Mastering Orbital Stretch Wrapper Safety: Key Procedures for Pallet Load Security
In today's demanding logistics and warehousing environments, maximizing efficiency while upholding stringent safety standards is paramount. The orbital stretch wrapper stands out as a vital piece of equipment, expertly designed to secure pallet loads rapidly and reliably. While indispensable for streamlining packaging operations, these machines introduce specific safety considerations that require careful management. This guide details essential procedures to enhance safety when operating orbital stretch wrappers for pallet loads, fostering a secure and productive workplace.
Understanding the Orbital Stretch Wrapper Mechanism
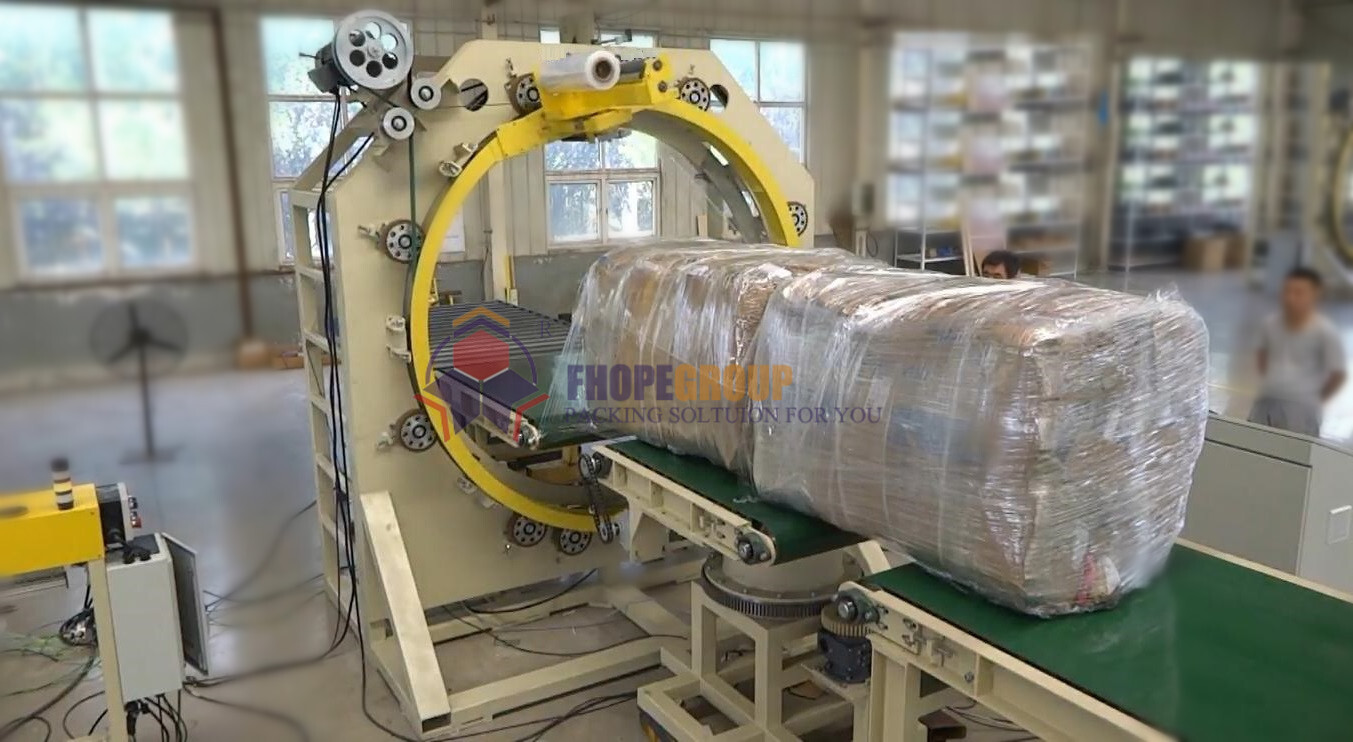
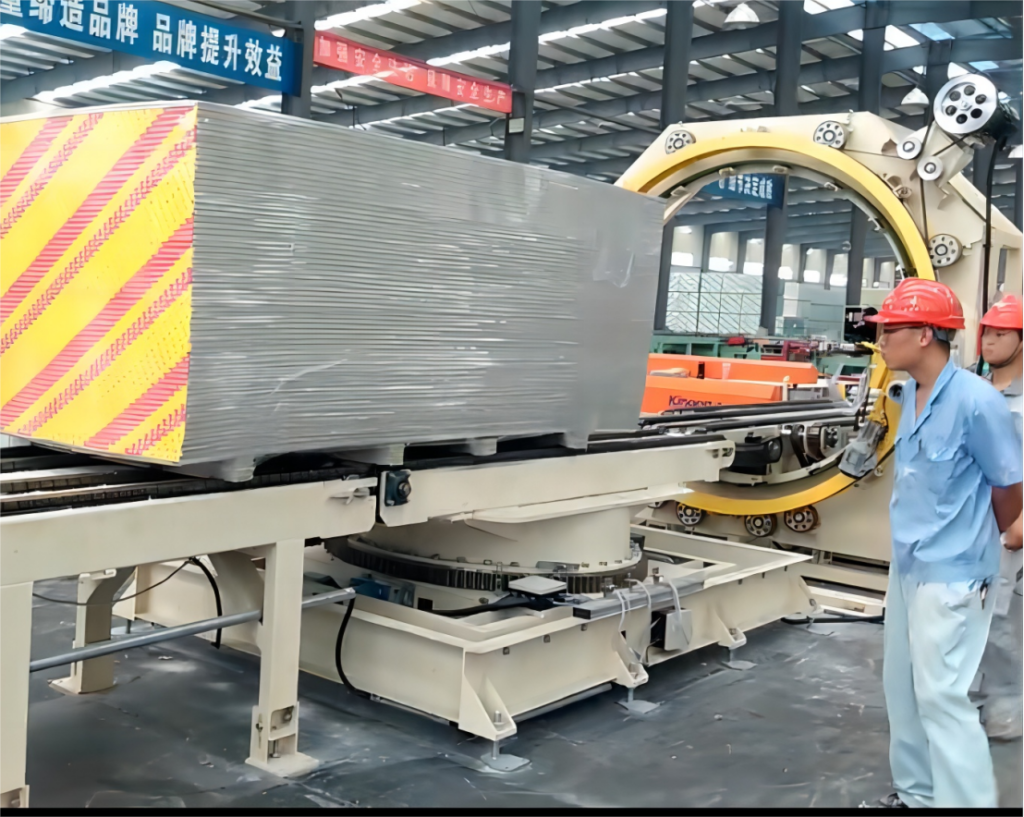
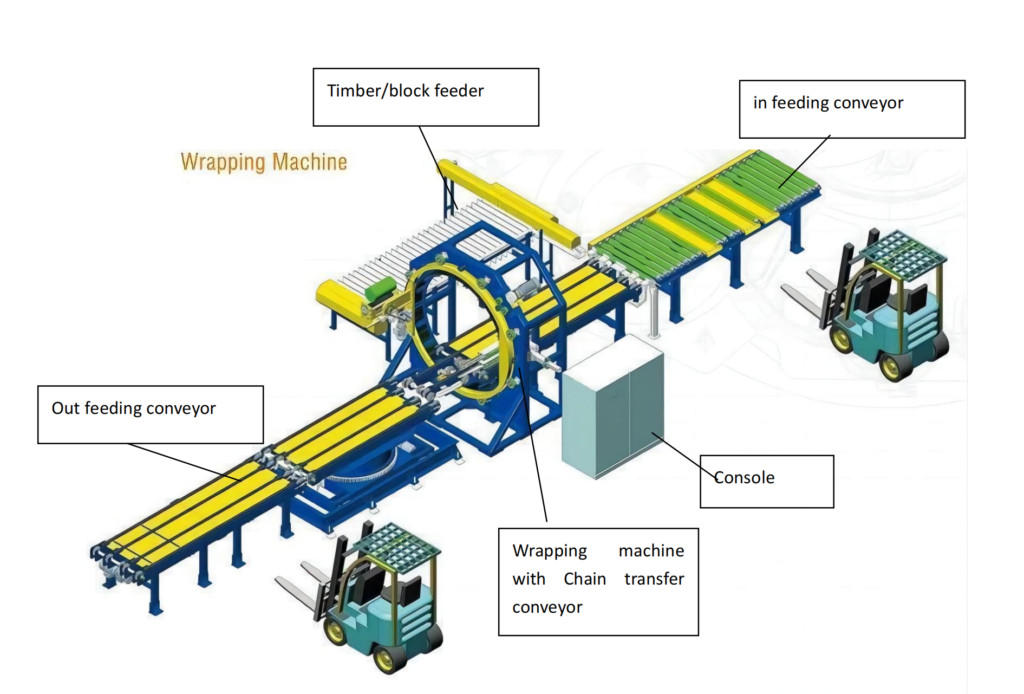
Before implementing safety protocols, a clear understanding of the orbital stretch wrapper's function is necessary. Unlike turntable or rotary arm models, an orbital stretch wrapper applies stretch film horizontally as the film delivery system orbits around a stationary pallet load. This design makes it particularly suitable for securing unstable, oversized, or irregularly shaped loads.
