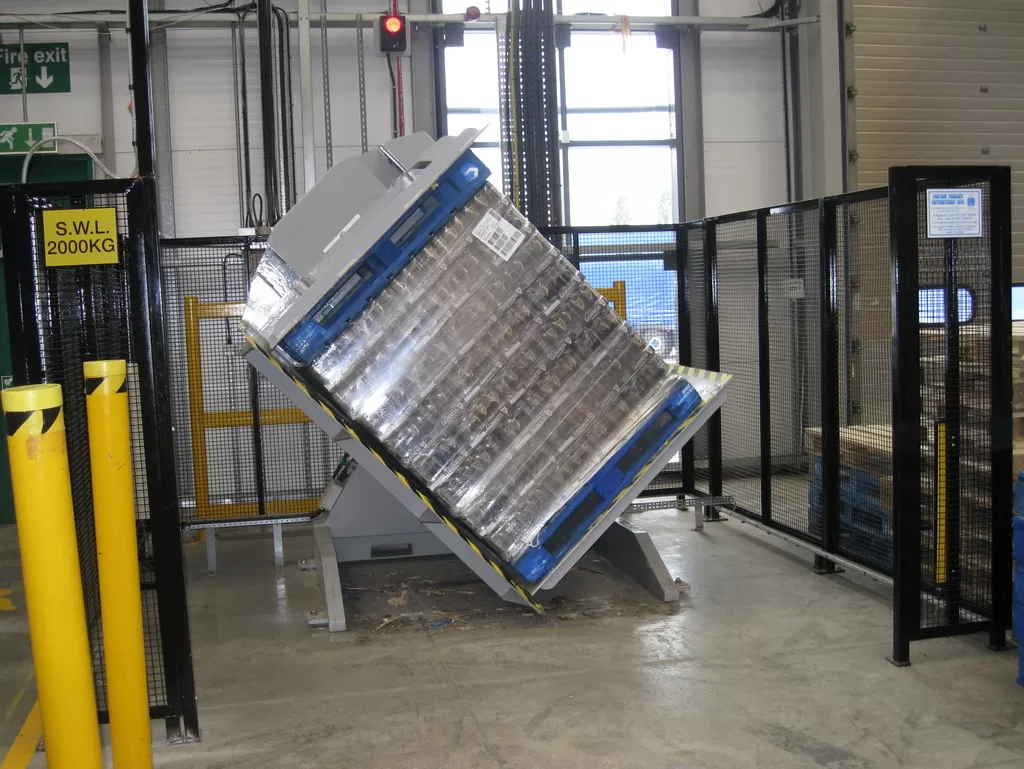
What Are the Safety Guidelines for Operating Mold Upenders?
Operating mold upenders safely is paramount in industrial environments to prevent accidents and ensure efficiency. These powerful machines, while incredibly useful, require strict adherence to safety protocols to protect personnel and materials. Understanding and implementing these guidelines is crucial for a safe and productive workplace.
Safety guidelines for operating mold upenders include pre-operation checks, proper loading and securing of molds, maintaining a safe clearance zone, and adherence to lockout/tagout procedures during maintenance. Operators must be trained and authorized, and machines should be regularly inspected and maintained to ensure safe and efficient operation.
Mold upenders are indispensable tools in manufacturing, but their safe operation hinges on a comprehensive understanding and strict application of safety guidelines. Let’s delve into the essential safety measures that every operator and facility manager should know to ensure a secure and productive working environment.
