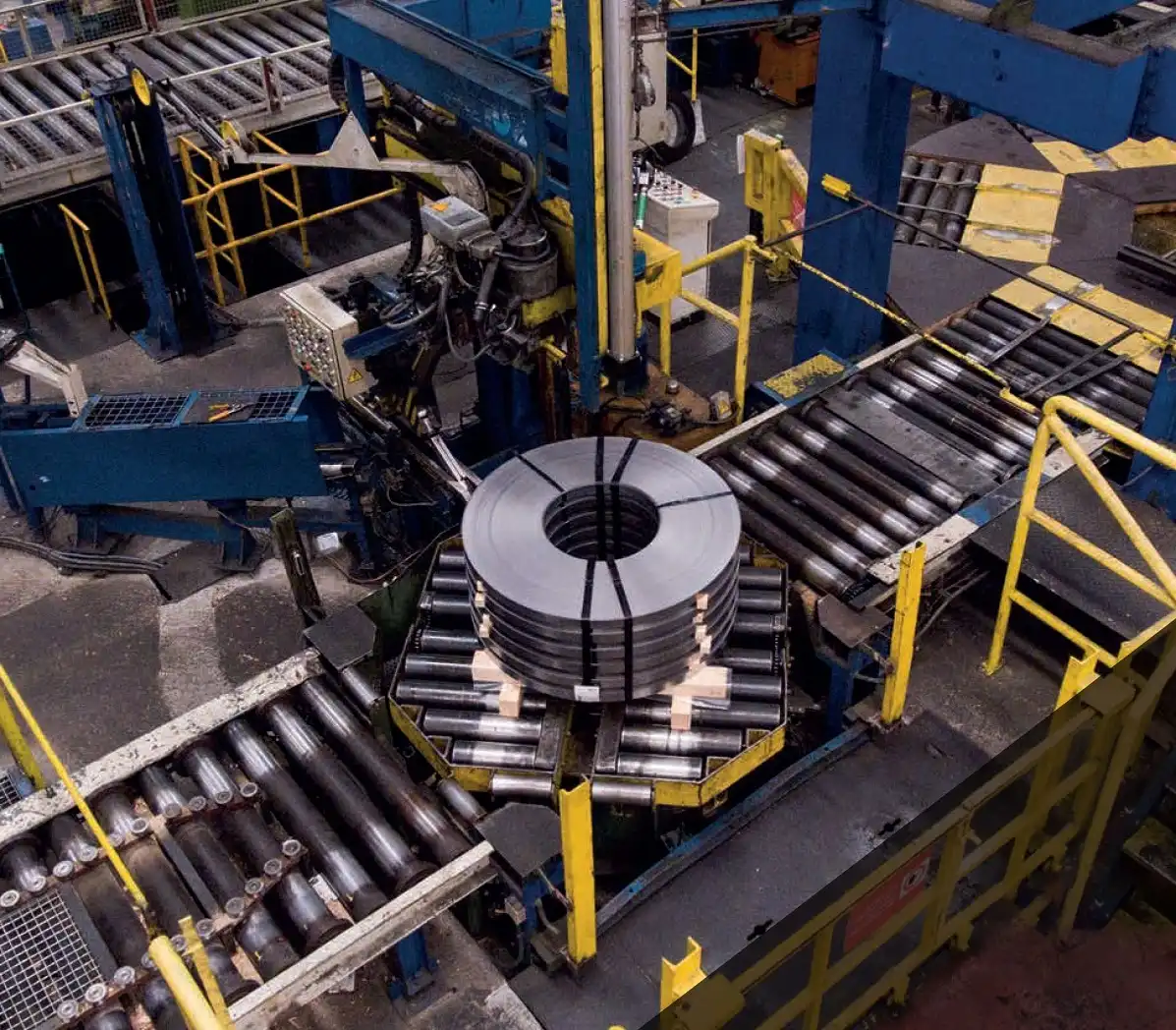
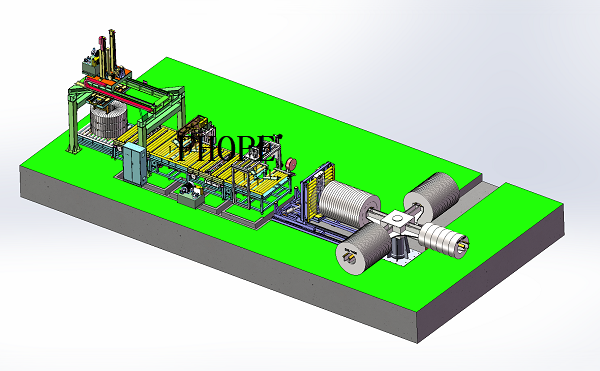
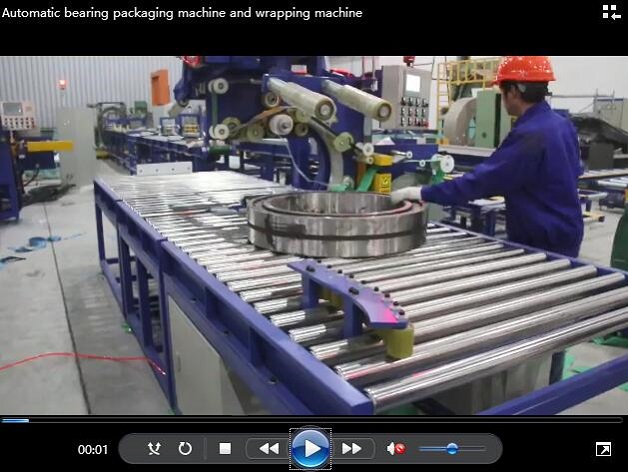
Real Leading Manufactuer In steel Wire Coil Packaging Machine
Enhancing Efficiency with Steel Wire Coil Packaging Machines: A Comprehensive Guide Efficiently packaging steel wire coils is crucial for manufacturers and processors to ensure product integrity during transport and