Understanding Automatic Online Steel Coil Strapping Machines for Efficient Packaging
Steel coils, whether slit or master coils, require secure packaging for safe handling, storage, and transportation. Automatic online steel coil strapping machines play a crucial role in modern metal processing and distribution centers by applying straps efficiently and consistently, integrating directly into the production or packaging line. This article explores the operation, components, benefits, and considerations associated with these essential industrial strapping systems.
1. What is an Automatic Online Steel Coil Strapping Machine?
An automatic online steel coil strapping machine is a piece of industrial equipment designed to apply circumferential straps (typically steel or heavy-duty plastic) around steel coils without manual intervention. "Online" signifies that it is integrated into a conveyor system or coil handling line, allowing coils to pass through the strapping station as part of a continuous process. These systems are vital for high-volume operations requiring speed, consistency, and reliability in coil packaging.
2. Key Operational Principles
The core function involves automatically placing, tensioning, and sealing straps around the coil. The typical process includes:
- Coil Positioning: The coil is transported via conveyor or transfer car and precisely positioned within the strapping machine's working area.
- Strap Feeding: The strapping head feeds the required length of strap material (from a large dispenser coil) around the circumference of the steel coil.
- Tensioning: Once the strap encircles the coil, a tensioning mechanism pulls it tight to a pre-set level, ensuring the coil wraps are held securely. Proper tension is critical to prevent coil shifting or unwinding.
- Sealing/Joining: The machine securely joins the strap ends. Common methods include notch joints or seal-less joints (using punching/interlocking) for steel straps, or heat/friction welds for plastic straps.
- Strap Cutting: After sealing, the strap material is cut from the supply coil.
- Coil Exit: The strapped coil is released to move down the line for further processing, storage, or shipping.
Many systems can rotate the coil or move the strapping head to apply multiple straps at different positions (e.g., radial strapping).
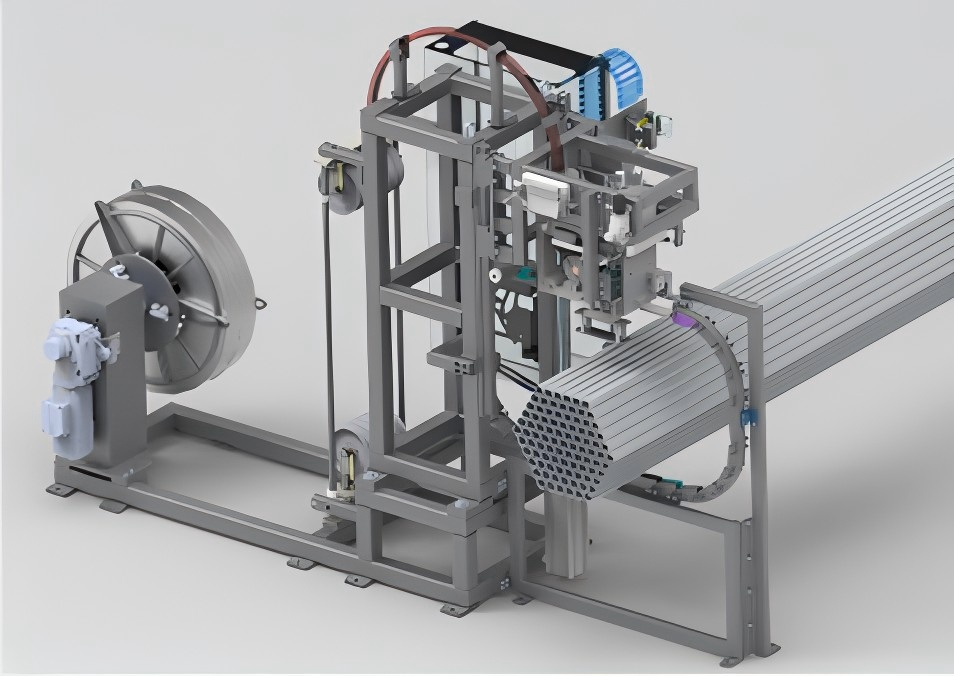
3. Understanding Strapping Levels and Patterns
Automated systems can be programmed for different strapping requirements, often referred to by levels indicating the number and pattern of straps:
- Level 2 Strapping: Generally involves applying two straps circumferentially around the coil. This provides basic securement suitable for stable coils or less demanding transport conditions.
- Level 3 Strapping: Typically applies three or more straps. The pattern might involve evenly spaced circumferential straps or potentially overlapping or specific angled placements depending on the coil's characteristics and the required load stability. This offers enhanced security for heavier coils, sensitive materials, or more rigorous handling and transport requirements.
The control system allows operators to select the appropriate strapping program based on the specific coil product code or production order requirements.
4. Core Components of an Automated Strapping System
These machines consist of several integrated subsystems:
- Strap Dispenser: Holds the large coil of strapping material and ensures smooth, tangle-free feeding.
- Strap Feeding Mechanism: Actively pulls the strap from the dispenser and guides it around the coil through a strap track or chute.
- Strapping Head: The heart of the machine, performing the tensioning, sealing, and cutting operations. Its design varies based on the strap type (steel/plastic) and sealing method.
- Strap Track/Chute: Guides the strap around the coil during the feeding cycle. Often retractable or designed to accommodate various coil diameters.
- PLC Control System: The brain of the operation, automating the sequence, controlling motors and actuators, monitoring sensors, storing strapping recipes (tension, number of straps, positions), and interfacing with the main plant control system (Level 2 or Level 3 automation integration).
- Sensors: Detect coil presence and position, monitor strap feeding, confirm strap tension, and check for faults (e.g., strap misfeed, end of coil).
- Safety Guarding: Physical barriers, light curtains, and emergency stop systems to protect personnel during operation.
