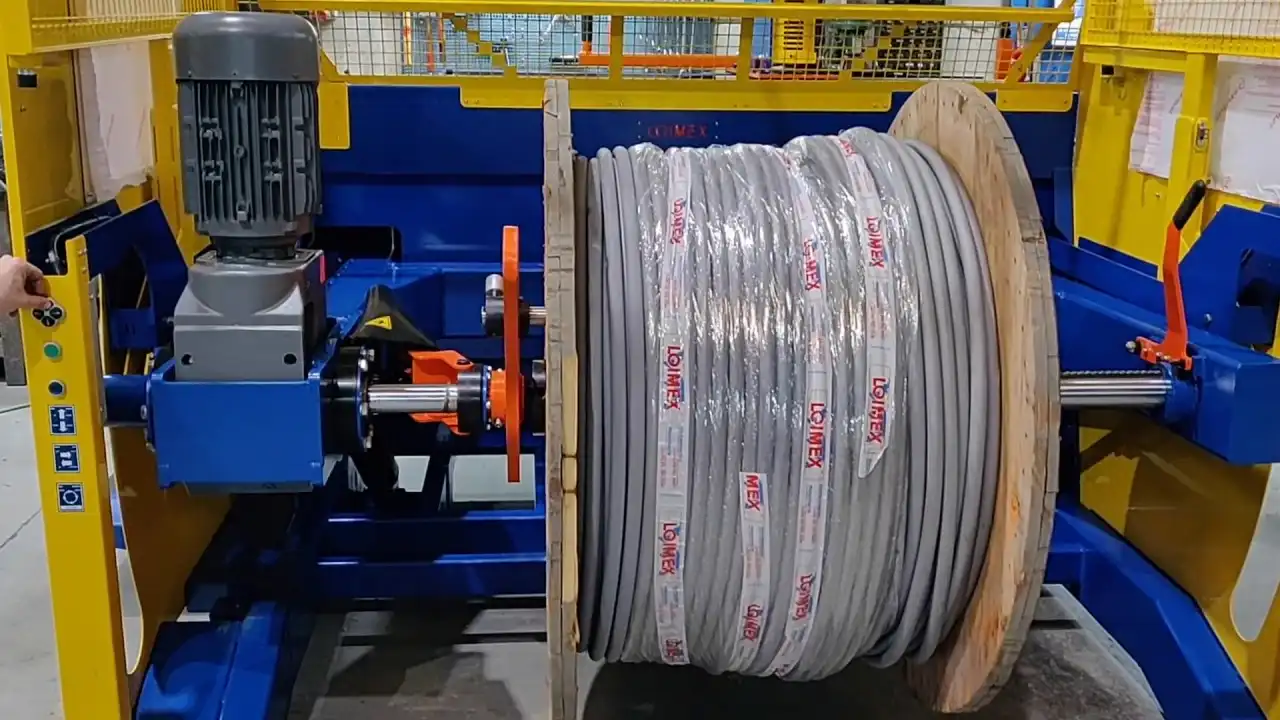
Are you tired of steel coils arriving at their destination damaged, dented, or corroded? Imagine the frustration of rejected shipments and the hit to your bottom line. Poor steel coil packing is a costly problem, but it doesn’t have to be. The solution? Mastering the art of effective steel coil packing.
Steel coil packing is crucial for protecting valuable metal products during storage and transportation. Proper packing involves using edge protectors, wrapping materials, and often specialized machinery to ensure coils are secure, stable, and shielded from damage caused by handling, moisture, and impact. This guide will walk you through the essential steps and best practices for achieving optimal steel coil packing, minimizing damage and maximizing customer satisfaction.
Ready to transform your steel coil packing process? Let’s dive in.

Understanding Steel Coil Protectors: Your First Line of Defense
Are you overlooking a simple yet critical component in your steel coil packing process that could save you thousands in damage costs? Many businesses struggle with preventable damage to steel coils simply because they underestimate the power of proper edge protection. Imagine eliminating dents, scratches, and crushed edges – it’s all within reach with the right protectors.
Steel coil protectors, also known as edge protectors or angle boards, are essential materials used to safeguard the vulnerable edges and surfaces of steel coils during handling, storage, and transit. They distribute pressure, prevent strapping damage, and offer crucial physical protection against impacts and abrasions. Types include inner and outer protectors, heavy-duty options for demanding applications, and specialized edge protectors designed for different coil orientations and weights. Choosing the correct protector is the first step in ensuring coil integrity.