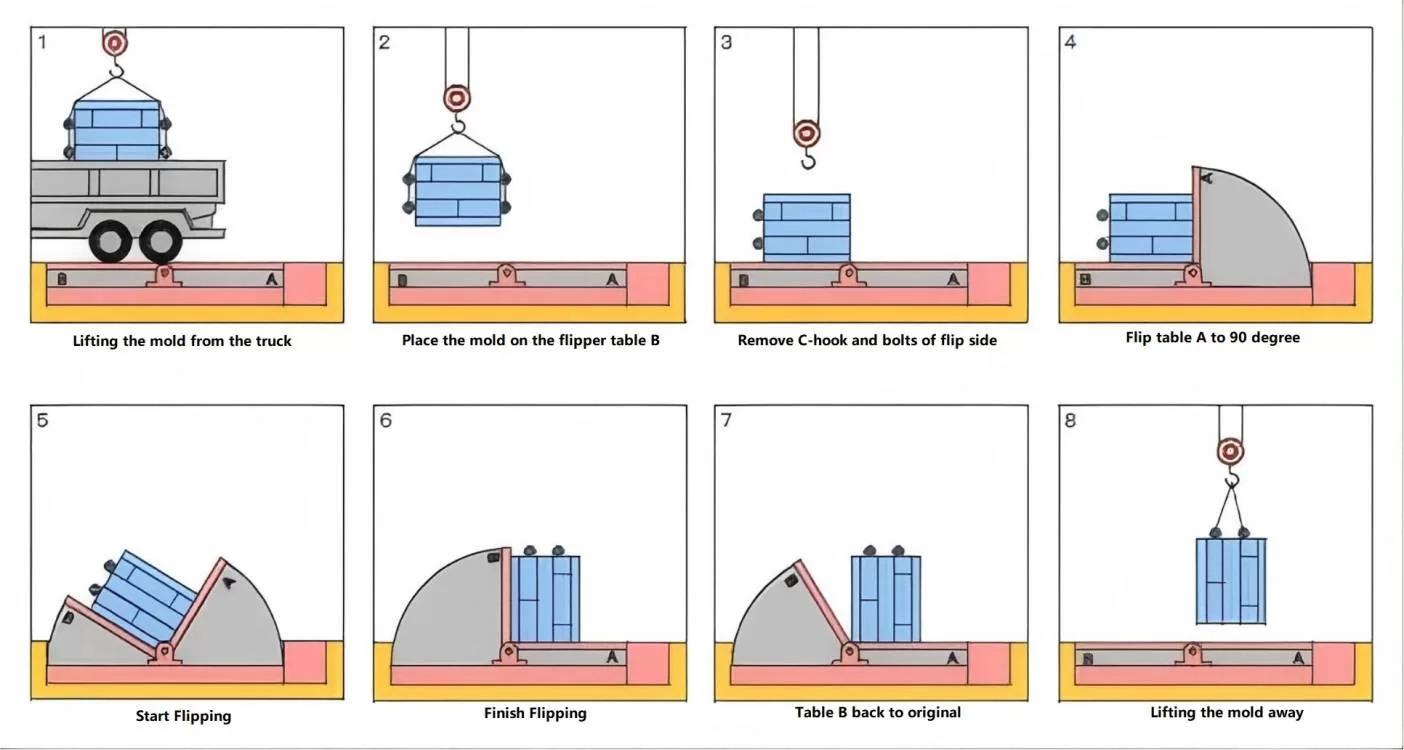
1. Core Safety Principles for Mold Upender Operation
Operating a mold upender involves inherent risks due to the heavy loads and mechanical movements. Adhering to core safety principles is not just about compliance; it’s about fostering a safety-first culture that protects every individual involved. These principles form the bedrock of safe operation and must be meticulously followed.
The core safety principles for operating mold upenders are centered around comprehensive training, regular equipment inspections, strict adherence to load limits, and maintaining a safe operational area. Prioritizing personnel safety through clear procedures and consistent enforcement of these principles is crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring efficient operations.
To ensure the highest standards of safety, several fundamental aspects need to be rigorously addressed. These can be categorized into operator qualifications, equipment readiness, load management, and environmental safety protocols.
Operator Qualification and Training
Only trained and authorized personnel should operate mold upenders. Comprehensive training programs should cover:
- Operational Procedures: Step-by-step instructions on how to correctly operate the specific model of mold upender.
