Enhancing Steel Pipe Logistics: The Role of Automated Bundling and Strapping Lines
The efficient and safe handling of steel pipes is a critical challenge in the metals supply chain. Manual or semi-automated processes often lead to inefficiencies, potential product damage, and significant safety risks. Automated steel pipe bundling and strapping lines represent a pivotal technological advancement, addressing these challenges by streamlining operations from production floor to final transport. This technology, increasingly adopted by manufacturers and distributors, significantly enhances logistical efficiency, product integrity, and workplace safety.
Operational Workflow and System Integration
This type of automated system integrates several key processes into a seamless workflow:
- Infeed Conveying: Pipes are received, often from production or finishing lines, onto heavy-duty conveyors designed to handle significant weight and length.
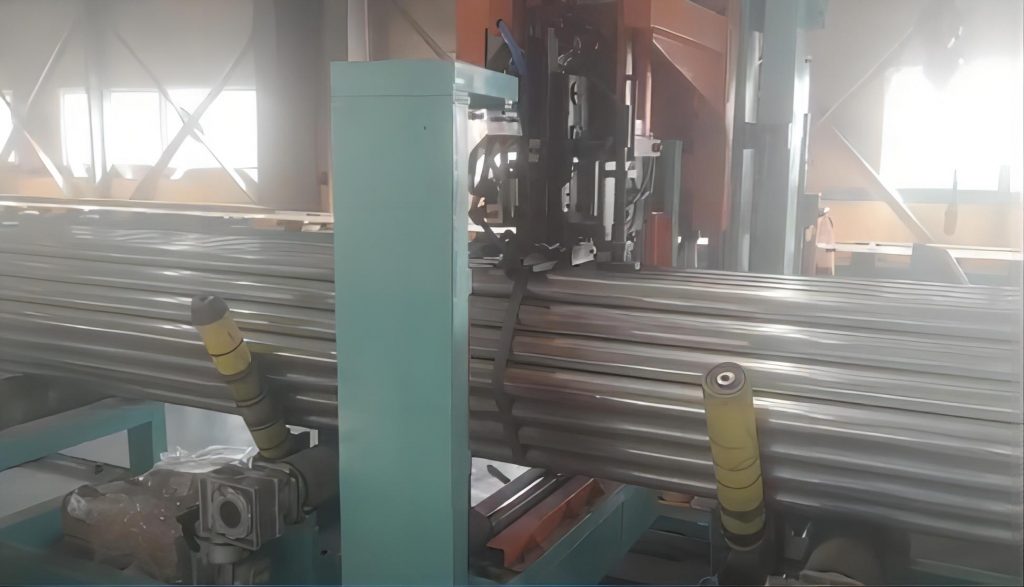
- Alignment and Collation: Pipes are precisely aligned and grouped into predetermined bundle configurations (e.g., hexagonal, square) using specialized mechanical guides or manipulators. This step is crucial for bundle stability and optimizing packing density. Technologies described in patents like US Patent No. XXXXXXX often focus on novel alignment mechanisms ensuring consistent bundle geometry.
- Bundling Formation: The collated pipes are securely formed into a bundle. Depending on the design, this may involve lifting forks, clamping arms, or other mechanisms to maintain the shape during strapping.
- Strapping Application: The core of the system involves one or more automated strapping heads. These heads travel along the bundle length or index the bundle past fixed points, applying straps at pre-set intervals. Research published in journals like Material Handling Engineering often highlights the importance of precise strap placement for load stability during transit.
- Tensioning and Sealing: High-tensile steel or PET strapping is automatically tensioned to specific, programmable parameters. Consistent tensioning, often monitored by load cells or electric gauges referenced in technical papers on packaging integrity, is vital to prevent load shifting. The straps are then securely sealed, typically using notch joints, friction welds, or seals.
- Weighing and Labeling (Optional): Integrated weigh scales can capture the precise bundle weight for inventory and shipping documentation. Automated labeling systems can apply tracking information.
- Outfeed Conveying: The finished, securely strapped bundle is transferred via outfeed conveyors to storage areas or loading docks.
