How to Ensure Minimum Downtime with a Well-Supported Steel Coil Packing Line
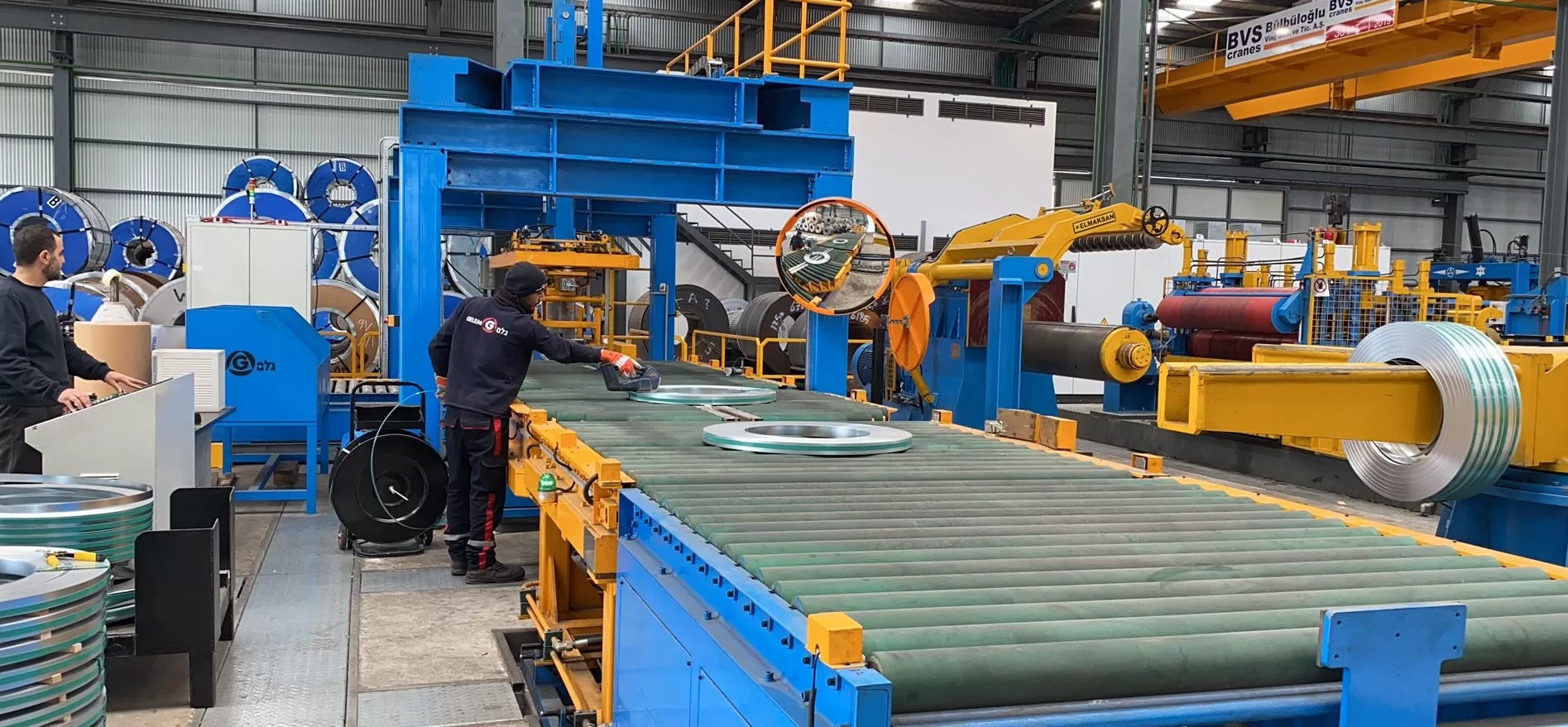

Introduction
In industrial manufacturing, particularly within the demanding steel sector, maintaining continuous operation and minimizing downtime are paramount for productivity and profitability. The steel coil packing line represents a critical stage where interruptions can severely impact overall operational efficiency. Unplanned downtime—whether stemming from equipment failure, inadequate maintenance, operator error, or poor system integration—translates directly into costly delays and lost revenue.
This article delves into essential strategies and best practices designed to minimize downtime on your steel coil packing line. By focusing on proactive measures such as robust preventive and predictive maintenance, real-time system monitoring, comprehensive operator training, efficient material management, and optimized system design, companies can significantly enhance the reliability and performance of their packing operations. We will provide actionable insights applicable to steel coil packing lines of all scales, ensuring smoother workflows and reduced maintenance overheads.
