What Kind of Maintenance Do Steel Coil Packing Lines Require?
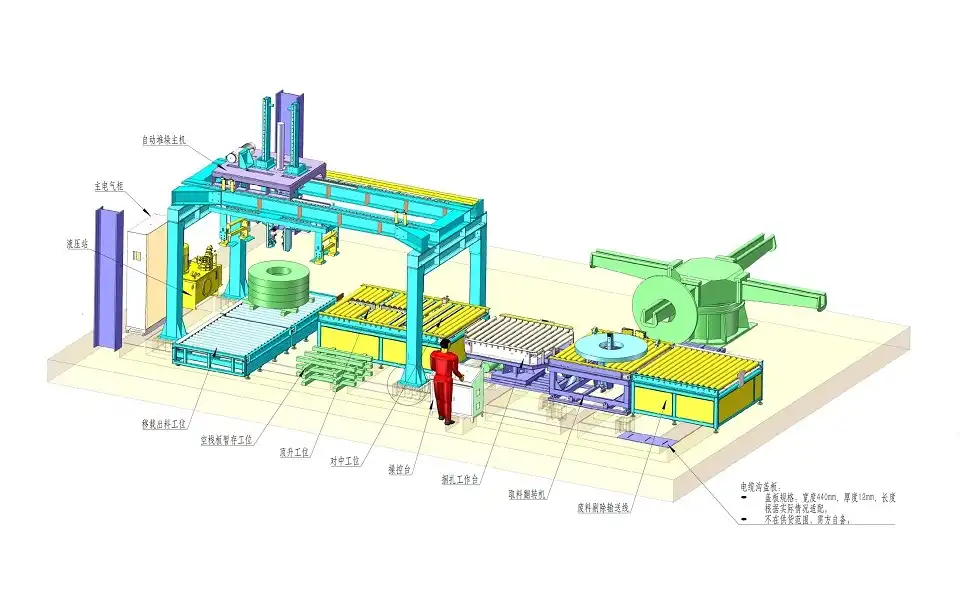
Steel coil packing lines are essential automated systems designed to protect valuable steel coils during transportation and storage. These sophisticated lines handle wrapping, strapping, and labeling, ensuring coils reach their destination securely. However, like all industrial machinery, consistent and thorough maintenance is vital for optimal performance, preventing costly downtime, and maximizing the equipment's lifespan.
This guide details the necessary maintenance tasks for steel coil packing lines, emphasizing preventive strategies and best practices. We will explore how diligent upkeep directly impacts operational efficiency, workplace safety, and overall profitability in steel processing and handling environments.
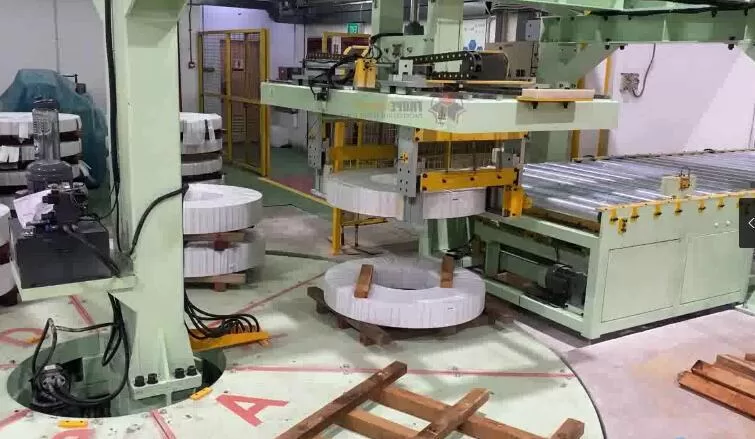

1. Why Regular Maintenance is Crucial for Steel Coil Packing Lines
Steel coil packing lines integrate complex components like conveyors, coil upenders, wrapping units, and strapping machines. Neglecting their maintenance can quickly lead to decreased efficiency, unexpected equipment failures, potential product damage, and serious safety hazards. A proactive maintenance program is not just about upkeep; it's an investment in operational continuity and safety.
