How Do You Ensure Your Mold Upender Works Perfectly After Installation?
Just installed a new mold upender? Excitement can quickly turn to anxiety if you’re unsure it will perform flawlessly and safely. Improper post-installation checks can lead to operational failures, costly downtime, and even safety hazards. Ensure your investment delivers peak performance from day one with a structured validation process.

Ensuring your mold upender works perfectly involves a systematic validation process encompassing Installation Qualification (IQ), Operational Qualification (OQ), and Performance Qualification (PQ). This multi-stage approach verifies correct installation against specifications, confirms all operational functions work as intended without load, and validates performance under actual production conditions with representative molds, guaranteeing safety, reliability, and efficiency right from the start.
This rigorous testing sequence might seem extensive, but it’s the bedrock of reliable and safe operation for such critical machinery. Skipping steps introduces risks you can’t afford. Let’s delve into each stage to understand how they collectively guarantee your mold upender’s perfect performance.
Installation Qualification (IQ): Laying the Foundation for Flawless Operation
The journey to perfect operation begins the moment installation concludes. Before even powering up your new mold upender, confirming every component is correctly installed and meets all specifications is paramount. This foundational step, known as Installation Qualification (IQ), prevents issues stemming from incorrect setup, ensuring the machine is physically sound and ready for the subsequent testing phases, safeguarding both personnel and the equipment itself.
Installation Qualification (IQ) is the documented verification that the mold upender and its ancillary systems have been installed and configured according to the manufacturer’s specifications and user requirements. It meticulously checks the physical installation aspects: mechanical integrity, correct utility connections (electrical, hydraulic, pneumatic), safety feature placement (guards, sensors, E-stops), environmental conditions (leveling, clearance), and the presence and correctness of essential documentation like manuals, drawings, and calibration certificates for critical components. This ensures the machine is correctly assembled in its designated operational environment before any functional testing begins.
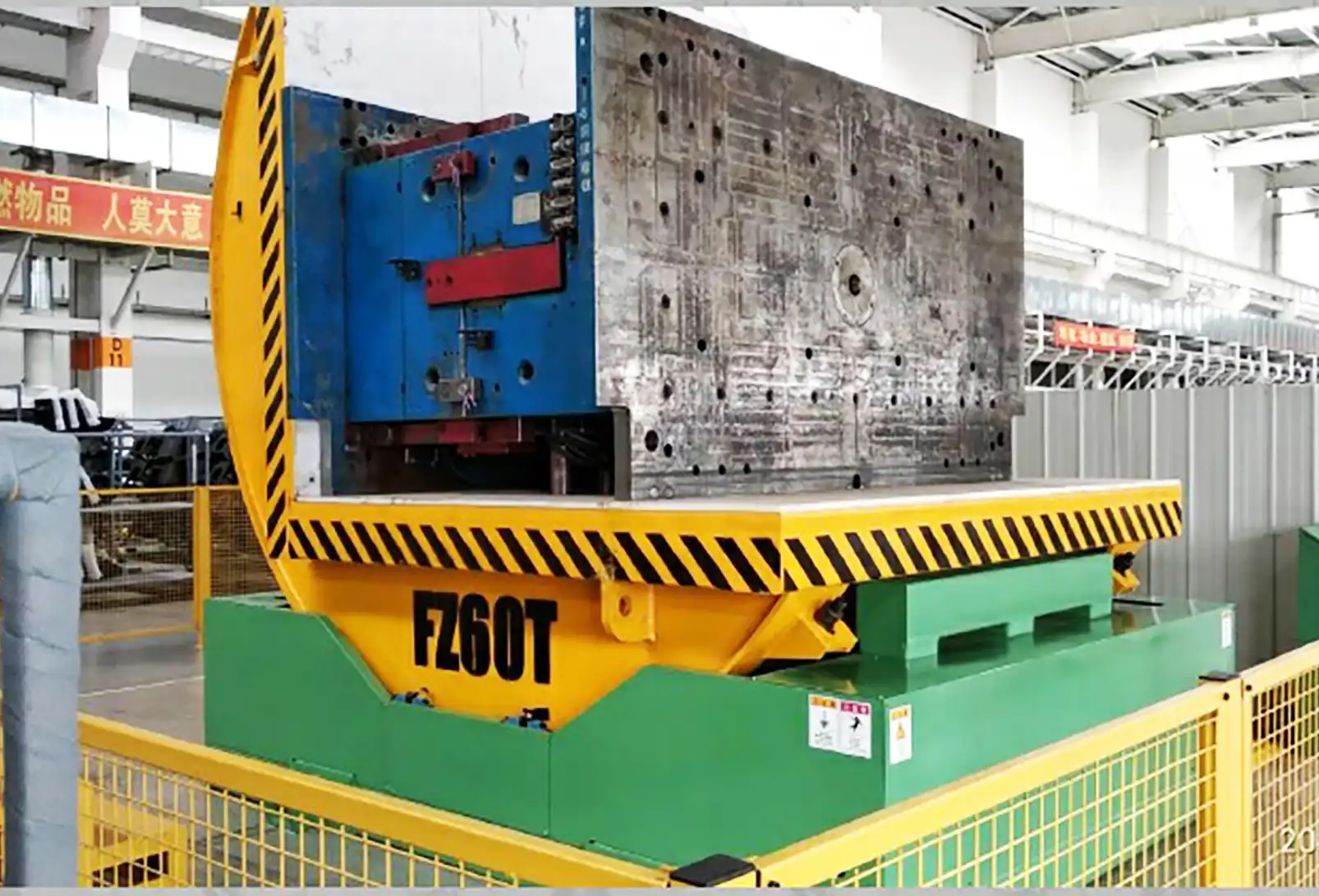

Key IQ Checks for Your Mold Upender
A comprehensive IQ process leaves no stone unturned. It involves a systematic checklist approach, verifying each critical aspect of the installation. This detailed examination confirms that the equipment received matches the purchase order, hasn’t sustained damage during transit or installation, and is integrated correctly into your facility’s infrastructure.
1. Mechanical Installation Verification:
- Assembly Check: Confirm all structural components (base, tilting platform, drive mechanisms) are assembled according to the manufacturer’s drawings. Check bolt torques where specified.
- Leveling and Anchoring: Verify the machine is perfectly leveled on the foundation and securely anchored as per requirements. Improper leveling can cause stress and operational issues.
- Clearances: Ensure adequate operational and maintenance clearances around the machine, free from obstructions.
- Guarding: Confirm all physical guards are correctly installed, undamaged, and secure.
2. Utility Connection Verification:
- Electrical: Verify power supply voltage, phasing, and grounding match machine specifications. Check wiring integrity, conduit routing, and connection tightness in the control panel and at motors/sensors.
- Hydraulic/Pneumatic: Confirm correct fluid types and levels (if applicable). Check hose/pipe routing for potential kinks or abrasion points. Verify pressure settings match specifications and there are no leaks.
3. Safety System Verification:
- Emergency Stops (E-stops): Confirm all E-stop buttons are physically installed in accessible locations as specified. (Functional testing occurs in OQ).
- Interlocks: Verify physical installation of safety interlock switches on access gates or guards. (Functional testing occurs in OQ).
- Presence Sensing Devices: Check installation and alignment of light curtains or safety scanners, if equipped.
4. Documentation Review:
- Manuals: Confirm receipt of operator, maintenance, and parts manuals.
- Drawings: Verify availability of electrical, hydraulic/pneumatic schematics and assembly drawings.
- Calibration Certificates: Check for certificates for critical components like load cells (if equipped) or pressure sensors.
- Component List: Cross-reference major components against the packing list and specifications.
IQ Checklist Example:
| Component/System | Checkpoint | Specification/Criteria | Result (Pass/Fail) | Comments/Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical | Base Leveling | Manufacturer Tolerance +/- X mm/m | Pass | |
| Anchor Bolt Torque | Y Nm | Pass | ||
| Tilting Platform Alignment | Visual & Measured | Pass | ||
| Electrical | Incoming Voltage | 480V +/- 10%, 3-Phase | Pass | Verified 478V |
| Control Panel Wiring | Neat, Secure, Labelled | Pass | ||
| Grounding Connection | Verified Continuity | Pass | ||
| Hydraulic | Fluid Level & Type | ISO VG 46, Full Mark | Pass | |
| Hose Connections (Leaks) | No visible leaks | Pass | ||
| Safety | E-Stop Button Installation | Accessible per drawing | Pass | |
| Safety Guard Fitment | Secure, No Gaps | Pass | ||
| Documentation | Operator Manual Received | English, Rev 2.1 | Pass | |
| Electrical Schematics | Matches Panel Layout | Pass |
Completing the IQ phase provides documented evidence that the mold upender is correctly installed and ready for the next stage: powering up and testing its functions.