1. Understanding Common Causes of Downtime in Steel Coil Packing Lines
Identifying the root causes of interruptions is the first crucial step toward mitigating downtime. In steel coil packing lines, common culprits include:
- Mechanical Failures: Breakdowns in core components like motors, conveyor systems, sensors, wrapping units, or strapping heads are frequent sources of unplanned stops.
- Operator Errors: Incorrect machine parameter settings, improper coil handling techniques, or insufficient operator training can lead to malfunctions, jams, or safety incidents causing delays.
- Material Stockouts: Running out of essential packing materials such as steel or PET strapping, stretch film, or protective wraps inevitably halts the line until supplies are restocked.
- Software and Control System Glitches: In automated lines, software bugs, communication errors between PLC controllers, or sensor malfunctions can disrupt the packing sequence.
- Ineffective Maintenance: While scheduled maintenance is necessary, poorly planned, overly frequent, or inefficiently executed maintenance activities can paradoxically increase overall downtime.
- Integration Issues: Poor integration between different machines or systems within the line (e.g., coil transport, weighing, packing, labeling) can create bottlenecks or communication failures.
Pinpointing the primary contributors to downtime within your specific operation allows for the implementation of targeted, effective countermeasures.
2. The Critical Role of Preventive Maintenance Programs
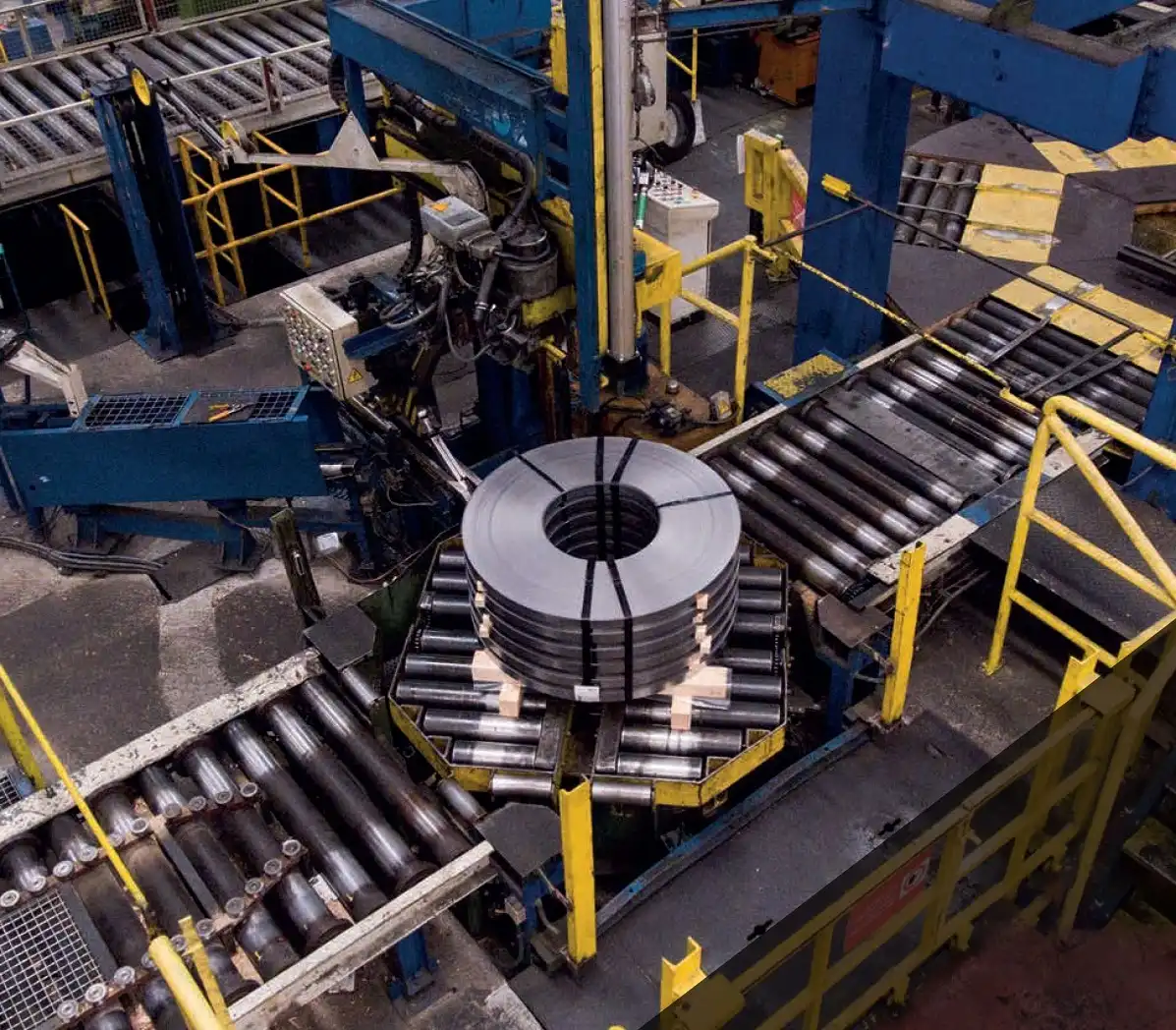

A structured preventive maintenance (PM) program is one of the most potent tools for reducing unexpected equipment failures and associated downtime. Unlike reactive maintenance (fixing things after they break), PM focuses on scheduled inspections, lubrication, cleaning, adjustments, and component replacements to prevent failures before they occur.