- Safety Protocols: Detailed training on all safety guidelines, emergency stop procedures, and risk identification.
- Equipment Familiarization: Understanding the machine’s components, controls, and safety features.
- Load Handling: Proper techniques for loading, securing, and unloading molds of various sizes and weights.
- Emergency Procedures: Training on how to respond to malfunctions, power outages, or accidents.
Pre-Operation Inspection Checklist
Before each operation, a thorough inspection must be conducted to ensure the upender is in safe working condition. This checklist should include:
- Visual Inspection: Check for any visible damage, loose parts, leaks (hydraulic), or wear and tear.
- Safety Device Check: Verify that all safety guards, limit switches, and emergency stops are in place and functioning correctly.
- Control Function Test: Test all controls (up, down, stop) to ensure they respond smoothly and accurately.
- Hydraulic System Check (if applicable): Inspect hydraulic hoses, fittings, and fluid levels for leaks or damage.
- Area Clearance: Ensure the area around the upender is clear of obstructions and personnel.
Load Capacity and Stability
Exceeding the load capacity or improperly loading the mold can lead to catastrophic failures. Strict adherence to these guidelines is crucial:
- Rated Load Capacity: Never exceed the upender’s rated load capacity, which is clearly stated on the machine’s nameplate.
- Load Centering: Always center loads on the platform to maintain balance and prevent tipping.
- Securing the Load: Ensure the mold is securely fastened to the platform using appropriate clamps, straps, or fixtures before initiating rotation.
- Load Dimensions: Verify that the mold dimensions are within the upender’s specifications and do not overhang the platform.
Maintaining a Safe Operational Environment
The environment around the mold upender must be controlled to minimize risks:
- Clearance Zone: Establish and maintain a safe clearance zone around the upender, ensuring no personnel enter this area during operation.
- Warning Systems: Utilize warning lights, alarms, or signage to indicate when the upender is in operation.
- Floor Condition: Ensure the floor around the upender is level, stable, and free from debris or slip hazards.
- Lighting: Adequate lighting is essential for clear visibility during loading, operation, and unloading.
By diligently applying these core safety principles, facilities can significantly mitigate the risks associated with mold upender operation, creating a safer and more efficient workplace. Prioritizing these fundamentals protects personnel, prolongs equipment life, and ensures operational continuity.

To further elaborate on ensuring operational safety, consider the following table which outlines critical safety checks and their frequency:
| Safety Check | Frequency | Procedure | Responsible Personnel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Before Each Use | Check for damage, loose parts, leaks | Operator |
| Safety Device Functionality | Before Each Use | Test emergency stops, limit switches, safety guards | Operator |
| Control System Test | Before Each Use | Verify responsiveness and accuracy of all controls | Operator |
| Hydraulic/Pneumatic System Check | Daily/Weekly | Inspect hoses, fittings, fluid/air levels, pressure | Maintenance |
| Load Capacity Verification | Monthly | Recalibrate load sensors, review load history | Maintenance/Supervisor |
| Comprehensive Maintenance | Quarterly/Annually | Detailed inspection, lubrication, parts replacement as per manufacturer guidelines, operation check. | Maintenance |
This structured approach to safety checks ensures that all critical aspects of mold upender operation are regularly monitored and maintained, significantly reducing the likelihood of accidents and equipment failures.
2. Step-by-Step Safe Operating Procedures
Safe operation of a mold upender is not just about understanding safety principles; it’s about consistently following a detailed procedure every time the machine is used. A step-by-step approach ensures that no critical safety measure is overlooked, minimizing risks and maximizing efficiency.
The step-by-step safe operating procedure for mold upenders begins with pre-operation checks, followed by careful mold loading and securing. Initiate rotation only after confirming safety clearances and monitoring the process until completion. Finally, ensure safe unloading and post-operation shutdown to complete the cycle safely.
A well-defined operating procedure should cover every phase of mold upender use, from initial setup to post-operation shutdown. This structured approach ensures consistency and reduces the chance of human error.