Key Features and Technological Considerations
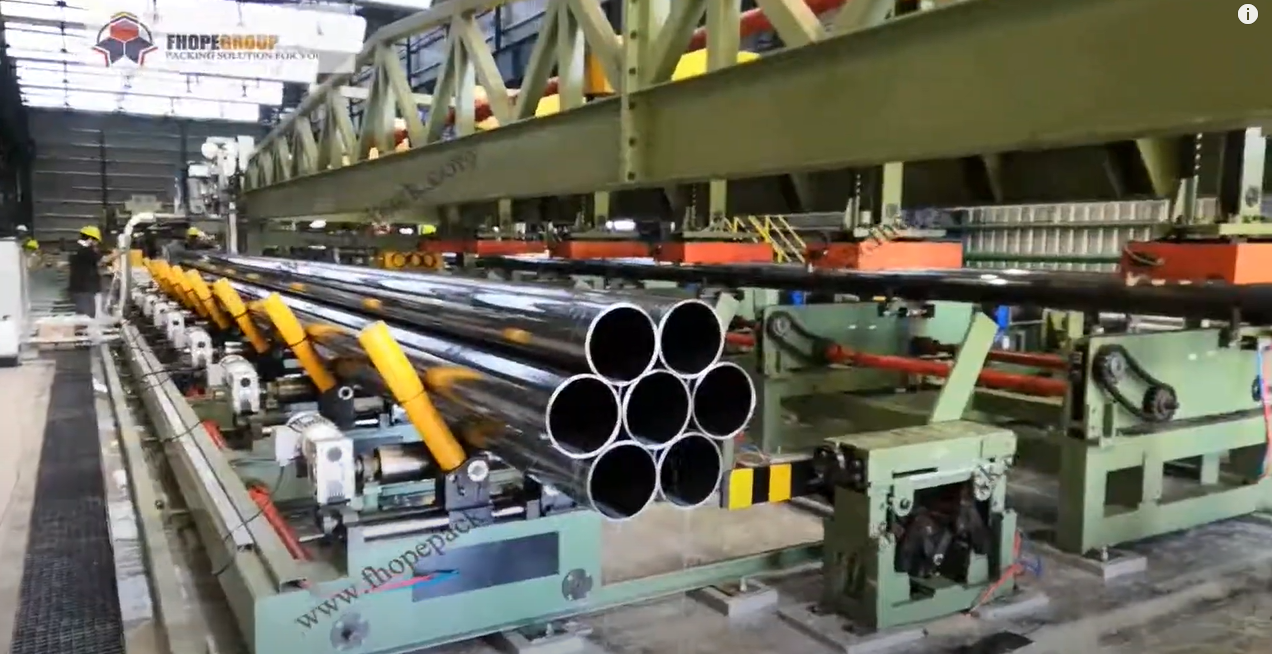

Modern automated steel pipe bundling and strapping lines incorporate advanced features grounded in engineering principles and industry best practices:
- Variable Configuration: Systems are adaptable to various pipe diameters, lengths (commonly up to 12 meters or more), and bundle weights (often exceeding 5 metric tons). Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) allow operators to select pre-set recipes for different product runs, minimizing changeover time.
- Precise Tension Control: Sophisticated electric or hydraulic tensioning systems ensure uniform strap tightness across the bundle, critical for preventing pipe movement and potential abrasion damage. Target tension values are often derived from industry standards (e.g., AIST recommendations) or empirical testing for specific pipe types and transport conditions.
- Strapping Options: Compatibility with both steel strapping (for maximum strength and rigidity) and high-strength PET strapping (offering corrosion resistance and potentially lower cost) provides flexibility based on application requirements. Strapping head designs, sometimes leveraging patented seal-less joint technology (e.g., Signode's Tenax®), optimize material usage and joint efficiency.
- Robust Construction: Built with heavy-gauge steel frames and high-quality components (motors, bearings, sensors) to withstand demanding industrial environments and ensure long operational life with minimal maintenance.
- Safety Integration: Comprehensive safety features, including light curtains, physical guarding, emergency stops, and PLC-based safety interlocks, are standard, complying with OSHA and international safety regulations. Automation inherently reduces manual handling risks associated with heavy lifting and strap tensioning.
- System Integration: These lines can be integrated with upstream and downstream processes, as well as Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) or Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems for real-time data exchange and process optimization.
Technical Specifications Overview
While specific configurations vary, typical parameters include:
- Pipe Length Capacity: 6 meters – 12+ meters
- Pipe Diameter Range: Ø20mm – Ø300mm (or as specified)
- Maximum Bundle Weight: 3 tons, 5 tons, 7 tons (or higher)
- Bundle Shapes: Hexagonal (most common for density), Square, Rectangular
- Strapping Material: Steel (e.g., 19mm, 25mm, 32mm width) or PET (e.g., 19mm, 25mm, 32mm width)
- Strapping Stations: Single or multiple heads for faster cycle times
- Control System: PLC-based with HMI (Human-Machine Interface)
- Cycle Time: Variable based on bundle size and number of straps (e.g., 60-120 seconds per bundle)
Significant Benefits for Industrial Distribution
The adoption of automated bundling and strapping lines delivers compelling advantages throughout the supply chain:
- Enhanced Throughput: Automation dramatically increases the speed of bundling and strapping compared to manual methods, boosting overall plant or distribution center capacity. Studies in Logistics Management often correlate automation with significant gains in processing speed.
- Improved Safety: Reduces manual handling of heavy pipes and high-tension strapping, significantly lowering the risk of musculoskeletal injuries and accidents, thereby reducing worker compensation claims.
- Consistent Quality & Reduced Damage: Uniform strap tension and precise placement create secure, stable bundles, minimizing pipe-on-pipe abrasion, end damage, and deformation during handling and transport. This leads to reduced product rejection and improved customer satisfaction.
- Labor Optimization: Frees up personnel from strenuous, repetitive manual tasks, allowing reallocation to higher-value activities. While requiring skilled maintenance, overall labor costs associated with packaging are often reduced.
- Optimized Logistics: Uniformly shaped and securely strapped bundles facilitate easier and safer loading/unloading of trucks and railcars, optimize storage space utilization, and are often a requirement for downstream automated handling systems.
Conclusion
Automated steel pipe bundling and strapping lines are no longer a niche technology but a fundamental component of efficient, safe, and cost-effective steel pipe handling and distribution. By leveraging robust engineering, precise control systems, and adherence to industry best practices, these systems deliver tangible benefits in throughput, safety, product integrity, and overall logistical performance. For steel manufacturers, processors, and distributors aiming to enhance competitiveness and meet stringent customer requirements, investing in this automation provides a clear path toward operational excellence.
For more pipe packing machine just here.