Key Elements of an Effective PM Strategy:
- Scheduled Inspections: Conduct regular, detailed inspections of critical machinery components—conveyors, rollers, hydraulic systems, pneumatic components, wrapping arms, strapping tools, safety guards—to identify signs of wear, misalignment, or potential failure.
- Lubrication and Cleaning: Adhere strictly to lubrication schedules using the correct lubricants for all moving parts. Keep machinery clean and free from dust, debris, and fluid leaks, which can cause friction, overheating, or blockages.
- Wear Part Replacement: Proactively replace parts known to have a finite lifespan (e.g., belts, chains, bearings, seals, cutting blades) based on manufacturer recommendations or operational history, rather than waiting for them to fail. Develop a schedule based on operating hours or cycles.
- Calibration and Adjustment: Regularly calibrate sensors, check alignments, and adjust settings to ensure equipment operates within specified tolerances for optimal performance and quality.
Implementing a rigorous PM program significantly decreases the probability of sudden breakdowns, extends equipment lifespan, and improves the overall reliability of the steel coil packing line.
3. Leveraging Real-Time Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance
Modern technology offers powerful tools for moving beyond preventive maintenance towards predictive maintenance (PdM), driven by real-time monitoring.
Harnessing IoT and Sensors:

Integrating Internet of Things (IoT) sensors into the packing line allows for continuous monitoring of crucial operational parameters:
- Vibration Analysis: Detects imbalances, misalignments, or bearing wear in motors and rotating equipment.
- Thermal Imaging: Identifies overheating components in electrical panels, motors, or bearings.
- Pressure Monitoring: Checks hydraulic and pneumatic system performance.
- Motor Current Signature Analysis (MCSA): Assesses motor health and efficiency.
- Oil Analysis: Monitors lubricant condition and detects wear particles.
How Real-Time Data Minimizes Downtime:
- Early Anomaly Detection: Sensors flag deviations from normal operating conditions in real-time (e.g., rising temperature, increased vibration), alerting maintenance teams to potential issues before they cause a catastrophic failure.
- Remote Monitoring Capabilities: Dashboards allow maintenance staff and operators to monitor system health remotely, enabling swift responses even outside standard working hours.
- Data Analytics for Prediction: Analyzing historical and real-time sensor data allows maintenance teams to predict when specific components are likely to fail. This enables scheduling maintenance interventions precisely when needed, minimizing unplanned downtime and optimizing maintenance resources.
Predictive maintenance uses data-driven insights to proactively address potential failures, drastically reducing unexpected stops, lowering repair costs, and maximizing equipment uptime and Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE).
4. Implementing Efficient Packing Material Management
Running out of essential consumables is a preventable cause of downtime. A robust material management system ensures a continuous supply of packing materials like strapping, stretch film, corner protectors, and labels.
Best Practices for Material Management:
- Automated Inventory Tracking: Utilize systems (e.g., sensors on material dispensers, integration with ERP/MES) to monitor stock levels in real-time. Set up automatic alerts or reorder triggers when supplies reach predefined minimum levels.
- Supplier Relationship Management: Cultivate strong relationships with reliable suppliers capable of consistent quality and timely deliveries. Consider agreements that guarantee expedited shipping for urgent needs.