Key benefits of regular maintenance include:
- Extended Equipment Lifespan: Properly maintained machinery suffers less wear and tear, significantly extending its operational life and return on investment.
- Minimized Unplanned Downtime: Preventive checks and timely repairs prevent sudden breakdowns, keeping the production line running smoothly and predictably.
- Enhanced Workplace Safety: Regular inspections identify and rectify potential hazards like worn parts or malfunctioning safety guards, reducing accident risks.
- Improved Packaging Quality: Well-maintained equipment ensures consistent and correct application of packaging materials, protecting the coil integrity.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Proactive maintenance avoids expensive emergency repairs, replacement parts, and production losses associated with unexpected failures.
Understanding these benefits highlights the importance of integrating a structured maintenance routine into daily operations.
2. Essential Daily Maintenance Checks
Daily maintenance involves quick but critical tasks primarily focused on cleanliness, visual inspection, and basic lubrication. These routines help catch minor issues before they escalate.
Key Daily Maintenance Tasks:
- Clean Critical Areas: Remove dust, debris, grease, and stray packaging material from sensors, rollers, conveyor belts, wrapping units, and strapping heads. Contaminants can interfere with sensors or cause excessive wear on moving parts.
- Verify Sensor Functionality: Visually inspect photocells, proximity sensors, and limit switches. Ensure they are clean, unobstructed, and correctly aligned to detect coil presence and dimensions accurately.
- Check Safety Guards and E-stops: Confirm all safety guards are securely in place and emergency stop buttons are functional and accessible.
- Inspect for Fluid Leaks: Quickly check hydraulic and pneumatic lines, fittings, and cylinders for any signs of leaks.
- Basic Lubrication: Apply lubricant to specified points (like chains or sliding mechanisms) as per the manufacturer's daily recommendations to ensure smooth movement and reduce friction.
- Monitor Control Panel Indicators: Check for any warning lights or error messages on the HMI or control panel and report them immediately.
Performing these checks at the start or end of each shift establishes a baseline for reliable operation.
3. Implementing Weekly and Monthly Preventive Maintenance
Weekly and monthly maintenance tasks involve more in-depth inspections and adjustments, targeting mechanical, electrical, hydraulic, and pneumatic systems to ensure long-term reliability.
Recommended Weekly Maintenance Tasks:
- Inspect and Tighten Fasteners: Machine vibration can loosen bolts, nuts, and screws. Check critical connections, especially around motors, gearboxes, and moving assemblies, tightening as necessary.
- Check Belts, Chains, and Conveyors: Inspect conveyor belts for proper tension, tracking, and signs of wear (fraying, cracks). Check drive chains for correct tension and lubrication.
- Examine Wrapping/Strapping Units: Inspect film/strap dispensers, cutters, and sealing/welding mechanisms for wear, damage, or residue buildup. Clean and adjust as needed.
- Inspect Pneumatic System Components: Check air filters, regulators, and lubricators (FRL units). Drain water traps/filters. Listen for air leaks around fittings, hoses, and valves.
- Inspect Hydraulic System: Check hydraulic fluid levels and look for leaks around hoses, fittings, cylinders, and pumps. Monitor operating pressure if gauges are present.
Recommended Monthly Maintenance Tasks:
- Thorough Cleaning: Perform a more extensive cleaning than the daily routine, accessing areas under guards or inside cabinets (ensure proper lockout/tagout procedures). Clean electrical cabinets carefully with approved methods.
- Detailed Electrical Inspection: Check wiring connections in control panels and junction boxes for tightness and signs of overheating. Inspect cables and conduits for damage.
- Lubrication Service: Perform more comprehensive lubrication of bearings, gearboxes, and other components according to the manufacturer's lubrication schedule and specifications.
- Sensor Calibration Check: Verify the accuracy of critical sensors (e.g., load cells, positioning sensors) and calibrate if necessary, following manufacturer guidelines.
- Inspect Structural Components: Check the machine frame, supports, and welds for any signs of stress, cracks, or damage.
