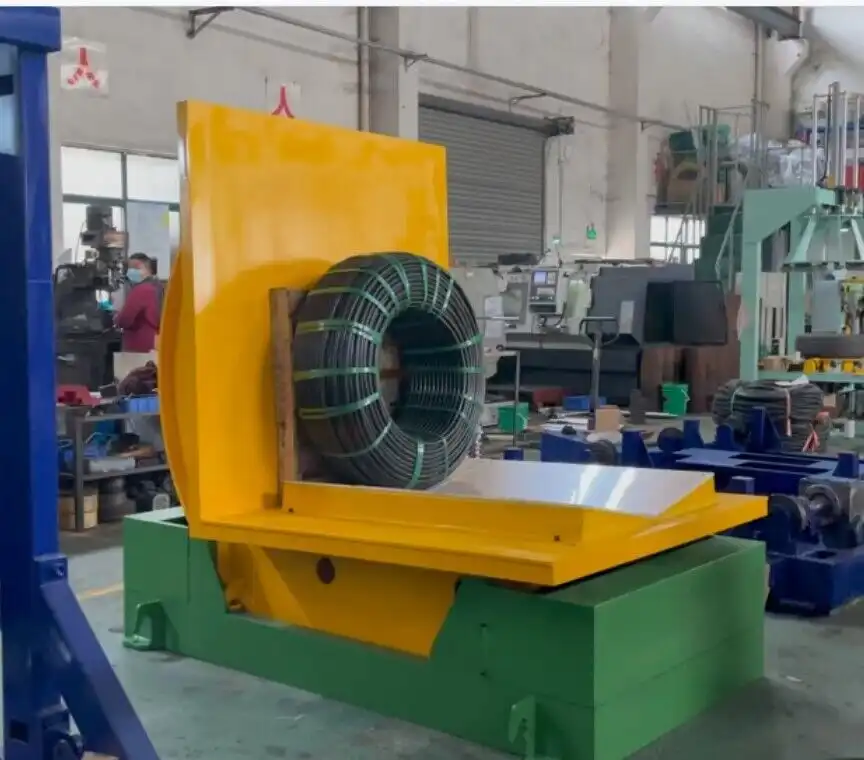
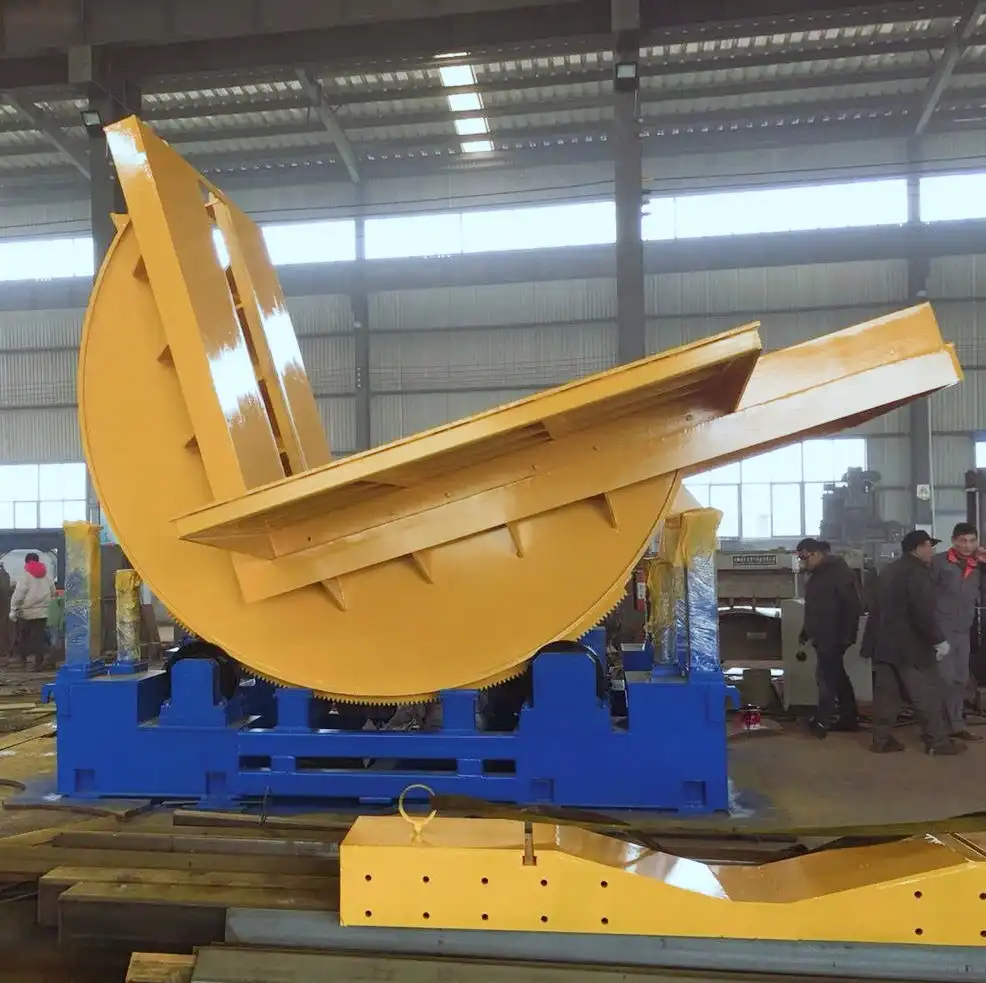
Industrial operations involving heavy materials often require specialized equipment for safe and efficient handling. While hydraulic upenders and mold upenders both lift and rotate substantial loads, they are designed with distinct purposes and advantages. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right machine for your specific needs. Hydraulic upenders offer notable versatility for various load types, whereas mold upenders provide specialized precision primarily for handling molds. This guide compares these two essential pieces of industrial equipment to help you determine the best fit for your operational requirements.
Choosing between a hydraulic upender and a mold upender involves considering factors like load type, required precision, safety protocols, and overall workflow efficiency. Although they share a core function—tilting heavy objects—their design nuances cater to different industrial applications. A hydraulic upender is often the go-to for general manufacturing and logistics due to its adaptability, while a mold upender is indispensable in industries like injection molding or casting, where careful handling of valuable molds is paramount.
For professionals in manufacturing, metalworking, or molding industries, grasping the functional distinctions between these upenders is essential for optimizing operations and ensuring workplace safety. Let's delve into a detailed comparison.
Hydraulic Upender vs. Mold Upender: Key Differences
| Feature | Hydraulic Upender | Mold Upender |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Versatile tilting for various heavy loads (coils, dies, pallets) | Specialized tilting for safe and precise mold handling |
