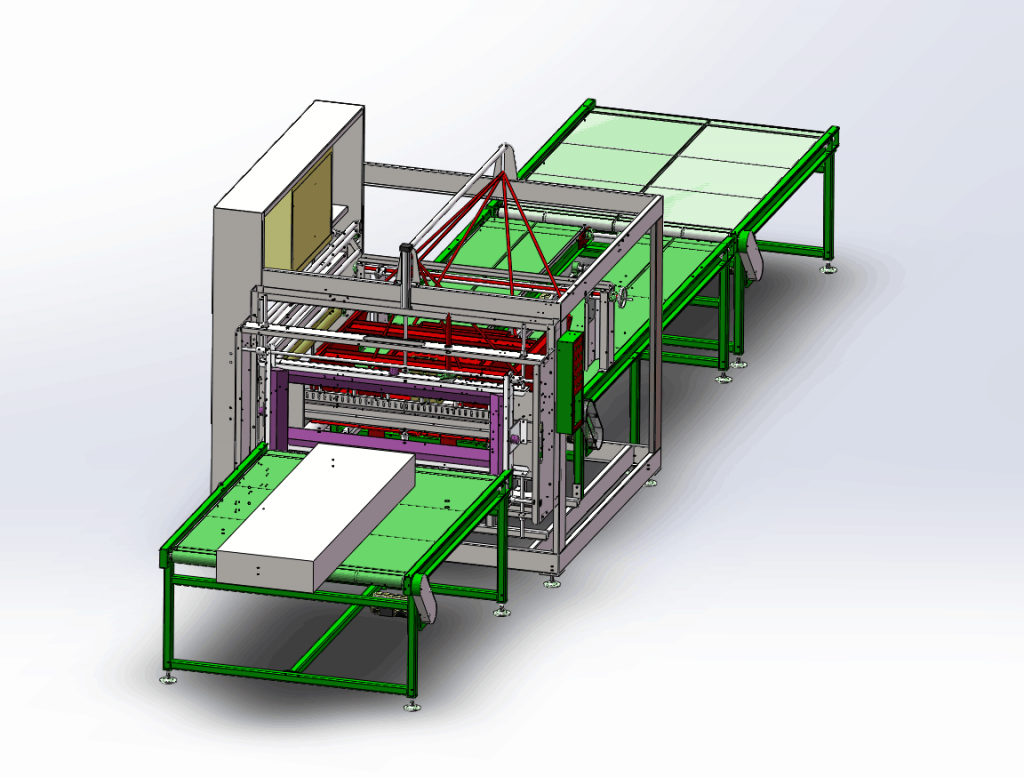
Optimizing Large Flat Product Packaging: An In-Depth Look at Automated Panel Bag Packing Machines
In industries ranging from furniture manufacturing and construction materials to automotive components and electronics, the efficient and secure packaging of large, flat, or panel-shaped products presents a significant logistical challenge. Manual or semi-automated processes can be labor-intensive, inconsistent, and prone to damaging products during handling and transit. Addressing these issues, [automated panel bag packing machines] offer a sophisticated solution, streamlining operations and enhancing product protection through integrated bagging, sealing, and often shrink-wrapping capabilities.
These systems represent a convergence of advancements in material handling, film technology, and automation control, as highlighted in various packaging industry analyses and patent literature focusing on automated wrapping systems (e.g., concepts related to USPTO Class B65B for wrapping diverse articles).
Core Operational Workflow and Technology
A typical automated panel bag packing machine executes a seamless sequence designed for high throughput and reliability:
-
Infeed and Positioning: Products are introduced via a feeding conveyor, often equipped with sensors and guides for precise alignment. This ensures the panel enters the bagging station correctly, crucial for consistent package quality. Advanced systems may incorporate optical sensors or mechanical guides referenced in automation patents (like those improving object centering for wrapping) to handle variations in product dimensions automatically.
-
Bag Formation/Dispensing: Depending on the configuration, the machine either forms a bag from a roll of flat film (often polyethylene or polyolefin) or uses pre-opened bags on a roll. For roll-stock systems, the film is precisely dispensed, folded, and cut to match the product dimensions.