Key operational components typically include:
- Film Delivery System: Dispenses and pre-stretches the film.
- Orbital Ring: The main assembly that rotates around the pallet load, carrying the film delivery system.
- Conveyor System (if applicable): Transports pallets into and out of the wrapping zone.
- Control Panel: Interface for machine operation, settings adjustments, and diagnostics.
- Safety Guarding: Physical barriers and sensors designed to protect operators.
Familiarity with these components is fundamental to recognizing potential hazards and implementing effective safety practices.

The Critical Importance of Pallet Wrapping Safety
Prioritizing safety in pallet wrapping operations extends beyond regulatory compliance; it's about safeguarding personnel, protecting goods, and maintaining operational continuity. Lapses in safety involving orbital stretch wrappers can result in:
- Severe Operator Injuries: Entanglement, crushing, or impact hazards.
- Product Damage: Improper wrapping can lead to load instability and damage during handling.
- Operational Disruptions: Accidents cause costly downtime for repairs and investigations.
- Negative Workplace Impact: Reduced morale and potential damage to the company's reputation.
Investing in robust safety measures directly contributes to improved operational efficiency, employee well-being, and overall business performance.

Key Step 1: Comprehensive Operator Training and Qualification
Effective safety begins with thorough operator training. A robust program should cover:
Foundational Knowledge
- Principles of stretch wrapping and load containment.
- Detailed understanding of the specific orbital wrapper model's components, functions, and limitations.
- Identification and function of all safety features (guards, E-stops, sensors).
- Recognition of potential hazards associated with operation and maintenance.
- Basic risk assessment for different load types and operating conditions.
Practical Skills Development
Supervised, hands-on operation of the machine across various scenarios.
Proper techniques for film loading, threading, and splicing.
Diagnosing and resolving common operational faults safely.
Proficiency in executing standard operating procedures (SOPs) and emergency shutdown protocols.

orbital stretch wrapper for panel 6 sides wrapping (3) Qualification and Ongoing Competency
Assessment through written and practical tests to confirm understanding and skill.
Formal certification or authorization before unsupervised operation.
Mandatory periodic refresher training to address complacency and introduce updates.
Only trained and formally qualified personnel should operate orbital stretch wrappers.
Key Step 2: Rigorous Pre-Operation Safety Inspections
A systematic pre-operation check is non-negotiable and should be performed before every shift or startup.
Machine Condition Check
- Inspect the machine structure for visible damage, loose components, or signs of wear.
- Verify all safety guards, interlocks, and light curtains (if equipped) are present, secure, and functioning correctly. Test emergency stop buttons.
- Check the film delivery system for correct film threading and roller condition.
- Listen for unusual noises during a brief test run (if safe and part of the procedure).
Work Area Assessment
Ensure the designated operating zone around the wrapper is clear of obstructions, debris, spills, and unauthorized personnel.
Confirm adequate lighting for clear visibility of the machine and its surroundings.
Verify safety signage (warnings, PPE requirements) is legible and correctly placed.

funiture packing machine (2) Load and Film Verification
Confirm the correct type, gauge, and width of stretch film is loaded for the application.
Inspect incoming pallet loads for stability, proper stacking, and compatibility with the wrapper's capacity.
Consistent pre-operation checks proactively identify and mitigate risks before wrapping commences.