Pre-Operational Setup
Before starting any mold upending operation, several crucial steps must be completed:
- Area Inspection: Ensure the area around the mold upender is clear of obstructions, tools, and personnel. Establish a clearly marked safety zone around the machine.
- Equipment Check: Perform the pre-operation inspection checklist as detailed in Section 1, verifying all safety devices and controls are functioning correctly.
- Load Assessment: Verify the weight and dimensions of the mold to be upended, ensuring they are within the upender’s rated capacity and suitable for the machine.
- Securing Devices Ready: Ensure that all necessary securing devices (clamps, straps, V-saddles) are readily available and in good working condition.
Mold Loading and Securing
Proper loading and securing of the mold are critical to prevent accidents during rotation:
- Positioning the Mold: Use appropriate lifting equipment (overhead crane, forklift) to carefully position the mold near the upender platform.
- Gentle Placement: Slowly and gently lower the mold onto the upender platform, ensuring it is centered and stable.
- Engage Securing Mechanisms: Securely fasten the mold to the platform using clamps, straps, or V-saddles. Double-check that all securing devices are properly tightened and engaged.
- Final Stability Check: Manually check the mold’s stability on the platform before proceeding. Ensure there is no wobble or shifting.
Initiating and Monitoring Rotation
Rotation must be controlled and monitored closely to ensure safety:
- Clearance Confirmation: Re-verify that the area around the upender is clear and all personnel are outside the safety zone.
- Control Activation: Activate the upender controls (typically a push-button pendant) to initiate rotation. Use smooth, controlled movements.
- Continuous Monitoring: Continuously monitor the rotation process, watching for any unusual noises, vibrations, or jerky movements. Be ready to use the emergency stop if necessary.
- Controlled Stop: Release the control button to stop rotation at the desired orientation (usually 90 degrees). Allow the machine to come to a complete stop before proceeding.
Unloading and Post-Operation
Safe unloading and proper shutdown procedures are the final steps in a safe operation:
- Stability Check Post-Rotation: Before unloading, ensure the mold is stable in its new orientation.
- Disengage Securing Mechanisms: Carefully release the clamps, straps, or securing devices.
- Safe Unloading: Use appropriate lifting equipment to carefully lift and remove the mold from the upender platform.
- Return to Starting Position: Return the upender platform to its initial horizontal or vertical position, ready for the next operation.
- Power Down and Secure: Turn off the main power supply to the upender and engage any maintenance locking devices to secure the machine when not in use.