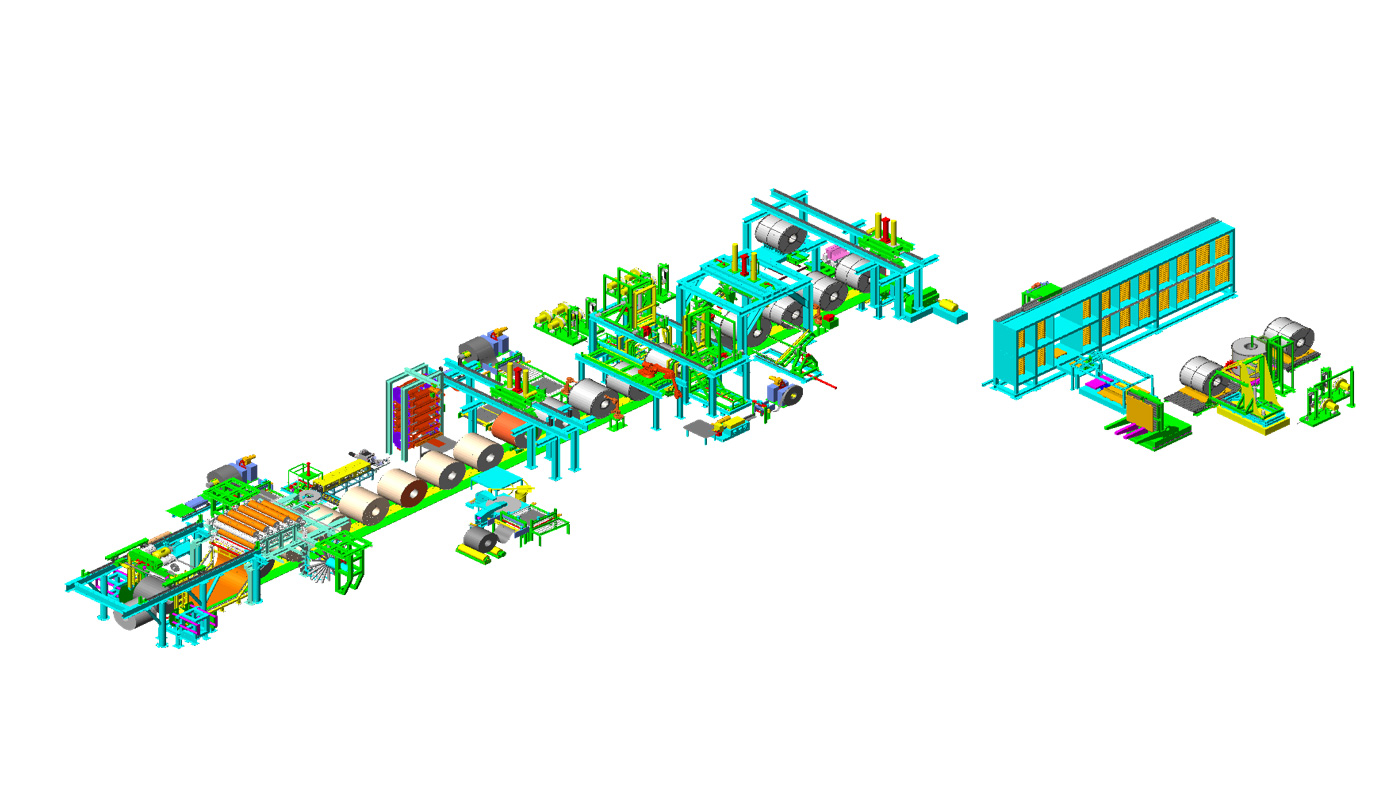
To truly master steel coil packing, understanding the nuances of steel coil protectors is paramount. Let’s delve deeper into the world of these unsung heroes of material protection.
Types of Steel Coil Protectors: A Detailed Breakdown
Steel coil protectors aren’t a one-size-fits-all solution. The market offers a variety of types, each designed for specific needs and applications. Choosing the right protector is crucial for effective packing and damage prevention. Let’s break down the main types and their characteristics:
Inner Protectors vs. Outer Protectors
The primary distinction lies in their application point.