Key Step 3: Accurate Machine Setup and Parameter Adjustment
Correct machine setup is critical for achieving secure load containment and ensuring safe operation. Pay close attention to:
Film Tension and Pre-stretch Settings
- Adjust film tension according to load characteristics and stability requirements. Insufficient tension compromises load security; excessive tension can crush products or cause film breaks.
- Set the correct pre-stretch level (if adjustable) to optimize film usage and load holding force.
- Re-evaluate and adjust settings when changing film types or load configurations significantly.
Operational Speed Configuration
Set appropriate orbital ring and conveyor speeds based on load weight, stability, and dimensions.
Utilize slower speeds for exceptionally tall, unstable, or complex loads until stability is confirmed.

orbital stretch wrapper for panel 6 sides wrapping (2) Dimensional Adjustments
Ensure any adjustable guides, supports, or wrapping parameters (e.g., wrap counts at top/bottom) are correctly set for the specific pallet dimensions being processed.
Double-check settings after adjustments or changeovers.
Improper setup not only risks product damage but can create unstable loads hazardous during subsequent handling and transport.
Key Step 4: Safe Pallet Load Handling Procedures
Moving large pallet loads into and out of the wrapping zone presents specific hazards that require defined procedures.
Loading Safety
- Always use appropriate material handling equipment (MHE), such as forklifts or pallet jacks, operated by trained personnel.
- Approach the wrapper smoothly and position the load accurately within the designated wrapping area or onto the conveyor.
- Confirm the load is stable and properly centered before initiating the wrap cycle. Never attempt to manually stabilize a load while MHE is positioning it.
Unloading Safety
- Ensure the wrapping cycle is fully complete and the machine has stopped before approaching the pallet.
- Exercise caution when engaging the wrapped load with MHE, recognizing potential changes in weight distribution or dimensions.
- Visually inspect the wrapped load's integrity and stability before transporting it away from the wrapping area.
Key Step 5: Establishing and Maintaining a Safe Operating Zone
Demarcating and controlling the area around the orbital stretch wrapper is essential for preventing collisions and unauthorized access.

Zone Definition
- Clearly mark the operational footprint of the machine, including pallet entry/exit points and the orbital ring's movement path, using floor tape, painted lines, or physical barriers.
- Ensure sufficient clearance within the zone for safe MHE maneuvering during loading and unloading.
Access Control Measures
- Implement strict policies restricting entry into the operating zone to trained operators and authorized maintenance personnel only.
- Utilize clear signage indicating mandatory PPE, restricted access, and potential hazards (e.g., moving machinery).
Traffic Flow Management
- Design clear, designated pathways for MHE and pedestrian traffic around the wrapping station to prevent conflicts.
- Consider installing safety mirrors at blind corners or integrating warning lights that activate during machine operation.
Effective zone control minimizes the risk of personnel encountering moving machine parts or interfering with MHE operations.

Key Step 6: Consistent Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
While engineering controls and safe procedures are primary, appropriate PPE provides crucial operator protection.
Standard PPE Requirements
- Safety Glasses: Protect eyes from potential flying debris or snapping stretch film.
- Steel-Toed Safety Boots: Guard against foot injuries from dropped items or collisions with pallets/MHE.
- High-Visibility Vest: Ensures the operator is easily seen by MHE operators in the vicinity.
- Cut-Resistant Gloves: Recommended during film roll changes, threading, or minor adjustments to protect hands.
PPE Program Management
- Provide appropriate, well-fitting PPE to all authorized operators.
- Train employees on the correct use, limitations, care, and maintenance of their assigned PPE.
- Implement a system for regular inspection and replacement of worn or damaged PPE.
Consistent and correct PPE use is a vital component of a comprehensive safety strategy.
Key Step 7: Preparedness for Emergency Situations
Despite preventative efforts, the potential for emergencies exists. Having clear procedures and accessible equipment is critical.
Emergency Stop (E-Stop) Readiness
- Ensure all operators know the precise location and function of all E-stop buttons on the machine.
- Regularly test E-stop circuits as part of the maintenance schedule.
- Train operators on when and how to activate an E-stop immediately in hazardous situations.
First Aid and Fire Safety Provisions
- Maintain adequately stocked, easily accessible first aid kits near the wrapping station.
- Ensure appropriate fire extinguishers (typically Class ABC) are available, inspected, and operators are trained in their use.