Operational Qualification (OQ): Verifying Intended Functionality
With the Installation Qualification successfully completed, you’ve confirmed the mold upender is physically installed correctly. The next critical phase is Operational Qualification (OQ). This stage involves powering up the machine and systematically testing every function and control feature without placing an actual mold or load onto it. OQ verifies that the machine operates as designed through its full range of motion and that all safety systems function correctly under controlled, no-load conditions.
Operational Qualification (OQ) rigorously tests the mold upender’s functions according to predefined procedures to ensure it operates within specified limits. This includes verifying control sequences, testing the full tilting range (e.g., 0-90 degrees), checking operational speeds, confirming limit switch activations, and crucially, testing all safety features like emergency stops, interlocks, and presence sensing devices to ensure they perform their intended protective functions effectively.
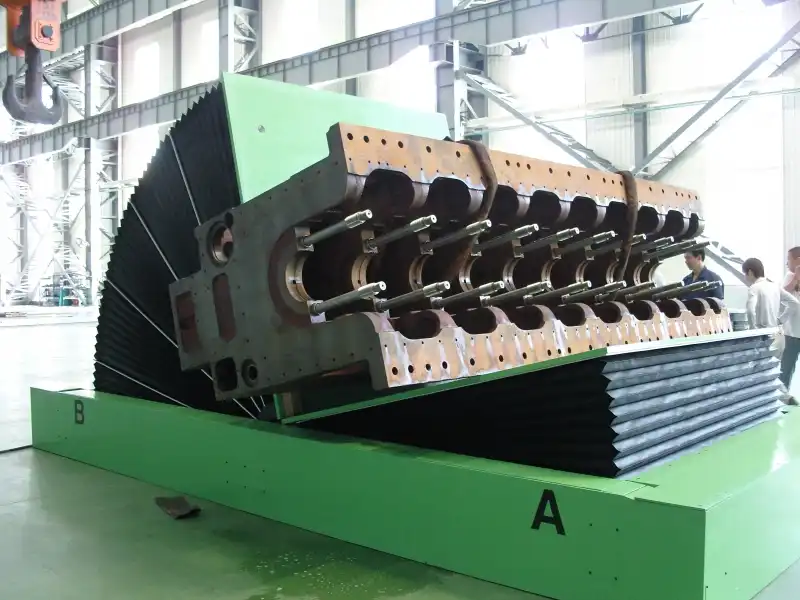

Executing Comprehensive OQ Tests
OQ moves beyond static checks into dynamic testing, observing the machine in action. It’s about ensuring the "brain" (control system) and the "muscles" (drive systems) work together correctly and safely. A structured approach is vital.
1. Control System Tests:
- Power On/Off: Verify correct start-up and shutdown sequences.
- Control Interface: Test all buttons, switches, touch screen inputs (if applicable) on the operator panel. Confirm responses are immediate and correct. Check indicator lights and alarms.
- Mode Selection: If different operating modes exist (e.g., manual, automatic), verify selection and corresponding functionality.
2. Movement and Sequence Tests (No Load):
- Tilting Function: Initiate the tilt cycle. Verify smooth movement through the entire range (e.g., 0 to 90 degrees and back). Listen for any unusual noises from drives or bearings.
- Rotation Function (if applicable): Test rotation in both directions through the specified range. Ensure smooth, controlled movement.
- Limit Switches/Sensors: Confirm that movement stops precisely when upper and lower limit switches or position sensors are activated. Check for over-travel.
- Speed Controls: If adjustable speeds are available, test operation at minimum, maximum, and intermediate settings. Verify smooth transitions.
3. Safety Function Tests:
- Emergency Stop Activation: While the machine is in motion (tilting/rotating), press each E-stop button. Confirm that all motion stops immediately and safely as designed. Verify reset procedure.