| Common Industries | Manufacturing, Logistics, Automotive, Metalworking, Paper | Injection Molding, Die Casting, Plastic Molding, Tool & Die Shops |
| Load Capacity Range | High, adaptable to diverse shapes and substantial weights | Moderate to High, tailored specifically to common mold sizes and weights |
| Key Safety Features | General safety mechanisms (e.g., pressure sensors, emergency stops, overload protection) | Mold-specific safety (e.g., anti-slip platforms, secure locking systems, controlled rotation speed) |
| Operational Efficiency | High efficiency for flexible workflows involving varied items | Optimized efficiency for repetitive, secure mold rotations |
| Versatility | Highly adaptable to different load types and sizes | Primarily focused on mold handling; limited versatility for other load types |
| Design Focus | Robust construction for general heavy lifting and rotating tasks | Precision engineering for mold protection and stability during rotation |
| Ideal Choice For | Operations requiring flexibility to handle varied heavy loads | Operations centered around frequent and precise mold handling |
1. Core Functions and Industrial Applications
1.1. Defining How Each Upender Handles Tasks
Hydraulic upenders are the workhorses of many industrial settings, designed for broad applicability. Their powerful hydraulic systems enable the smooth movement and rotation of diverse items, including steel coils, paper rolls, dies, engines, and large assemblies. This makes them exceptionally valuable in manufacturing facilities, warehouses, and logistics hubs where handling a variety of load shapes and sizes is routine.