-
Inner Protectors: These are designed to fit inside the eye of the steel coil. They provide crucial support and prevent the coil from collapsing or deforming inwards, especially important for heavy coils or during vertical stacking. Inner protectors often come in circular or segmented designs to match the coil’s inner diameter.
-
Outer Protectors: As the name suggests, outer protectors are applied to the outer circumference and edges of the coil. They shield the outer surface from impacts, strapping pressure, and general handling damage. Outer protectors can be strips, corner boards, or wrap-around designs, offering varying degrees of coverage.
Heavy-Duty Protectors: For Demanding Applications
For particularly heavy coils or harsh shipping environments, standard protectors might not suffice. Heavy-duty protectors are engineered for enhanced strength and durability. They are typically made from thicker, denser materials and may incorporate reinforced designs to withstand extreme pressure and impact. Industries dealing with very heavy gauge steel or long-distance, rough transit often rely on heavy-duty protectors.
Edge Protectors: Focusing on the Most Vulnerable Areas
Edge protectors specifically target the sharp edges of steel coils, which are highly susceptible to damage. These can be simple angle boards, V-boards, or U-channels made from cardboard, plastic, or even metal for extreme protection. Edge protectors prevent edge crushing, strap indentation, and protect workers from sharp edges during handling.
Material Matters: Construction of Steel Coil Protectors
The material of construction significantly impacts the protector’s performance and suitability for different applications. Common materials include:
-
Cardboard: Cost-effective and recyclable, cardboard protectors are suitable for lighter coils and less demanding transport. They offer good edge protection and cushioning.
-
Plastic: More durable and water-resistant than cardboard, plastic protectors are ideal for coils exposed to moisture or requiring repeated use. Recycled plastic options are also increasingly available, aligning with sustainability goals. Lamiedge, as mentioned in the source material, is an example of a recycled plastic edge protector.
-
Laminated Board: Combining layers of paper and adhesive, laminated boards offer enhanced strength and rigidity compared to single-layer cardboard. They are a good balance of cost and performance.
-
Metal: For the most demanding applications, metal protectors, typically steel, provide the ultimate protection against heavy impacts and extreme conditions. However, they are heavier and more expensive.
To summarize the key differences, consider this table:
| Protector Type | Application Focus | Material Examples | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inner Protector | Coil Eye Support | Cardboard, Laminated Board | Prevents inward collapse, stacking stability | Limited outer edge protection | Heavy coils, vertical stacking |
| Outer Protector | Outer Circumference & Edges | Cardboard, Plastic, Laminated Board | Comprehensive surface and edge protection | May not be sufficient for very heavy loads | General coil protection, various transport modes |
| Heavy-Duty Protector | Extreme Conditions | Thick Cardboard, Reinforced Plastic, Metal | Maximum protection, high durability | Higher cost, heavier | Very heavy coils, rough handling, long distances |
| Edge Protector | Coil Edges | Cardboard, Plastic, Metal | Targeted edge protection, prevents strap damage | May require combination with other protectors | Preventing edge crushing, strap damage, worker safety |
By understanding these different types and their characteristics, you can make informed decisions to select the most appropriate steel coil protectors for your specific packing needs and ensure your coils arrive in perfect condition.
Choosing the Right Edge Protector Machine: Automation for Efficiency
Are you spending countless hours manually applying edge protectors to steel coils? Imagine boosting your packing efficiency and consistency while reducing labor costs. Many businesses are turning to automated edge protector machines to revolutionize their steel coil packing process. But with so many options available, how do you choose the right one?
Selecting the correct edge protector machine is crucial for optimizing your steel coil packing process. Factors to consider include the volume of coils you process, the types of protectors you use (inner, outer, edge), the level of automation desired, and specific machine features like cutting, punching, and wrapping capabilities. Machines range from semi-automatic, requiring manual feeding of materials, to fully automatic lines that handle the entire process from protector forming to application.
Choosing the right machine is an investment that can significantly impact your productivity and the quality of your steel coil packing. Let’s explore the key considerations and machine types to help you make the best choice.
Key Factors in Machine Selection: A Practical Guide
Investing in an edge protector machine is a significant decision. To ensure you choose a machine that meets your needs and provides a good return on investment, consider these key factors:
1. Production Volume and Speed Requirements
-
Assess your throughput: How many steel coils do you need to pack per day or per week? Higher volume operations demand faster, more automated machines.
-
Consider machine speed: Machine specifications usually include production speed in meters per minute (m/min). Match the machine speed to your required output. The provided material mentions speeds up to 80m/min for some models.