- Strategic Buffer Stock: Maintain a calculated buffer stock of critical packing materials onsite to mitigate unexpected supply chain disruptions, shipping delays, or sudden increases in production volume.
- Quality Control: Ensure incoming materials meet quality specifications to avoid jams or equipment malfunctions caused by substandard consumables.
Efficient material flow prevents interruptions caused by stockouts, keeping the packing line productive.
5. Investing in Comprehensive Operator Training and Skill Development
Well-trained operators are crucial for minimizing downtime caused by human error. Insufficient knowledge can lead to incorrect machine operation, improper troubleshooting, safety breaches, and failure to recognize early warning signs of equipment problems.
Key Training Focus Areas:
- Machine Operation & Setup: Ensure operators are proficient in starting, stopping, setting parameters (for different coil sizes, materials, packing specifications), and performing changeovers efficiently and correctly.
- Basic Troubleshooting: Train operators to identify and resolve common minor issues (e.g., clearing jams, resetting faults, adjusting sensors) safely and quickly, reducing reliance on maintenance staff for simple problems.
- Preventive Checks: Empower operators to perform basic daily checks (e.g., visual inspections, listening for unusual noises, checking fluid levels) as part of their routine.
- Safety Procedures: Rigorous training on all safety protocols, including lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures, emergency stops, and safe material handling, is essential to prevent accidents that cause downtime and injury.
- Understanding Automation: Familiarize operators with the control system interface, alarm interpretation, and the overall logic of the automated line.
Investing in ongoing training, perhaps using simulators or hands-on workshops, empowers operators to run the line efficiently, perform minor maintenance, and contribute significantly to uptime.
6. The Role of Automation in Enhancing Uptime
Automation is fundamental to modern packing line efficiency and reliability. By minimizing manual intervention, automation reduces variability and the potential for human error.
How Automation Improves Reliability:
- Consistent Wrapping and Strapping: Automated systems apply wrapping film and straps with consistent tension and placement, improving package integrity and reducing material waste or failures associated with manual application.
- Automated Diagnostics & Fault Recovery: Modern PLCs and control systems often include sophisticated self-diagnostic capabilities. They can pinpoint issues quickly, display clear error messages, and sometimes even initiate automated recovery sequences, reducing troubleshooting time.
- Continuous and Optimized Flow: Automation enables smooth, continuous operation, minimizing unnecessary stops and starts. Robots and automated conveyors handle coils efficiently, optimizing throughput.
- Integration with Monitoring Systems: Automation systems readily integrate with IoT sensors and analytics platforms, providing the data needed for predictive maintenance and performance optimization.
Strategic implementation of automation reduces manual errors, speeds up processes, and provides the foundation for data-driven maintenance strategies, all contributing to reduced downtime.
7. Optimizing System Design for Reliability and Maintainability
The inherent design of the steel coil packing line significantly impacts its susceptibility to downtime. A well-engineered system prioritizes reliability, ease of maintenance, and efficient flow.
Key Design Considerations for Maximum Uptime:
- Modularity: Designing the line with distinct, modular sections allows individual components (e.g., a specific conveyor, the wrapping station) to be isolated for maintenance or repair without necessarily shutting down the entire line. Quick-disconnect features for power and data can further speed up module replacement.
- Redundancy: Where feasible and cost-effective, incorporate redundancy for critical components. Examples include dual power supplies, bypass conveyor routes, or parallel workstations for critical processes. This ensures continued operation even if one component fails.
- Accessibility for Maintenance: Ensure equipment layout provides safe and easy access for routine maintenance tasks (lubrication, inspection, part replacement) and troubleshooting. Avoid cramped spaces or designs that require extensive disassembly for simple tasks.
- Robust Component Selection: Specify high-quality, durable components known for reliability in harsh industrial environments. Consider factors like duty cycle, environmental conditions (dust, temperature), and load requirements.
- Integrated and User-Friendly Controls: Utilize a centralized HMI (Human-Machine Interface) with intuitive controls, clear diagnostics, and comprehensive status information. This simplifies operation and speeds up troubleshooting.
- Buffer Zones: Incorporate buffer zones or accumulation conveyors between key processes to decouple operations slightly. This prevents a minor slowdown or stoppage at one station from immediately halting the entire line.
An optimized system design inherently reduces failure points and simplifies maintenance, leading to fewer interruptions and shorter recovery times.