- Review Safety System Functionality: Test safety interlocks, light curtains, and emergency stop circuits more comprehensively.
Adhering to this schedule proactively addresses wear and tear, preventing larger, more costly failures.
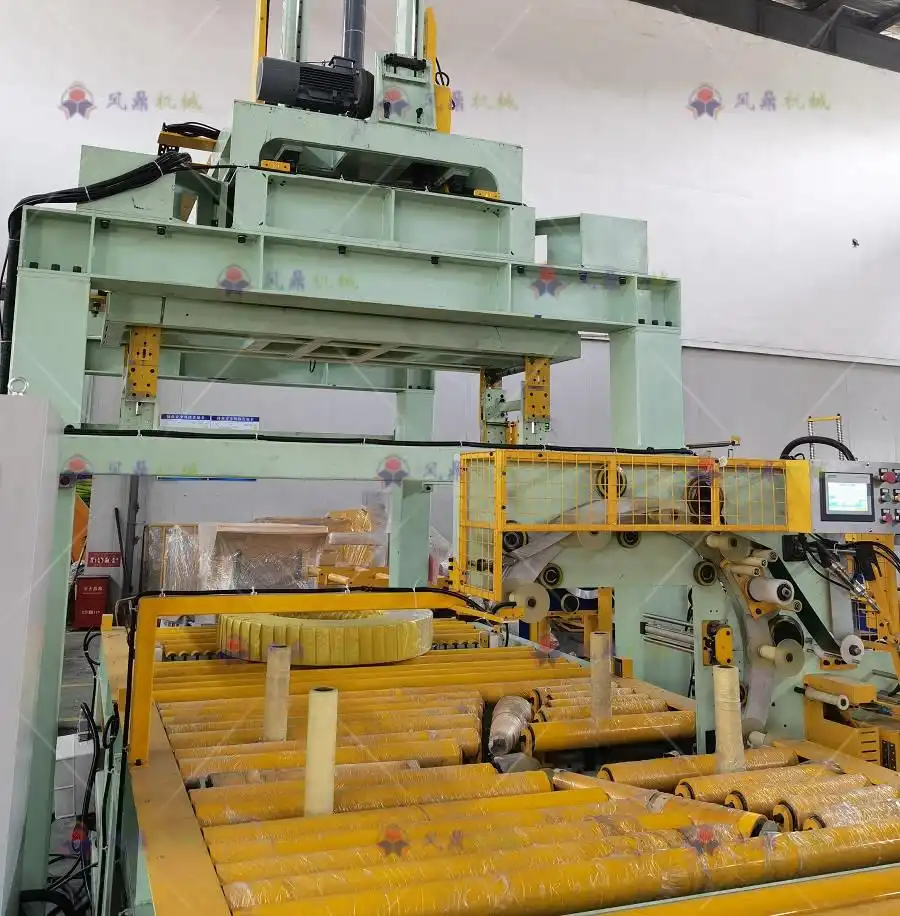

4. Leveraging Predictive Maintenance Technologies
Modern steel coil packing lines increasingly incorporate Industry 4.0 concepts, including predictive maintenance (PdM). PdM utilizes sensors and data analysis to anticipate potential equipment failures before they happen.
How Predictive Maintenance Enhances Upkeep:
- Condition Monitoring Sensors: Sensors integrated into critical components (motors, bearings, gearboxes, hydraulic systems) continuously monitor parameters like vibration, temperature, pressure, and fluid condition.
- Data Analysis: This real-time data is analyzed, often using machine learning algorithms, to detect anomalies and predict potential failures based on deviations from normal operating patterns.
- Proactive Alerts: Maintenance teams receive alerts when a component shows signs of degradation, allowing them to schedule repairs during planned downtime, before a catastrophic failure occurs.
While PdM requires an initial investment, its benefits include optimizing maintenance schedules (performing maintenance only when needed), further reducing unplanned downtime, and extending component life by addressing issues at the earliest stage.

Get Your Best Solution !