By consistently following these step-by-step procedures, operators can significantly reduce the risks associated with mold upender operation. This structured approach ensures that safety is integrated into every aspect of the process, from start to finish.
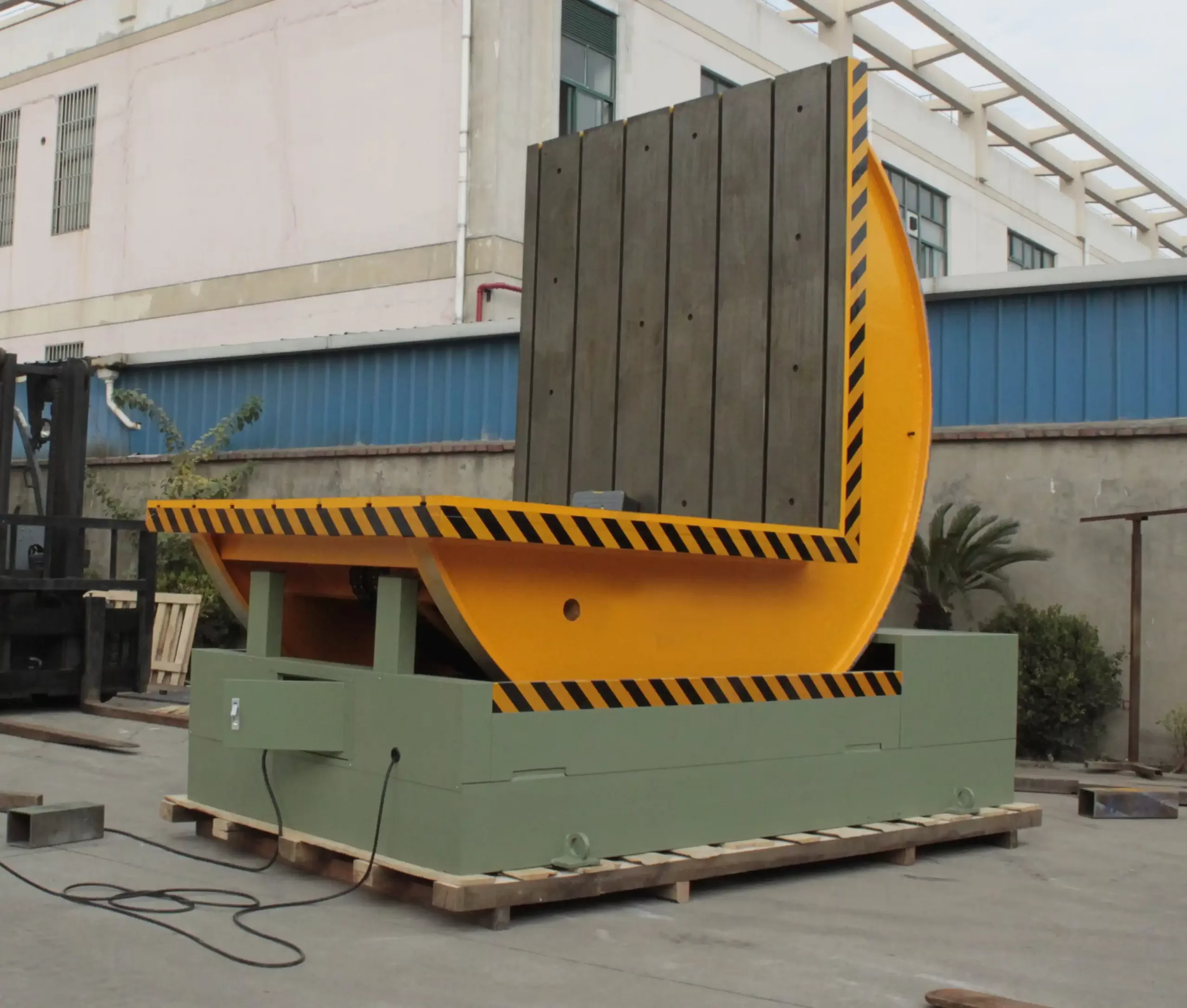

To illustrate the importance of each step in the operating procedure, consider the potential hazards and mitigation strategies associated with each phase:
| Operational Phase | Step | Potential Hazard | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Operational Setup | Area Inspection | Personnel in danger zone, obstructions | Clear area, establish safety zone, warning systems |
| Equipment Check | Malfunctioning safety devices, equipment failure | Pre-operation checklist, thorough inspection | |
| Load Assessment | Overloading, incompatible mold | Verify load weight and dimensions, check rated capacity | |
| Securing Devices Ready | Inadequate securing, device failure | Inspect devices, ensure correct type and condition | |
| Mold Loading & Securing | Positioning Mold | Dropping mold, instability | Use proper lifting equipment, controlled movements |
| Gentle Placement | Impact damage to upender or mold | Slow, controlled lowering, ensure centered placement | |
| Engage Securing Mechanisms | Mold shifting during rotation | Double-check securing devices, ensure tight and secure | |
| Final Stability Check | Unstable load, potential tipping | Manual stability check, correct any imbalances before operation | |
| Initiating & Monitoring | Clearance Confirmation | Personnel in danger zone, obstructions | Final area check, ensure safety zone is clear |
| Control Activation | Uncontrolled movement, jerky motion | Smooth, controlled activation, trained operator | |
| Continuous Monitoring | Unforeseen malfunctions, equipment failure | Observe operation closely, be ready for emergency stop | |
| Controlled Stop | Abrupt stop, load shifting | Smooth deceleration, allow machine to come to complete stop | |
| Unloading & Post-Operation | Stability Check Post-Rotation | Mold tipping after rotation | Verify stability before releasing securing devices |
| Disengage Securing Mechanisms | Sudden release, mold shifting | Gradual release, controlled movements | |
| Safe Unloading | Dropping mold, personnel injury | Proper lifting equipment, controlled lifting and removal | |
| Return to Starting Position | Machine left in unsafe state | Reset platform, prepare for next operation | |
| Power Down & Secure | Unauthorized use, accidental activation | Turn off power, engage locking devices |
This detailed hazard analysis and mitigation table underscores the critical safety considerations at each step of the mold upender operating procedure. Adherence to these guidelines is essential for preventing accidents and ensuring a safe working environment.