-
Bagging and Sealing: The panel is inserted into the bag. High-precision sealing devices (commonly heat-based, utilizing technologies like L-bar sealers or continuous side sealers) create a secure closure. Consistent seal integrity is paramount, preventing ingress of dust, moisture, and contaminants—a key focus in packaging research literature discussing barrier properties.
-
Shrink Wrapping (Optional but Common): For applications requiring tighter conformity and enhanced stability, the bagged panel proceeds through a shrink tunnel. Controlled hot air circulation causes the shrink film (like POF - Polyolefin) to contract uniformly around the panel. This secures the product, minimizes internal movement, and provides a taut, professional finish suitable for retail or distribution. Modern shrink tunnels focus on energy efficiency and uniform heating, topics often discussed in trade publications like Packaging World.
-
Discharge: The finished package is discharged onto an outfeed conveyor for palletizing or further handling.
Key Features and Technical Specifications
The effectiveness of a panel bag packing machine lies in its design and capabilities. Critical parameters include:
- Machine Type: Fully Automatic Operation
- Control System: PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) with intuitive HMI (Human-Machine Interface) touchscreen. Allows for recipe storage, parameter adjustments, and diagnostics.
- Maximum Packing Dimensions:
- Length: 2000mm
- Width: 600mm (Note: Customization for larger dimensions is often possible)
- Operational Speed: Up to 1-3 bags per minute (dependent on panel size, film type, and configuration)
- Compatible Bag Materials: Polyethylene (PE), Polyolefin (POF), and potentially other heat-sealable films. Film thickness compatibility is also a key specification.
- Sealing Method: Heat Sealing (Specific type: L-bar, side seal, etc., impacts speed and seal appearance)
- Power Requirements: Typically 380V, 50Hz, 3-phase (Varies by region and machine scale)
- Machine Footprint (Approximate):
- Length: 6200mm
- Width: 2400mm
- Height: 2100mm
- Machine Weight (Approximate): 800kg
- Standard Features: Adjustable bag sizing, automatic product detection and alignment, safety interlocks.
- Origin: Made in China (Common for competitive machinery, important to verify component quality and support)
- Warranty: 2 years (Standard varies by manufacturer)
Applications Across Industries
The versatility of panel bag packing machines makes them invaluable in diverse sectors:
- Furniture Manufacturing: Packaging tabletops, cabinet doors, flat-packed furniture components.
- Building Materials: Wrapping insulation panels, drywall sheets, flooring planks, doors, and windows.
- Automotive: Securing body panels, interior trim pieces, large gaskets.
- Electronics: Protecting large screens, solar panels, server components.
- Printing & Signage: Packaging large-format prints, acrylic sheets, sign blanks.
Advantages and ROI Considerations
Investing in automated panel bagging technology delivers tangible benefits, aligning with trends highlighted in Industrial Distribution regarding warehouse automation and efficiency:
- Increased Throughput: Automation significantly outpaces manual bagging, directly boosting production capacity.
- Labor Savings: Reduces the need for manual labor in repetitive packing tasks, allowing personnel reallocation to higher-value activities.
- Consistent Quality: Automated processes ensure uniform bag sizing, sealing, and shrink wrapping, enhancing package appearance and protection.
- Material Optimization: Precise film dispensing and cutting minimize waste compared to manual methods.
- Enhanced Product Protection: Secure seals and optional shrink wrapping reduce the risk of scratches, moisture damage, and contamination during storage and shipping, leading to lower return rates.
- Adaptability: Modern machines can often handle a range of product sizes and film types with minimal changeover time, increasing operational flexibility.
Conclusion
Automated panel bag packing machines equipped with bag making, filling, and shrink-wrapping capabilities represent a crucial technology for industries handling large, flat products. By integrating robust mechanical design with sophisticated PLC controls, these systems offer significant improvements in efficiency, consistency, and product protection. For distributors and manufacturers seeking to optimize their end-of-line packaging operations, reduce labor costs, and ensure product integrity throughout the supply chain, investing in this type of automation provides a clear path toward achieving those goals. The adaptability and proven performance make it a strategic asset for maintaining competitiveness in demanding industrial environments.