5. How Proactive Maintenance Enhances Workplace Safety
Safety is paramount in environments handling heavy steel coils. Equipment failures on a packing line can lead to severe accidents. Regular maintenance is a fundamental aspect of risk mitigation.
Key safety risks addressed by maintenance:
- Strapping/Wrapping Failures: Worn tensioners, cutters, or seals in strapping/wrapping units can lead to improperly secured coils, posing a risk of falling or shifting during handling and transport. Regular inspection and adjustment prevent this.
- Mechanical Failures: Worn bearings, gears, or chains can seize or break, causing sudden stops or uncontrolled movement. Lubrication and inspection minimize these risks.
- Electrical Hazards: Loose wiring, damaged insulation, or malfunctioning components can lead to electrical shocks or fires. Electrical inspections are critical.
- Hydraulic/Pneumatic Malfunctions: Hose bursts, valve failures, or pressure loss can cause sudden movements or component failures. Regular checks of fluid levels, pressures, and system integrity prevent unexpected system behavior.
- Compromised Safety Devices: Ensuring safety gates, light curtains, and E-stops function correctly through regular testing is vital for operator protection.
A well-maintained packing line is inherently safer, protecting personnel from hazards associated with equipment malfunction.
6. Developing a Tailored Maintenance Schedule
A standardized, documented maintenance schedule is key to ensuring all necessary tasks are performed consistently. This schedule should be tailored to the specific packing line model, its operating environment, usage intensity, and the manufacturer's recommendations.
A comprehensive schedule typically includes:
- Task List: Detailed descriptions of each maintenance task (e.g., "Inspect conveyor belt tracking," "Lubricate wrapping ring bearings").
- Frequency: Clearly defined intervals (Daily, Weekly, Monthly, Quarterly, Annually).
- Daily: Cleaning, basic visual checks, E-stop verification.
- Weekly: Belt/chain tension, fastener checks, pneumatic system inspection.
- Monthly: Deeper cleaning, electrical checks, detailed lubrication, sensor checks.
- Annually: Major component inspection/overhaul, potential replacement of high-wear parts (based on condition or hours), comprehensive system calibration and testing.
- Responsibility: Assigning specific tasks to trained personnel (operators vs. maintenance technicians).
- Documentation: A system for recording task completion, findings, and any corrective actions taken.
Consult the equipment manufacturer's manual for baseline recommendations and adjust the schedule based on operational experience and conditions.

7. Best Practices for Effective Maintenance Record-Keeping
Accurate and detailed maintenance records are invaluable. They provide a history of the equipment's health, support troubleshooting, inform future maintenance decisions, and may be required for compliance purposes.
Key Aspects of Good Record-Keeping:
- Log All Activities: Record every maintenance task performed, including routine checks, preventive maintenance, repairs, and parts replaced.
- Include Details: Note the date, the technician performing the work, the specific components serviced, findings (e.g., "bearing noisy," "belt frayed"), actions taken, and parts used.
- Track Component Lifecycles: Recording part replacements helps track lifespan and can inform predictive maintenance models or inventory management.
- Utilize Digital Systems: A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is highly recommended. CMMS software helps schedule tasks, track work orders, manage parts inventory, store maintenance history, and generate reports.
- Analyze Trends: Regularly review maintenance logs to identify recurring problems, components with high failure rates, or trends that might indicate a need for operational changes or equipment upgrades.
Effective record-keeping transforms maintenance from a simple checklist into a data-driven strategy for continuous improvement.
Conclusion
Maintaining a steel coil packing line is not merely a background task; it is fundamental to the efficiency, safety, and profitability of steel handling operations. A structured approach combining daily checks, preventive maintenance schedules (weekly, monthly, annually), and potentially predictive technologies ensures these complex systems operate reliably.
Consistent cleaning, lubrication, inspection, and adjustment prevent costly breakdowns, extend the machinery's service life, ensure consistent packaging quality, and critically, protect the workforce from preventable accidents. By investing time and resources into a robust maintenance program, supported by diligent record-keeping, businesses can maximize the performance and longevity of their vital steel coil packing equipment.

Get Your Best Solution !