- Safety Interlocks: Test gate/guard interlocks by opening them during operation (if safe design allows testing this way, otherwise simulate). Confirm motion stops immediately. Verify machine cannot start with interlocks open.
- Presence Sensing Devices (Light Curtains/Scanners): Interrupt the beam/detection zone during motion. Verify immediate stop. Test reset procedures.
- Overload Protection (Simulation): If possible and safe, simulate an overload condition (e.g., electronically if drive supports it) to verify protection trips.
4. Calibration Verification (where applicable):
- Positional Accuracy: Use measuring tools (e.g., digital level, protractor) to verify the tilted angle matches the control system display or setpoint at various positions.
- Speed Verification: Measure actual cycle time against specified or set speed parameters.
Documenting the results of each OQ test step is crucial. Any deviation from expected behavior must be investigated, rectified, and retested until the machine operates perfectly according to its design specifications under no-load conditions. Only then is it safe to proceed to Performance Qualification.
Performance Qualification (PQ): Real-World Validation Under Load
Your mold upender is installed correctly (IQ) and its functions operate perfectly without load (OQ). But will it handle the heavy demands of your actual molds safely and consistently? Performance Qualification (PQ) is the critical final validation step, designed to answer precisely that question, ensuring reliability under real-world stress.
Performance Qualification (PQ) demonstrates and documents that the mold upender consistently performs according to specifications under normal operating conditions with actual or simulated loads (representative molds). This involves testing with molds of varying weights and sizes (up to the machine’s rated capacity), verifying cycle times, checking stability during tilting, and ensuring repeatable, reliable performance over multiple cycles, proving its suitability for production use.
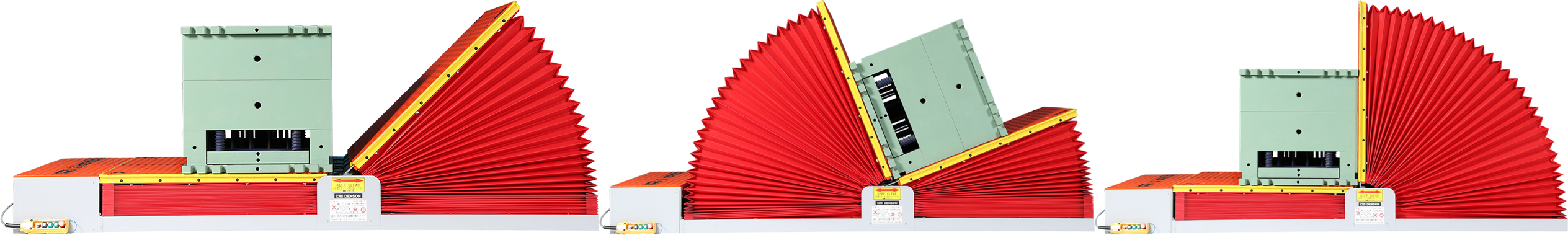
Simulating Production Scenarios in PQ
PQ bridges the gap between controlled testing and actual production. It involves challenging the machine with the tasks it will perform daily, verifying it can do so reliably and safely.
1. Load Testing:
- Minimum and Maximum Load: Test the upender with loads representing the minimum and maximum weight molds it’s rated for. Verify smooth operation, absence of motor strain or hydraulic system stress.
- Representative Loads: Use molds (or test weights simulating molds) of typical sizes and weights encountered in your production. Observe the full tilt cycle.
- Center of Gravity Variations: If possible, test with loads having different centers of gravity (within safe operational limits) to assess stability.
2. Cycle Testing and Repeatability:
- Multiple Cycles: Run the upender through numerous consecutive tilt cycles with a representative load. Monitor for consistency in performance, cycle time, and positioning accuracy.
- Consistency Checks: Ensure the machine stops accurately at the desired angle repeatedly. Check for any signs of performance degradation over multiple cycles (e.g., overheating, speed variation).
3. Stability Assessment:
- During Tilt: Carefully observe the machine and load for any signs of instability, excessive vibration, or rocking during the tilting motion, especially when handling heavier or awkwardly shaped molds.
- At Rest (Tilted): Verify the machine holds the load securely at the fully tilted position without drift or creep (particularly important for hydraulic systems).
4. Operator Interaction and Workflow:
- Loading/Unloading: Simulate or perform the actual process of loading a mold onto the upender and unloading it after tilting, verifying clearances and ease of operation.