-
Scalability: Think about future growth. Choose a machine that can handle potential increases in production volume.
2. Protector Type and Machine Versatility
-
Types of protectors: Do you primarily use edge protectors, inner protectors, outer protectors, or a combination? Some machines are specialized for specific protector types, while others offer greater versatility. Machines like the "Automatic edgeboard making machine with cutting and punching funcation" are designed for producing edge protectors themselves, adding another layer of automation.
-
Size range: What are the dimensions of the steel coils you pack? Ensure the machine can accommodate the width and thickness of protectors required for your coil sizes. The "ZHGQ-120" model mentioned handles edge board widths from 25-120mm.
-
Adjustability: Look for machines with adjustable settings for protector length, width, and thickness to handle variations in coil sizes and protector specifications.
3. Level of Automation: Semi-Automatic vs. Automatic
- Semi-automatic machines: These machines automate certain aspects of the process, like forming or applying protectors, but often require manual feeding of materials and coil handling. They are a good option for lower volume operations or businesses transitioning to automation. The provided material lists several semi-automatic machines for inner and outer protectors.
- Automatic machines: Fully automatic machines integrate all steps of the protector production and application process. They often include features like automatic paper feeding, gluing, cutting, punching, and even robotic coil handling. Automatic machines are ideal for high-volume production and maximizing efficiency. The "Automatic machine for making steel coil edge protector" and "Automatic edgeboard making machine with cutting and punching funcation" represent this higher level of automation.
4. Machine Features and Functionality
- Cutting and Punching: Some machines integrate cutting and punching functions to create custom protector shapes and features, like notches for specific coil circumferences. The "ZHJ120AS for cutting and punching funcation 2-in-1 machine" highlights this capability.
- Gluing Systems: For laminated protectors, consider the gluing system. "2-in-1 gluing system" and options for single or double-sided gluing offer flexibility in protector construction.
- Control Systems: PLC and servo motor control, as mentioned in the "Advantage of EDGEBOARD MACHINE" section, ensure precise cutting, accurate operation, and ease of use.
- Safety Features: Look for machines with safety features like warning alarms and emergency stops to protect operators.
5. Cost and Return on Investment (ROI)
- Initial investment: Automatic machines are generally more expensive than semi-automatic ones. Consider your budget and financing options.
- Operating costs: Factor in energy consumption, maintenance, and consumable costs (glue, protector materials).
- Labor savings: Automation can significantly reduce labor costs associated with manual packing.
- Damage reduction: Quantify the potential savings from reduced coil damage due to more consistent and effective packing.
- Calculate ROI: Compare the total cost of ownership with the potential benefits (increased efficiency, reduced costs, improved quality) to determine the ROI and payback period.
To help visualize the differences, consider this comparison table:
| Feature | Semi-Automatic Machine | Automatic Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Automation Level | Partial automation, manual material feeding/handling | Full automation, minimal manual intervention |
| Production Speed | Typically lower | Typically higher |
| Labor Requirement | Higher | Lower |
| Versatility | May be limited to specific protector types | Often more versatile, handling various protector types |
| Features | Basic forming/application functions | Advanced features like cutting, punching, integrated lines |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher initial investment |
| Best Suited For | Lower volume, transitioning to automation | High volume, maximizing efficiency |
By carefully evaluating these factors and comparing different machine options, you can select the edge protector machine that best aligns with your operational needs, budget, and long-term goals for steel coil packing efficiency and quality.
Step-by-Step Guide to Steel Coil Packing with Machines: From Start to Finish
Steel coil packing might seem complex, but with the right machines and a systematic approach, it can be streamlined and efficient. Are you looking for a clear roadmap to optimize your steel coil packing process using machinery? Many businesses seek a step-by-step guide to ensure consistent and effective packing every time.
Steel coil packing with machines involves a series of well-defined steps, starting with coil preparation and protector application, followed by wrapping and securing the packed coil for safe transport. Automated or semi-automatic machines play a crucial role in each stage, enhancing speed, precision, and consistency. This step-by-step guide outlines the key stages and considerations for effective machine-assisted steel coil packing.
Let’s break down the process into manageable steps, providing a practical guide to steel coil packing with machines.
The Steel Coil Packing Process: A Detailed Walkthrough
Effective steel coil packing is a multi-stage process. Here’s a detailed breakdown of each step when utilizing machines:
Step 1: Coil Preparation
- Inspection: Before packing, inspect the steel coil for any existing damage, rust, or contaminants. Address any issues before proceeding.