3. Regular Maintenance and Inspection Schedules
Consistent maintenance and inspection are vital for ensuring the long-term safe and efficient operation of mold upenders. Neglecting maintenance can lead to equipment malfunctions, increased safety risks, and costly downtime. Establishing and adhering to a regular maintenance schedule is a proactive approach to safety and operational reliability.
Regular maintenance and inspection schedules for mold upenders are essential to preemptively identify and address potential issues. Daily checks by operators, weekly to monthly maintenance tasks by trained personnel, and annual comprehensive inspections ensure continuous safe and efficient operation, minimizing downtime and enhancing safety.
A comprehensive maintenance schedule should include daily, weekly/monthly, and annual tasks, each focusing on different aspects of the machine’s condition and performance.
Daily Maintenance Tasks (Operator Checks)
These are quick checks performed by the operator before each shift or operation:
- Visual Inspection: Check for any new damage, leaks, or loose parts since the last use.
- Safety Guard Check: Ensure all safety guards and covers are in place and secure.
- Control Function Test: Briefly test the up, down, and stop controls to ensure they are responsive.
- Emergency Stop Test: Verify the emergency stop button immediately halts machine operation.
- Unusual Noise or Vibration Check: Listen for any unusual noises or vibrations during a dry run (without load).
Weekly/Monthly Maintenance Tasks (Trained Personnel)
These tasks should be performed by trained maintenance personnel on a regular schedule:
- Lubrication: Lubricate all moving parts as per the manufacturer’s recommendations, including bearings, pivot points, and chains (if applicable).
- Hydraulic System Inspection (if applicable): Check hydraulic fluid levels, inspect hoses and fittings for leaks, and examine pump and valve functionality.
- Electrical System Check: Inspect wiring, connections, and control panels for damage or loose connections.
- Chain/Drive System Inspection (if applicable): Check chain tension, sprocket wear, and overall condition of the drive system.
- Limit Switch Adjustment: Verify the proper functioning and adjustment of limit switches to prevent over-travel.
- Bolt and Fastener Tightening: Check and tighten all bolts, nuts, and fasteners to ensure structural integrity.
Annual Comprehensive Inspection (Qualified Technicians)
A detailed annual inspection should be conducted by qualified technicians or service professionals:
- Structural Integrity Assessment: Thoroughly inspect the frame, platform, and welds for cracks, deformations, or fatigue.
- Hydraulic/Pneumatic System Overhaul: Conduct a detailed inspection and testing of the entire hydraulic or pneumatic system, including cylinders, pumps, valves, and lines. Replace filters and fluids as needed.
- Electrical System Overhaul: Detailed inspection of all electrical components, wiring, controls, and safety circuits. Test and calibrate sensors and limit switches.
- Drive System Overhaul: Inspect and replace worn chains, sprockets, gears, or belts. Check motor and gearbox condition.
- Load Testing: Perform load tests to verify the upender’s capacity and safety under maximum load conditions.
- Safety System Certification: Recertify all safety systems, including emergency stops, guards, and warning devices, to meet regulatory standards.