5. Integration into Coil Packing Lines
Integrating an automatic strapping machine into a coil packing line offers significant advantages:
- Increased Throughput: Automating the strapping process eliminates manual bottlenecks, enabling higher processing speeds that match upstream production rates.
- Consistency: Ensures every coil is strapped with the correct tension and strap placement according to specifications, improving package quality and load security.
- Data Integration: Advanced systems can communicate with plant MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) or ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems, receiving strapping instructions per coil ID and reporting back operational data.
- Reduced Labor: Frees up personnel from manual strapping tasks, allowing them to focus on other value-added activities.
Integration requires careful planning regarding line layout, conveyor speeds, communication protocols, and safety interlocks between different pieces of equipment.
6. Benefits of Automated Steel Coil Strapping
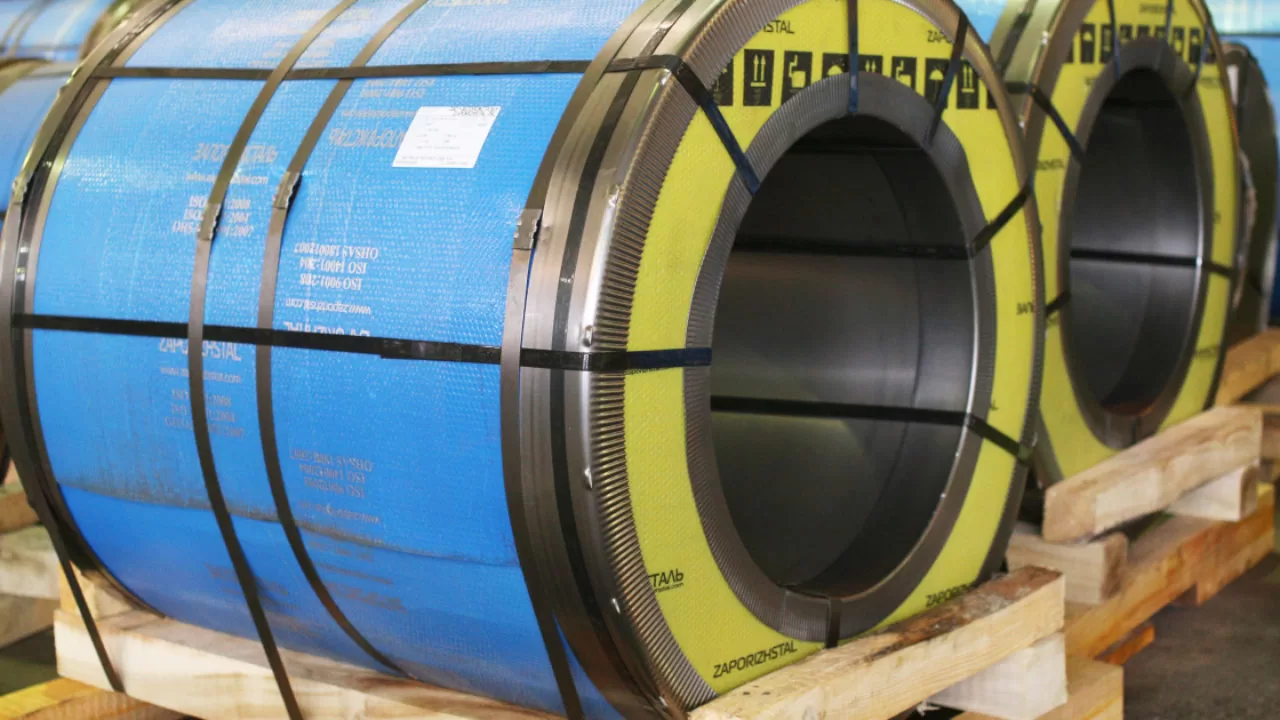

- Enhanced Safety: Reduces manual handling of heavy coils and strapping tools.
- Improved Load Security: Consistent tension and placement minimize the risk of coil damage during transit.
- Higher Efficiency: Faster cycle times compared to manual or semi-automatic methods.
- Cost Savings: Reduced labor costs, potentially lower strap consumption due to optimal tensioning, and less product damage.
- Process Reliability: Predictable and repeatable strapping performance.
7. Considerations When Selecting a System
Choosing the right automatic steel coil strapping machine involves evaluating several factors:
- Coil Specifications: Range of coil diameters, widths, and weights to be handled.
- Throughput Requirements: Number of coils to be strapped per hour/shift.
- Strap Type: Compatibility with required steel or plastic strap specifications (width, thickness, tensile strength).
- Strapping Patterns: Ability to perform the required number and placement of straps (Level 2, Level 3, etc.).
- Operating Environment: Space constraints, temperature, dust levels.
- Control System Needs: Level of automation required, integration capabilities with existing plant systems.
- Maintenance Access: Ease of access for routine maintenance and repairs.
8. Maintenance for Optimal Performance
Like any industrial machinery, automatic strapping systems require regular maintenance for long-term reliability:
- Cleaning: Regularly remove dust, debris, and strap fragments, especially around the strapping head and feed mechanisms.
- Lubrication: Follow manufacturer recommendations for lubricating moving parts.
- Inspection: Periodically check wear parts like cutters, tension wheels, grippers, and sealing components.
- Calibration: Ensure tensioning systems are accurately calibrated.
- Preventive Maintenance: Adhere to the manufacturer's scheduled maintenance plan.
Conclusion
Automatic online steel coil strapping machines are indispensable assets in facilities handling large volumes of steel coils. By automating the strapping process and integrating seamlessly into production lines, they enhance packaging efficiency, improve load security, increase worker safety, and contribute significantly to overall operational productivity. Understanding their operation, components, and maintenance requirements is key to leveraging their full potential in demanding industrial environments.