8. Partnering with Reliable Equipment Manufacturers and Service Providers
The quality of the packing line equipment and the support provided by the manufacturer are critical factors in long-term uptime.
Choosing the Right Partners:
- Proven Industry Experience: Select manufacturers with a strong track record and demonstrated expertise in designing and building robust packing lines specifically for the steel industry. Review case studies and seek references.
- Quality and Durability: Prioritize equipment built with high-quality materials and components designed for longevity and reliable performance under demanding conditions.
- Responsive After-Sales Support: Ensure the manufacturer offers comprehensive support, including:
- Prompt Technical Assistance: Access to knowledgeable technicians for troubleshooting (remote and onsite).
- Readily Available Spare Parts: A reliable supply chain for critical spare parts to minimize repair delays.
- Maintenance Services & Training: Availability of manufacturer-provided maintenance services and operator/maintenance training programs.
- Customization Capabilities: Choose a partner who can tailor the equipment design to your specific operational needs, coil types, space constraints, and integration requirements for optimal performance.
Strong partnerships with reputable suppliers provide access to reliable equipment, essential expertise, and timely support, forming a crucial foundation for minimizing downtime.
9. Driving Continuous Improvement with Data and Feedback
Minimizing downtime is an ongoing process, not a one-time fix. Utilizing operational data is key to identifying opportunities for continuous improvement.
Leveraging Data for Optimization:

- Track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Monitor metrics such as Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), Mean Time To Repair (MTTR), cycle times, and material waste. Analyze trends to pinpoint recurring problems or areas needing optimization.
- Establish Feedback Loops: Create processes where data insights directly inform operational and maintenance strategies. For example, if data shows frequent jams at a specific transfer point, investigate and implement design or process modifications. Use sensor data to refine PM schedules.
- Conduct Thorough Root Cause Analysis (RCA): When downtime incidents occur, don't just fix the immediate problem. Use structured RCA methodologies (like the 5 Whys or Fishbone diagrams) combined with operational data to identify the fundamental underlying cause(s) and implement corrective actions to prevent recurrence.
- Operator Feedback: Regularly solicit feedback from operators and maintenance staff, as they often have valuable firsthand insights into daily operational challenges and potential improvements.
A culture of data-driven continuous improvement ensures the packing line becomes progressively more reliable and efficient over time.
10. Conducting Regular System Audits and Reviews
Periodic, systematic audits of the packing line provide a holistic assessment of its health and identify potential risks before they lead to significant downtime.
Key Audit Areas:
- Equipment Condition Assessment: Go beyond routine PM checks. Conduct in-depth inspections of major systems and components to assess wear, potential obsolescence, and overall condition relative to performance expectations.
- Process Efficiency Review: Analyze the entire packing workflow, looking for bottlenecks, inefficiencies, unnecessary manual handling, or opportunities for automation upgrades. Compare current performance against benchmarks or original design specifications.
- Maintenance Program Effectiveness: Review PM records, PdM data, spare parts inventory, and maintenance procedures. Is the current strategy effective? Are tasks being completed on time? Are the right metrics being tracked?
- Safety and Compliance Check: Ensure the line adheres to all current safety regulations (machine guarding, LOTO, emergency systems) and industry standards. Non-compliance can lead to forced shutdowns, fines, and safety incidents.
- Technology Review: Assess if current automation, sensors, or control systems are still optimal or if newer technologies could offer significant improvements in reliability or efficiency.
Regular audits provide a structured way to proactively identify weaknesses and opportunities, ensuring the long-term health and uptime of the steel coil packing line.
Conclusion
Minimizing downtime in a steel coil packing line is achievable through a multifaceted approach encompassing proactive maintenance, advanced monitoring, smart automation, efficient resource management, skilled personnel, and optimized system design. Implementing robust preventive and predictive maintenance strategies, leveraging real-time data from sensors and IoT devices, ensuring continuous material supply, investing in operator training, optimizing the physical layout and control systems, and fostering strong supplier partnerships are all crucial elements.
Furthermore, embracing a culture of continuous improvement fueled by data analysis and regular system audits ensures that the packing line adapts and evolves to maintain peak performance. By diligently applying these best practices, steel manufacturers can significantly reduce costly unplanned interruptions, enhance operational efficiency, lower maintenance expenditures, and ultimately improve their bottom line. The result is a reliable, highly productive steel coil packing system that consistently meets production demands with minimal downtime.