Mold upenders, conversely, are purpose-built for the specific task of handling molds. They incorporate features that ensure stability, security, and precise control during the rotation process. This focus is critical in high-precision environments like plastic injection molding, die casting, and tool and die shops, where protecting expensive and delicate molds from damage is a top priority.
1.2. Tailored Uses Across Different Industries
The versatility of hydraulic upenders makes them suitable for a wide range of industries. Manufacturers dealing with raw materials (like metal coils or paper rolls), automotive assembly lines handling engine blocks, or logistics centers repositioning heavy pallets benefit significantly from their adaptability. They function as a multi-purpose tool capable of integrating into various production or handling workflows.
Mold upenders serve a more specialized niche. Their design is optimized for industries where molds are frequently moved, inspected, cleaned, or prepared for production. The ability to rotate heavy molds safely and accurately prevents damage, reduces setup times, and enhances worker safety, making them indispensable in molding and casting operations.
1.3. Selecting the Right Upender Based on Primary Function
The decision between a hydraulic and a mold upender ultimately comes down to the primary function required in your daily operations. If your core task involves handling molds—especially valuable or complex ones used in injection molding, die casting, or similar processes—the mold upender's specialized design offers significant advantages. Its focus on stability, secure locking, and controlled rotation minimizes the risk of mold damage and ensures precise positioning, which is crucial for maintaining production quality and safety.
Conversely, if your facility handles a wide variety of heavy items beyond molds, the hydraulic upender's versatility is likely the better choice. Its ability to adapt to different load shapes, sizes, and weights makes it suitable for dynamic environments in general manufacturing, warehousing, or metal processing. This adaptability enhances operational flexibility and efficiency, allowing a single machine to perform multiple tilting tasks, thereby potentially reducing equipment costs and floor space usage.
2. Comparing Load Capacity and Handling Capabilities
2.1. Understanding Load Strengths and Limitations
Hydraulic upenders are typically engineered for high load capacities, capable of handling exceptionally heavy and often irregularly shaped objects. Their robust hydraulic systems provide significant lifting power, making them suitable for demanding industrial applications involving loads weighing many tons. The capacity range can often be customized to meet specific operational needs.
Mold upenders, while also built for heavy loads, have capacities generally tailored to the typical weight range of molds used in industries like plastics and die casting. While some can handle very large molds, their design often prioritizes controlled movement and stability within a specific weight range over sheer maximum lifting power.
2.2. Mold-Specific Capacity Considerations and Stability
The load capacity of a mold upender is intrinsically linked to stability. These machines are designed not just to lift the mold's weight but to do so without abrupt movements or vibrations that could misalign mold components or cause damage. Features like wide bases, secure clamping or platform surfaces, and precisely controlled rotation speeds contribute to this stability, ensuring the integrity of the mold throughout the handling process.
2.3. Prioritizing Load Requirements Based on Application
When selecting an upender, carefully assess the maximum weight, dimensions, and shape of the loads you handle regularly. If your operations involve extremely heavy items or a wide variety of load types (coils, plates, machinery), a hydraulic upender with a high, adaptable load capacity is likely necessary. Its strength and flexibility provide a reliable solution for diverse heavy lifting requirements.
However, if your primary focus is handling molds within a known weight range, prioritize a mold upender whose capacity matches your needs while offering enhanced stability and mold-specific safety features. Over-specifying capacity might not be cost-effective if the additional strength isn't needed, whereas under-specifying poses significant safety risks. The key is aligning the machine’s capability with the specific demands of your mold handling tasks.