- Cleaning (Optional): Depending on the coil’s condition and customer requirements, cleaning might be necessary. This could involve wiping down the coil or using specialized cleaning solutions.
- Positioning: Properly position the coil for the protector application process. This might involve using coil tilters or manipulators to orient the coil correctly for machine access.
Step 2: Protector Application
This step varies depending on the type of protector and machine used:
-
Inner Protector Application:
- Machine Type: Semi-automatic or automatic inner protector making and applying machines.
- Process: The machine forms the inner protector (if using a making machine) and then applies it into the eye of the steel coil. This might involve expanding the protector inside the coil eye for a snug fit.
- Considerations: Ensure the inner protector diameter matches the coil eye diameter. For heavy coils, heavy-duty inner protectors are crucial.
-
Outer Protector Application:
- Machine Type: Semi-automatic or automatic outer protector applying machines, wrapping around edgeboard machines.
- Process: The machine applies outer protectors around the circumference and edges of the coil. This could involve wrapping strips of protector material or applying pre-formed corner boards. "Steel packaing wrapping around corner board machine" and "round edgeboard machine" are examples.
- Considerations: Overlap the protectors adequately for complete coverage. Ensure proper tension during application to secure the protectors without damaging the coil.
-
Edge Protector Application:
- Machine Type: Automatic edgeboard making machines with cutting and punching functions, semi-automatic edge protector applicators.
- Process: Machines can produce edge protectors from raw materials and apply them to the coil edges. Alternatively, pre-made edge protectors can be applied using semi-automatic applicators.
- Considerations: Select the correct edge protector profile (angle, V, U-shape) for the coil edges. Ensure secure attachment of edge protectors, often using tape or strapping.
Step 3: Wrapping (Optional but Recommended)
- Machine Type: Coil wrapping machines, stretch wrapping machines, wrapping around edgeboard machines. The "MultiWrapper" mentioned in the source is an example of a robotic coil wrapping machine.
- Process: Apply wrapping material around the coil after protector application. This provides additional protection against moisture, dust, and handling damage. Materials include stretch film, plastic wrap, or even paper.
- Considerations: Choose the appropriate wrapping material based on the environment and transport conditions. Ensure proper overlap and tension for effective sealing and protection. "Lamistretch Armour" is mentioned as extra strong film for heavy-duty handling.
Step 4: Securing and Strapping
- Machine Type: Strapping machines (manual, semi-automatic, automatic).
- Process: Apply strapping around the packed coil to secure the protectors and wrapping in place. Strapping can be steel, plastic, or composite, depending on the coil weight and security requirements.
- Considerations: Apply straps evenly and with appropriate tension to prevent shifting during transport but avoid over-tightening, which could damage the coil or protectors. Edge protectors are crucial under strapping to distribute pressure and prevent strap indentation.
Step 5: Labeling and Documentation
- Process: Apply labels to the packed coil with relevant information such as coil ID, weight, destination, and handling instructions. Generate necessary documentation like packing lists and shipping manifests.
- Considerations: Ensure labels are clear, durable, and comply with shipping regulations. Accurate documentation is crucial for tracking and delivery.
To visualize the process and machinery involved, consider this table:
| Step | Description | Machine Types Involved | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Coil Preparation | Inspect, clean (optional), position coil | Coil tilters, manipulators (optional) | Coil condition, cleanliness requirements, proper positioning |
| 2. Protector Application | Apply inner, outer, and/or edge protectors | Inner/outer protector machines, edgeboard machines | Protector type selection, size compatibility, secure application |
| 3. Wrapping (Optional) | Wrap coil with protective material | Coil wrapping machines, stretch wrappers | Material selection, overlap, tension |
| 4. Securing & Strapping | Apply strapping to secure protectors and wrapping | Strapping machines (manual, semi-auto, auto) | Strapping type, tension control, even distribution |
| 5. Labeling & Doc. | Label packed coil, generate documents | Label printers, documentation systems (manual or integrated) | Label clarity, durability, regulatory compliance, accuracy |
By following these steps and utilizing appropriate machines, you can establish a robust and efficient steel coil packing process that minimizes damage, maximizes productivity, and ensures your valuable steel coils reach their destination safely and in perfect condition.