To further illustrate the maintenance schedule, consider the following table outlining tasks and their frequencies:
| Maintenance Task | Daily (Operator) | Weekly/Monthly (Maintenance) | Annual (Technician) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Safety Guard Check | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Control Function Test | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Emergency Stop Test | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Unusual Noise/Vibration Check | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Lubrication | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Hydraulic System Inspection | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Electrical System Check | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Chain/Drive System Inspection | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Limit Switch Adjustment | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Bolt/Fastener Tightening | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Structural Integrity Assessment | ✓ | ||
| Hydraulic/Pneumatic System Overhaul | ✓ | ||
| Electrical System Overhaul | ✓ | ||
| Drive System Overhaul | ✓ | ||
| Load Testing | ✓ | ||
| Safety System Certification | ✓ |
Adhering to this structured maintenance schedule ensures that mold upenders remain safe, reliable, and efficient over their operational lifespan. Regular maintenance not only prevents accidents but also reduces downtime and extends the equipment’s service life, providing long-term cost savings and enhanced productivity.
4. OSHA and Regulatory Compliance
Operating mold upenders safely also involves strict adherence to regulatory standards, particularly those set by OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) in the United States. Compliance is not just a legal requirement; it is a fundamental aspect of ensuring worker safety and avoiding penalties. Understanding and implementing OSHA guidelines is crucial for any facility operating mold upenders.

OSHA compliance for mold upenders is primarily addressed through the General Duty Clause, requiring employers to provide a safe workplace free from recognized hazards. While no specific OSHA standards for mold upenders exist, adherence to general safety standards, proper training, regular inspections, and documented safety procedures are essential for meeting OSHA requirements and ensuring workplace safety.
Meeting OSHA requirements involves several key areas:
- General Duty Clause: Comply with OSHA’s General Duty Clause, which mandates employers to provide a workplace free from recognized hazards that could cause serious harm or death. This includes hazards associated with mold upender operation.
- Training and Authorization: Ensure all operators are properly trained and authorized to operate mold upenders. Training must cover safe operating procedures, hazard identification, and emergency response. Document all training activities.
- Regular Inspections and Maintenance: Implement a regular inspection and maintenance program as detailed in Section 3. Keep records of all inspections, maintenance, and repairs to demonstrate due diligence.
- Lockout/Tagout Procedures: Establish and enforce strict lockout/tagout procedures for all maintenance and repair work on mold upenders to prevent accidental startup during servicing.
- Hazard Communication: Comply with OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard, ensuring that employees are informed about potential hazards associated with mold upender operation, including mechanical and hydraulic risks. Provide clear safety signage and warnings.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Provide and require the use of appropriate PPE, such as safety shoes, gloves, and eye protection, for operators and maintenance personnel.
- Emergency Preparedness: Develop and communicate emergency action plans, including procedures for power outages, equipment malfunctions, and accidents. Ensure emergency stop buttons are easily accessible and functional.
- Record Keeping: Maintain accurate records of all safety-related activities, including training, inspections, maintenance, incident reports, and corrective actions. This documentation is essential for demonstrating OSHA compliance during inspections.
By proactively addressing these OSHA compliance areas, facilities can create a safer working environment, reduce the risk of accidents and OSHA violations, and demonstrate a commitment to worker safety and regulatory adherence. Compliance is not just about avoiding fines; it is about fostering a culture of safety and responsibility within the organization.
Conclusion
Operating mold upenders safely demands a holistic approach encompassing core safety principles, step-by-step procedures, regular maintenance, and regulatory compliance. By prioritizing comprehensive training, rigorous inspections, and strict adherence to guidelines, facilities can significantly mitigate the risks associated with these powerful machines. A commitment to safety not only protects personnel but also enhances operational efficiency and ensures long-term productivity in mold handling processes. Embracing these safety guidelines is an investment in a healthier, safer, and more successful industrial environment.