3. Evaluating Key Safety Features
3.1. Standard vs. Specialized Safety Mechanisms
Both types of upenders incorporate essential safety features, but their focus differs. Hydraulic upenders typically include general safety measures applicable to heavy machinery: • Emergency stop buttons • Hydraulic pressure relief valves to prevent overloading • Secure clamping systems (depending on model) • Audible or visual warning signals during operation
Mold upenders often add features specifically designed to protect molds and operators during the tilting process: • Anti-slip surfaces on loading platforms • Automated locking mechanisms or clamps tailored to secure molds firmly • Controlled, often variable, rotation speed to prevent sudden shifts • Interlocks that prevent operation if the mold is not secured correctly
3.2. Enhanced Safety for Precision Mold Handling
The safety features on a mold upender are paramount due to the high value and sensitivity of molds. Mishandling can lead to costly repairs, production downtime, and potential injuries. The specialized locking systems ensure the mold remains rigidly in place during the entire 90 or 180-degree rotation. Controlled speed minimizes inertial forces, crucial for large or complex molds with delicate components. These features collectively reduce the risk associated with mold handling significantly.

3.3. Choosing the Safest Upender Option for Your Workflow
The safest upender for your operation depends directly on the materials being handled. For diverse, heavy loads where the primary risk is dropping or instability due to varied shapes, a hydraulic upender with robust general safety features (overload protection, secure clamping appropriate for the load type) is essential. Ensure the model chosen has safety mechanisms suited to the range of items you handle.
If your workflow revolves around molds, the specialized safety features of a mold upender provide superior protection against the unique risks of mold handling. The investment in features like anti-slip platforms and precise locking systems directly translates to reduced risk of damage to expensive tooling and enhanced operator safety. Prioritize models with safety certifications relevant to your industry and region (e.g., CE marking).
4. Assessing Operational Efficiency and Workflow Impact
4.1. Impact of Speed and Adaptability on Workflows
Hydraulic upenders contribute to operational efficiency through their adaptability. They can often be quickly configured to handle different types of loads, minimizing downtime between tasks in environments with varied handling needs. Their relatively fast cycle times for standard rotations can speed up overall processes in manufacturing or logistics sequences.
Mold upenders enhance efficiency within their specialized domain. While their rotation speed might be deliberately controlled for safety, the setup and securing process is often streamlined for standard mold types. This predictability and security reduce handling time per mold, minimize errors, and allow for smoother integration into mold maintenance or production setup workflows.
4.2. Specialized Efficiency Gains in Mold-Handling Operations
In industries where molds are handled frequently (e.g., daily or multiple times per shift), the specialized efficiency of a mold upender yields significant benefits. Quick, secure loading and rotation cycles, reduced risk of damage (avoiding costly downtime for repairs), and ease of use for operators trained on a specific procedure all contribute to higher overall productivity compared to using a less specialized machine for the same task.
4.3. Balancing Versatility and Precision for Maximum Throughput
Choosing the most efficient upender involves balancing the need for versatility against the requirement for precision. If your operation demands flexibility to handle unpredictable or varied heavy loads, the hydraulic upender's adaptability offers greater overall efficiency by reducing the need for multiple specialized machines or complex manual handling procedures. Its power and broad capability streamline workflows involving diverse materials.
Conversely, if your workflow is centered predominantly around molds, the mold upender's precision and specialized features deliver targeted efficiency. By optimizing the specific task of mold rotation, it enhances throughput, minimizes risk, and ensures consistent handling quality. The efficiency gain comes from doing one task exceptionally well, which is often crucial in high-volume or high-precision molding environments.
Evaluate your workflow bottlenecks: Is the challenge handling diverse items quickly, or handling specific items (molds) safely and repetitively? The answer will guide you toward the upender type that offers the best efficiency boost for your unique operational context.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Ultimately, the selection between a hydraulic upender and a mold upender depends on a clear understanding of your operational priorities. Hydraulic upenders provide unmatched versatility and high load capacity, making them ideal for dynamic environments handling diverse heavy items in manufacturing, logistics, and metal processing.
Mold upenders excel in specialized applications, offering precision, stability, and enhanced safety features specifically designed for handling valuable molds in industries like injection molding and die casting. Their focused design optimizes workflows where mold rotation is a frequent and critical task.
By carefully evaluating your primary load types, required handling precision, safety imperatives, and workflow efficiency goals using the comparisons outlined above, you can confidently choose the upender machine that will best enhance productivity and safety within your specific industrial setting. Selecting the appropriate equipment is a key investment in operational excellence.