- Have designated personnel trained in first aid and CPR.
Documented Emergency Response Plan
- Develop and communicate a clear, site-specific plan outlining steps to take in various emergencies (e.g., injury, machine malfunction, fire).
- Include emergency contact information and procedures for machine shutdown and area evacuation if necessary.
- Conduct periodic drills to ensure familiarity and effectiveness of the plan.
A well-rehearsed emergency plan can significantly mitigate the severity of unforeseen incidents.
Key Step 8: Proactive Maintenance and Regular Inspections
A well-maintained orbital stretch wrapper is inherently safer and more reliable. Implement a structured maintenance program.
Routine Operator Checks
- Incorporate basic checks into the pre-operation inspection routine (e.g., listening for unusual noises, checking fluid levels if applicable).
- Train operators to report any observed abnormalities or malfunctions immediately.
Scheduled Preventive Maintenance (PM)
- Strictly adhere to the manufacturer's recommended PM schedule, covering lubrication, adjustments, and component wear checks.
- Maintain detailed logs of all maintenance activities, including dates, tasks performed, and parts replaced. Use qualified technicians for complex PM tasks.
Periodic Professional Inspections
- Arrange for periodic, in-depth inspections by the manufacturer's representative or a qualified third-party service provider.
- Address any deficiencies or recommendations identified during these inspections promptly and thoroughly.
Preventive maintenance identifies potential failures before they occur, preventing hazardous situations and unexpected downtime.
Key Step 9: Safe Stretch Film Handling and Storage Practices
Even the stretch film itself requires safe handling procedures.
Ergonomic Film Roll Handling
Train operators on proper lifting techniques to avoid back strain when handling heavy film rolls.
Utilize mechanical lifting aids or team lifting for particularly large or heavy rolls.
Exercise caution when cutting film or removing empty cores.

horizontal orbital stretch wrapper4 Proper Film Storage
Store stretch film rolls in a designated, clean, dry area, away from direct sunlight and sources of heat, which can degrade film properties.
Stack rolls securely to prevent them from falling. Follow supplier recommendations for maximum stack height.
Implement a First-In, First-Out (FIFO) inventory system to ensure older film is used first.
Waste Film Management
- Establish procedures for collecting and disposing of waste stretch film and empty cores promptly to prevent trip hazards.
- Explore opportunities for recycling used stretch film to support sustainability initiatives.
Attention to film handling minimizes ergonomic risks and maintains a tidy, safe work area.
Key Step 10: Cultivating a Culture of Continuous Safety Improvement
Achieving and maintaining a safe operating environment is an ongoing process that requires active participation and feedback.
Regular Safety Communication
- Conduct periodic safety meetings or toolbox talks specifically addressing pallet wrapping operations, recent incidents (if any), near misses, or changes in procedures.
- Encourage open discussion where operators feel comfortable raising safety concerns without fear of reprisal.
Valuing Operator Input
- Establish a formal or informal system for operators to easily report hazards, suggest safety improvements, or provide feedback on existing procedures.
- Demonstrate that management values this input by investigating suggestions and implementing feasible improvements.
Periodic Safety Audits
- Conduct regular internal safety audits of the orbital wrapping process, using a checklist based on these key steps and manufacturer guidelines.
- Use audit findings to identify systemic weaknesses, track safety performance trends, and refine safety protocols.
A proactive safety culture, driven by continuous improvement and open communication, is the most effective way to sustain a safe and efficient operation.
Conclusion: Integrating Safety for Peak Performance and Protection
The orbital stretch wrapper is a powerful tool for securing pallet loads efficiently. However, its operation demands a disciplined approach to safety management. By diligently implementing these ten key steps – encompassing comprehensive training, rigorous checks, proper procedures, regular maintenance, and a commitment to continuous improvement – businesses can significantly mitigate risks associated with these machines.
Prioritizing safety is not merely about compliance; it's a fundamental investment in your workforce, your products, and your operational integrity. A safe wrapping operation translates directly into reduced injuries, less product damage, minimized downtime, and enhanced employee morale. Ultimately, a workplace culture where safety is ingrained leads to a more productive, reliable, and sustainable business. Stay vigilant, stay informed about evolving best practices, and make safety the cornerstone of your pallet wrapping operations.