- Normal Operating Sequences: Run the machine through typical operational sequences as defined by your workflow.
PQ Test Parameters Example:
| Test Parameter | Load Condition | Target Specification | Acceptance Criteria | Measured Result | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cycle Time (0-90°) | 80% Max Rated Load (10 Ton) | 45 seconds +/- 5 sec | Within 40-50 seconds | 43 seconds | Pass |
| Cycle Time (90-0°) | 80% Max Rated Load (10 Ton) | 45 seconds +/- 5 sec | Within 40-50 seconds | 44 seconds | Pass |
| Positional Accuracy | Max Rated Load (12.5 Ton) | 90° +/- 0.5° | Within 89.5° – 90.5° | 90.1° | Pass |
| Stability Check | Max Rated Load (Asymmetrical CG) | No visible rocking/instability | Smooth, controlled motion | Smooth operation | Pass |
| Repeatability (5 cycles) | 50% Max Rated Load (6 Ton) | Cycle Time +/- 2 sec deviation | Max deviation <= 2 sec | Max deviation 1 sec | Pass |
| Hold Position (10 min) | Max Rated Load @ 90° | No detectable drift | No measurable angle change | No drift detected | Pass |
Successful completion of PQ provides the ultimate confidence that your mold upender is not just installed correctly and functional, but truly ready to perform its demanding job reliably and safely within your production environment. All IQ, OQ, and PQ results should be formally documented and signed off.
Documentation and Training: Sustaining Perfect Operation
Successfully completing IQ, OQ, and PQ is a major milestone, confirming your mold upender is ready for production. However, ensuring it continues to work perfectly relies heavily on two often-underestimated components: comprehensive documentation and thorough training. These elements provide the blueprint for sustained performance, safety, and effective maintenance throughout the machine’s lifecycle. Proper records serve as a baseline, while training empowers your team to operate and care for the equipment correctly.

Comprehensive documentation, including signed-off IQ/OQ/PQ protocols and reports, manufacturer manuals, schematics, and maintenance logs, provides essential reference points and proof of validation. Effective operator and maintenance training, based on this documentation and covering safe operation procedures, routine checks, troubleshooting, and preventative maintenance tasks, is crucial for maintaining the mold upender’s optimal performance and ensuring long-term operational reliability and safety. This knowledge transfer ensures that the rigorous standards established during commissioning are upheld day after day.
Maintaining meticulous records is non-negotiable. The validation reports (IQ, OQ, PQ) form the baseline data against which future performance can be compared. They are proof that the machine was performing correctly upon commissioning. Manufacturer manuals (operator, maintenance, parts) and technical drawings (electrical, hydraulic/pneumatic) are indispensable resources for daily operation and troubleshooting. Keeping a detailed maintenance log, recording all preventative maintenance actions, repairs, parts replaced, and any operational issues encountered, provides a valuable history for diagnostics and predicting future needs. Calibration records for critical sensors or instruments must also be maintained and kept up-to-date.
Equally important is investing in training. Operators need to be fully versed in the safe and efficient operation of the mold upender, including all control functions, loading/unloading procedures, safety features, and emergency protocols. They should understand the machine’s capacity limits and potential hazards. Maintenance personnel require specific training on preventative maintenance schedules and tasks (lubrication, inspections, filter changes), troubleshooting common issues using the provided schematics, and safe maintenance procedures (like lock-out/tag-out). Refresher training should be scheduled periodically, especially if procedures change or new personnel are assigned. This combination of robust documentation and skilled personnel is the key to maximizing the lifespan and maintaining the perfect, safe operation of your mold upender.
Conclusion
Ensuring your mold upender works perfectly after installation isn’t a matter of luck; it’s the result of a deliberate, structured validation process. By systematically executing Installation Qualification (IQ), Operational Qualification (OQ), and Performance Qualification (PQ), you verify every aspect, from the physical setup to functional checks and real-world load handling. This IQ/OQ/PQ methodology, combined with thorough documentation and effective training, transforms your new equipment from an unknown quantity into a reliable, validated asset. Performing diligent Post-installation checks through this framework is the most effective way to guarantee safety, maximize uptime, and achieve the operational excellence expected from your mold upender investment from day one and beyond.