Benefits of Automated Steel Coil Packing: Efficiency and Beyond
Are you still relying on manual steel coil packing methods? Imagine a packing process that is faster, more consistent, and reduces damage, all while lowering your operational costs. Many businesses are realizing the significant advantages of automating their steel coil packing lines.
Automating steel coil packing offers a multitude of benefits, extending beyond just increased speed. Automation leads to improved consistency in packing quality, reduced material waste, lower labor costs, enhanced worker safety, and ultimately, greater customer satisfaction due to fewer damaged shipments. Investing in automated packing solutions can transform your steel coil handling operations and provide a significant competitive advantage.
Let’s explore the key benefits of automated steel coil packing in detail.
Unlocking Efficiency and Quality: The Advantages of Automation
The shift to automated steel coil packing is driven by a desire for greater efficiency, cost savings, and improved product protection. Here are the key advantages in detail:
1. Increased Efficiency and Throughput
- Faster Packing Speeds: Automated machines operate at significantly higher speeds than manual packing, dramatically increasing throughput. The material mentions machine speeds of up to 80m/min for edgeboard production. Automated application further accelerates the entire packing process.
- Continuous Operation: Automated lines can often operate continuously with minimal downtime, maximizing production output.
- Reduced Cycle Times: Automation streamlines the entire packing cycle, from protector application to wrapping and strapping, reducing overall processing time per coil.
2. Enhanced Consistency and Quality
- Precise Application: Machines apply protectors and wrapping materials with greater precision and consistency than manual labor, ensuring uniform packing quality across all coils.
- Reduced Human Error: Automation minimizes the risk of human error in protector placement, strapping tension, and other critical packing steps, leading to more reliable protection.
- Improved Product Presentation: Consistent and professional packing enhances the visual appeal of your products and reinforces a quality image to customers.
3. Reduced Material Waste
- Optimized Material Usage: Automated machines can be programmed to use protector and wrapping materials more efficiently, minimizing waste and reducing material costs.
- Precise Cutting and Application: Automated cutting and application systems ensure that materials are used only where needed, avoiding unnecessary overlaps or excess material consumption.
4. Lower Labor Costs
- Reduced Manpower: Automation significantly reduces the number of workers required for packing operations. One automated line can often replace several manual packing stations.
- Lower Labor Expenses: Reduced manpower translates directly to lower labor costs, including wages, benefits, and training expenses.
- Re-deployment of Labor: Workers previously engaged in manual packing can be re-deployed to other value-added tasks within the organization.
5. Enhanced Worker Safety
- Reduced Manual Handling: Automation minimizes the need for manual handling of heavy steel coils and packing materials, reducing the risk of injuries like strains, sprains, and cuts.
- Safer Operating Environment: Automated machines often incorporate safety features like light curtains, emergency stops, and safety guarding, creating a safer working environment for operators.
- Ergonomic Improvements: Automation reduces repetitive and physically demanding tasks, improving ergonomics and reducing worker fatigue.
6. Improved Damage Reduction and Customer Satisfaction
- Superior Protection: Consistent and high-quality automated packing provides superior protection against damage during handling, storage, and transport.
- Reduced Damage Claims: Fewer damaged shipments lead to reduced damage claims, lower insurance costs, and improved profitability.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Customers receive products in perfect condition, leading to higher satisfaction, stronger relationships, and repeat business.
7. Scalability and Flexibility
- Adaptable to Production Changes: Automated lines can often be adjusted and re-programmed to accommodate changes in production volume or packing requirements.
- Scalable for Growth: Automation provides a scalable solution that can handle increasing production demands as your business grows.
- Integration with Other Systems: Automated packing lines can be integrated with other automated systems in your facility, such as conveyors, warehousing systems, and ERP systems, for seamless operations.
In summary, the benefits of automated steel coil packing are substantial and far-reaching. From increased efficiency and reduced costs to improved quality, safety, and customer satisfaction, automation offers a compelling pathway to optimize your steel coil handling operations and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Conclusion
Mastering steel coil packing is not just about wrapping metal; it’s about protecting your investment, ensuring customer satisfaction, and optimizing your operational efficiency. By understanding the critical role of edge protectors, choosing the right machinery, and implementing a systematic packing process, you can significantly reduce damage, lower costs, and elevate your steel coil handling operations. Embrace automation and best practices to transform your packing process from a potential bottleneck into a source of competitive advantage and lasting success.

